2898
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
because of the large length and slenderness ratio of the super-
long bored pile, the stiffness of pile-soil system is relative small.
This directly influences the bearing characteristics of the super-
long bored pile. According to the analysis of filed load tests
results (Zhang and Liu, 2009), the basic bearing behaviors of
super-long bored piles can be summarized as follows:
1. The pile load versus settlement curve (
Q
~
s
curve) has no
significant change in slope if sediment under the pile tip is
cleaned up or the pile tip is post grouted.
2. Under the ultimate bearing load, the pile top settlement is
mainly caused by pile shaft compression, especially the
compression of the upper half pile shaft. Moreover, the pile
shaft presents large plastic compression deformation under
very high load.
3. The mobilization of the pile shaft friction is asynchronous. In
other words, the pile shaft friction in the shallow soil layers
is mobilized before that in the deep layers. In the shallow
soil layers, due to the large relative displacement between
the pile shaft and the around soils, the pile shaft friction
usually reaches ultimate value, and is prone to softening. The
mobilization of the pile shaft friction in the deep soil layers
and the pile tip resistance is hysteretic due to the small
relative displacement between the pile shaft and the around
soils. The pile tip resistance is difficult to be mobilized
adequately due to the small pile tip deformation. The pile
shaft friction resistance occupied a fairly large proportion of
the pile ultimate bearing capacity. Therefore, super-long
bored pile can usually be identified as friction pile.
4. The mobilization of the pile shaft friction is correlated with
support condition at the pile tip. Not only the pile tip bearing
capacity is low but also the pile shaft friction resistance can
be cut down severely, when the bearing stratum is soft or the
sediment is thick under the pile tip. However, both the pile
tip resistance and pile shaft friction can be increased
significantly after the support condition is improved by post
grouting at pile tip.
3 SELECTION OF PILE TYPE AND PILE TIP BEARING
STRATUM
Considering post grouting or not, super-long bored pile can be
divided into normal pile, tip post grouted pile and tip and shaft
post grouted pile. It is difficult to guarantee the bearing
performance of the normal bored pile usually due to the
problems of pile shaft mud cake and pile tip sediment. The
sediment problem can be effectively solved by pile tip grouting
technique, which can help to improve the bearing behaviors of
the pile tip and pile shaft, and accordingly, the bearing capacity
of the pile can be greatly increased. Therefore, the pile tip
grouting technique is recommended for super-long bored pile.
When the pile tip is embedded very deeply, or soils around the
pile shaft are soft or settlement control of the pile is very strict,
pile shaft grouting can be implemented, which can further
improve bearing behaviors of the pile shaft and increase the pile
shaft friction. Post grouting technique was adopted for all the
projects listed in Table 1.
Although super-long bored pile is usually identified as
friction pile, the pile tip bearing condition has a great influence
on the mobilization of the pile shaft friction and the bearing
capacity and deformation characteristics of the pile. Therefore,
the deep and solid soil layers, such as rock, gravel layer and
sand layer, are often selected as bearing stratums for super-long
bored pile tip bearing stratums. As bearing behaviors of the soil
at the pile tip and the pile bearing capacity are improved by post
grouting, the shallower solid soil layer can be possibly selected
as bearing stratum. The depth of pile tip extended into the
bearing layer can also be decreased for this reason. Thus post
grouting technique has expanded the range of selection of pile
tip bearing stratum. This technique is benefit to shorten the
length of the pile, save engineering quantity, and achieve
optimization design of pile foundations.
4 FIELD LOAD TEST PILE DESIGN
Static filed load test is a basic and reliable method to obtain the
bearing behaviors of the super-long bored pile. It is also a
necessary link of inspection and optimization design of the pile
foundation. As a design principle of the test pile, test data and
technical parameters should be got as many as possible for
design and construction of pile foundation. Besides the general
contents, double steel sleeves, pile head, construction and
measurement requirements should be especially concerned
during the test pile design process.
