2099
Various use of diaphragm walls for construction of multilevel road junction – Design
and monitoring of displacements
Diverses utilisations de parois moulées pour la construction de l’intersection des routes à plusieurs
niveaux – Conception et le suivi des déplacements
Siemińska-Lewandowska A., Mitew-Czajewska M.
Warsaw University of Technology, Warsaw,Poland
Tomczak U.
Soletanche Polska Sp. z o.o., Warsaw, Poland
ABSTRACT: The paper presents various use of diaphragm walls for the construction of four-level junction in Warsaw. Diaphragm
walls were chosen as a best solution for abutments of 2 viaducts and 1 flyover, foundations (barrettes) under 7 pillars, 60 to 100cm
thick retaining walls with total length of over 570 running meters. In the paper detailed technical descriptions, geotechnical
conditions, predicted theoretical horizontal and vertical displacements of walls for all mentioned diaphragm wall applications are
presented. Finally, the comparison of the results of theoretical analysis and real scale monitoring results (displacements measurements
and load tests) in accordance with construction stages is presented and discussed.
RÉSUMÉ : Cet article présente différentes utilisations de parois moulées pour la construction d’une jonction de quatre niveaux à
Varsovie. Les parois moulées ont été choisies comme une meilleure solution pour les butées de 2 viaducs et 1 voie surélevée, les
fondations (barrettes) sous 7 piliers, des murs de soutènement épais de 60 à 100 cm avec une longueur totale de plus de 570 mètres.
Dans le document des descriptions techniques détaillées, des conditions géotechniques, les prévisions de déplacements horizontaux et
verticaux théoriques des murs pour toutes les applications de parois moulées mentionnées sont présentés. Enfin, la comparaison des
résultats de l'analyse théorique et les résultats en vraie grandeur (mesures de déplacements et de tests de charge) de la surveillance
conformément aux étapes de la construction est présentée et discutée.
KEYWORDS: diaphragm wall, deep excavation, foundation, barettes
1 INTRODUCTION
In Poland nowadays, especially before euro 2012, road network
and new motorways connecting Poland and Ukraine with
Western Europe are being built. Construction of Warsaw bypass
is the place were huge multilevel road junctions are built.
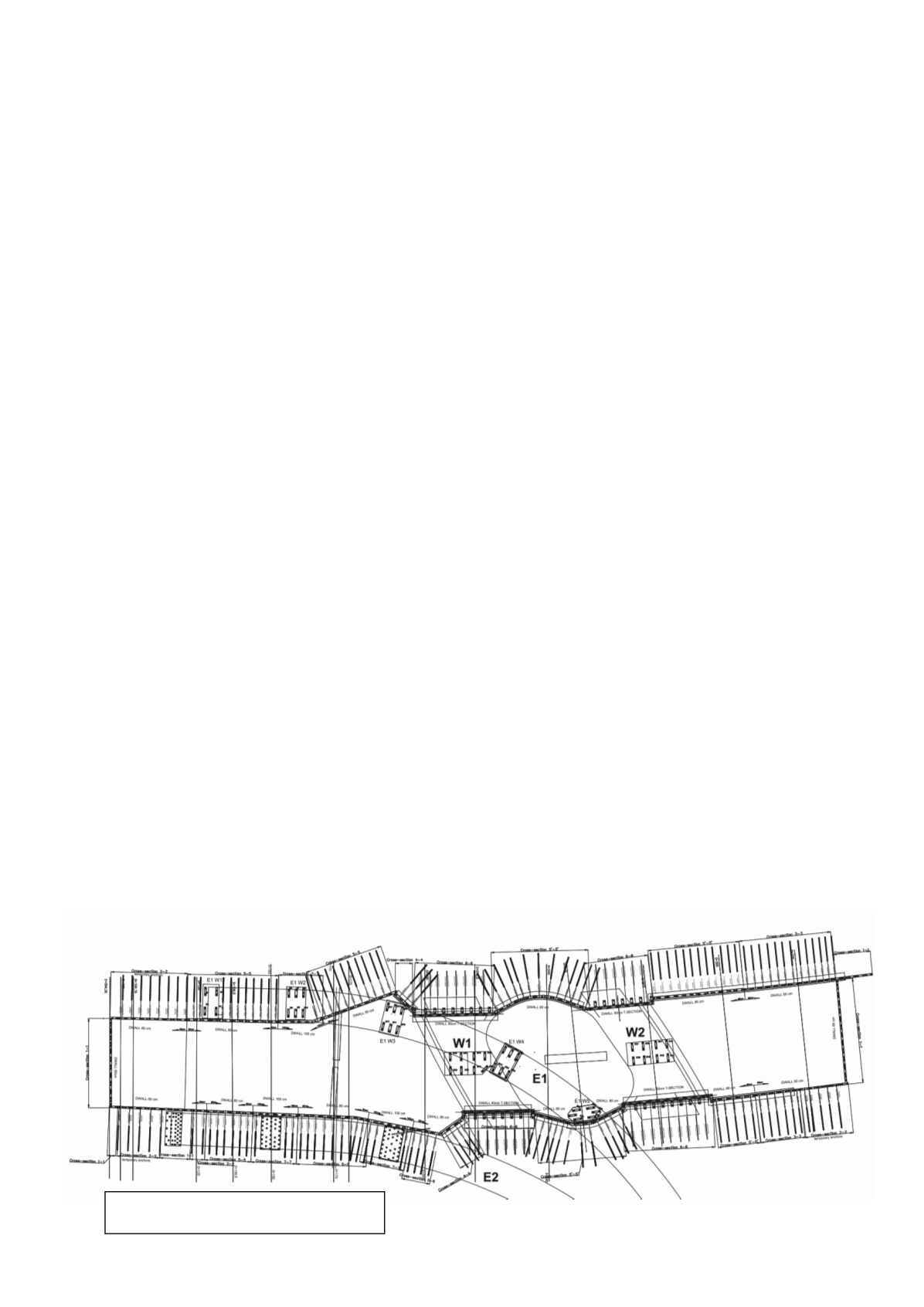
The case disscussed in the paper is 3 level road junction
consisting of 2 flyovers (indicated as E1, E2 at fig. 1) and 2
viaducts (indicated as W1, W2 at fig. 1). The original building
permit design assumed that the abutments and columns were to
be founded on large-diameter piles with the diameter 120 and
150 cm. The accompanying RC retaining walls and viaduct
abutments were to be erected in traditional formwork. The
original design assumed that the embedded part of the junction
was to be built with a temporary casing in the form of sheet
piling with an RC capping beam at the top. The walls were to be
anchored with 1 level of soil nails. Permanent structure was
designed as retaining walls connected with water tight
foundation plate. During the execution design stage,
due to economical and technological reasons, the solution was
much simplified - only diaphragm walls were used for all parts
of the structure, i.e. for:
-
excavation walls – retaining structures,
-
foundations – barrettes of viaduct columns as well as
barrettes of columns and abutments of flyovers,
-
viaduct abutments – T-shaped diaphragm walls.
The new solution allowed the significant shortening of
construction works through the use of diaphragm walls as
temporary and permanent structure. Figure 1 presents the
general arrangement of the discussed road junction and
indicates parts of the structure described in the paper.
In the design stage theoretical displacements and bearing
capacities of theses structures were calculated. During
construction, at each of disscussed structure parts, the real
Fig. 1 General arrangement