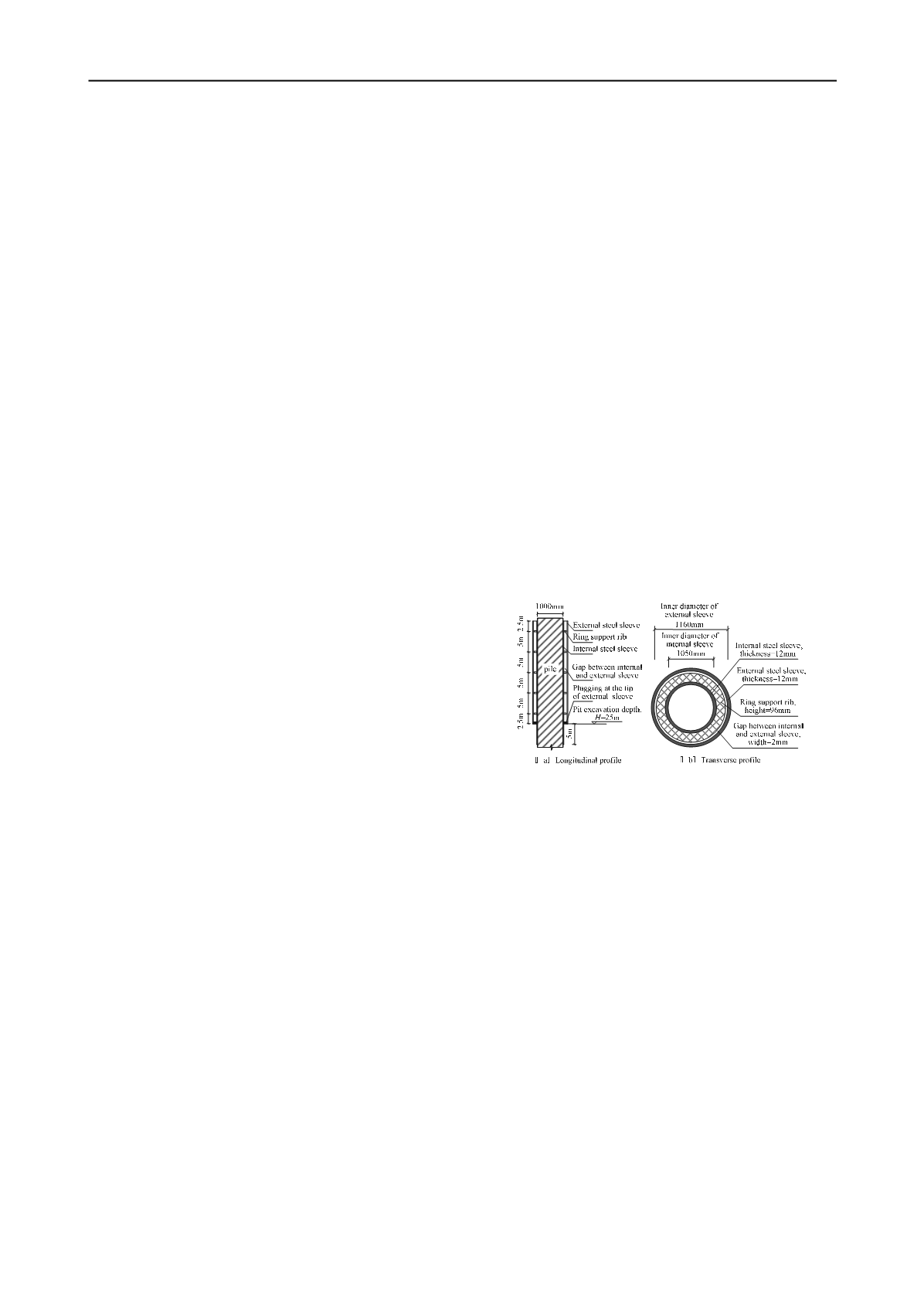
4.1 DOUBLE STEEL SLEEVES DESIGN
The base rafts of the super high-rise buildings are often deeply
buried. Therefore, it is necessary to concern how to reasonably
deduct the pile shaft friction in the excavation segment when
the load test is carried out at the ground surface. The pile test
with double steel sleeves isolating pile-soil contact in the pit
excavation segment can reasonably reflect the bearing behaviors
of pile (Wang et al, 2011). Double steel sleeves have been
applied in the pile load tests of several super high-rise building
projects, such as the Shanghai Center Tower, The Tianjin 117
Tower, The Wuhan Green land Tower, et al. The design
diagrams of double steel sleeves for the test piles of the
Shanghai Center Tower project are shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 Design diagrams of double steel sleeves for the test piles of the
Shanghai Center Tower project
4.2 PILE HEAD DESIGN
Super-long bored test piles often bear very large loads. For
example, the load applied to the field test pile of Wuhan Green
Land Tower reached 45000kN. Therefore, the test pile head
need to be special designed. According to loading condition and
test requirements, the pile head should be formed to provide a
plane surface which is normal to the axis of the test pile and
large enough to accommodate the loading and measuring
equipments. The pile head should be adequately reinforced or
protected to prevent damage caused by the concentrated loads
applied from the loading equipment. The pile head should be
concentric with the pile. The strength of the joint between the
pile head and the pile should be equivalent to that of the pile. If
the double steel sleeves are adopted for the test pile, measures
should be made to ensure that the head and the external sleeve
would not connect together during the construction process.
Figure 2 shows the design schematic diagrams of the test pile
head for the Shanghai Center Tower project. The anchor pile-
cross beam reaction devices were used in this field test. The
maximum load was 30000kN, which was applied using 8
hydraulic jacks. The capacity of each jack was 5000kN.


