2759
Visualization of Settlement Behavior for Friction Pile Group during Consolidation
Visualisation du tassement pour un groupe de pieux frottant lors d’une consolidation
Ishikura R.
Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan
Matsuda H., Igawa N.
Yamaguchi University, Ube, Japan
ABSTRACT: Combined technology by using surface stabilization and floating type deep mixing soil stabilization has been developed
as a method with acceptable settlement for maintaining the proper functioning of superstructures on deep soft soil layers. In this study,
in order to apply for the practice of this ground improvement technique, settlement properties and skin friction were investigated by
using two types of model tests and full scale FEM analysis in the consolidation process. For applying the image analysis to the model
test, it was clarified that vertical strain of soft clay in the upper part of the improved portion was restrained by transferring the load to
the deep soft soil layer. Further, from the analytic results, it was also found that full mobilization length of skin friction increased with
elapsed time and converged to the constant value under the consolidation condition.
RÉSUMÉ : Une technologie combinée comprenant une stabilisation de surface et des fondations de type pieux sur sol renforcé a été
développée pour limiter le tassement et assurer la stabilité des super structures dans les sols mous. Dans cette étude, afin d’analyser
cette technique d'amélioration du sol, le tassement et le frottement ont été étudiés à l’aide de deux types de modèle numérique à
grande échelle (MEF) pendant la phase de consolidation. Les essais sur modèles réduits ont montrés un transfert de la charge verticale
de la partie supérieure du massif renforcé vers la partie profonde sur sol mou. En outre, à partir des résultats, il a également été
constaté que la longueur de mobilisation du frottement augmente avec le temps et tend vers une valeur constante au cours de la
consolidation.
KEYWORDS: ground improvement, skin friction, consolidation, floating soil pile
1
INTRODUCTION
Economy and environmental safety have recently become very
important factors in the construction of soil structures. So it is
essential to develop the rational construction technique to
correspond with the diversity of performance. In this demand of
society, it is beginning to recognize the importance of the
technique that combines different individual methods.
Piled raft foundation has recently been considered as a
rational foundation type in Japan. This technology can reduce
raft settlement by combining piles with maintaining the safety
of the foundation on deep soft soil layers.
In the ground improvement field, combined technology by
using surface stabilization and floating type deep mixing soil
stabilization has also been developed. This technology has the
advantage to reduce the construction cost of soil structures on
deep soft soil layers. The structural form of the floating deep
mixing soil piles with shallow stabilization is similar to that of
the piled-raft foundation. In order to apply for the practice, it is
important to clarify the mechanical behavior of this improved
ground in relation to the combined effect between pile and raft.
In previous studies, several model tests for simulating this
type of improved ground were conducted to investigate the
influence of the improvement parameters such as improvement
ratio and improvement depth on the settlement (Bergado et al.,
1994; Miki et al., 2004; Ishikura et al., 2006). A method for
predicting the total settlement of this improved ground has been
previously proposed (Ishikura et al., 2006). On the other hand,
from the model tests of piled raft foundation conducted on soft
ground, it has been clarified that the failure of piled raft
foundations was caused by the block consisted of the pile and
soft clay enclosed within the pile group by Whitaker (1957).
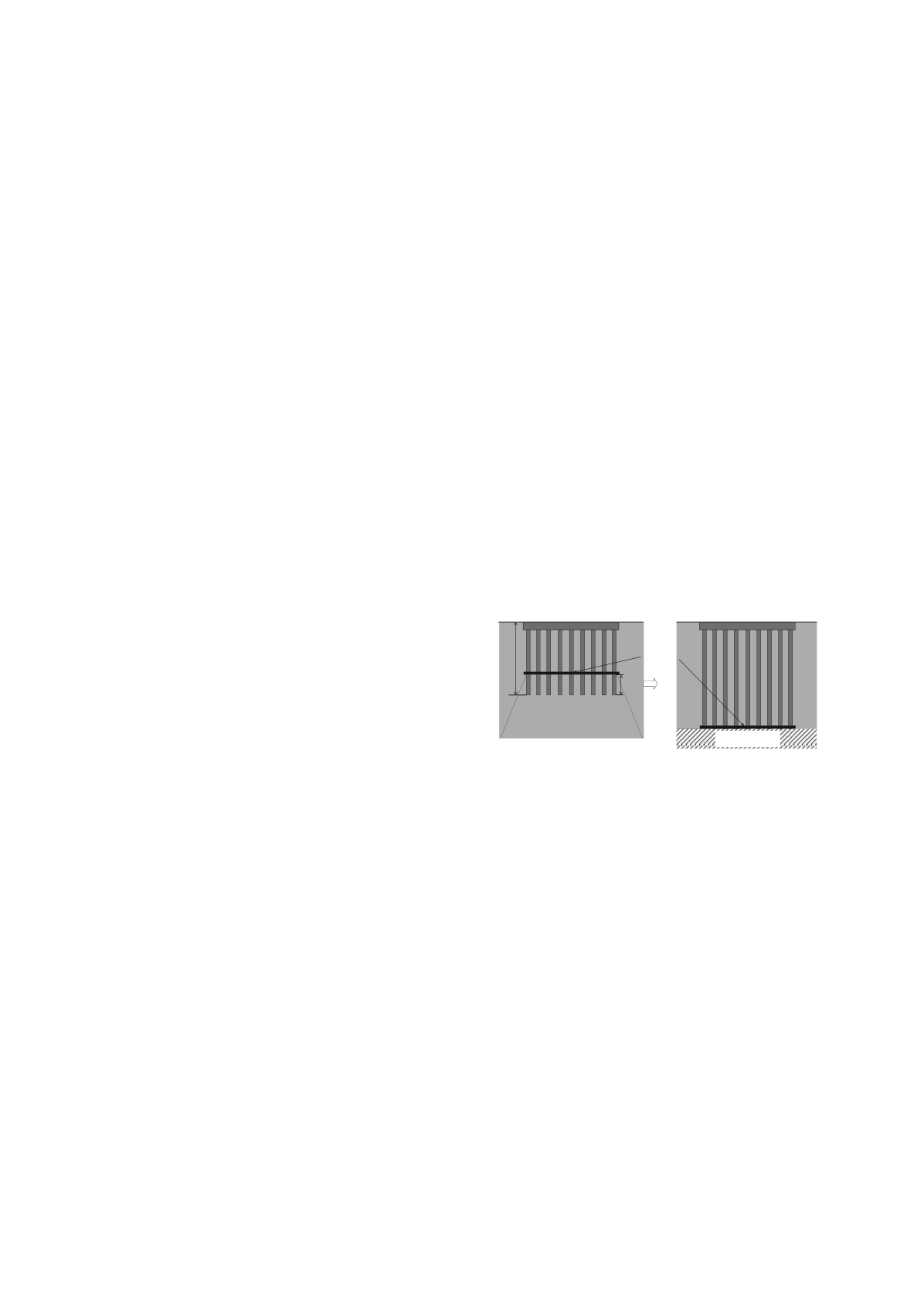
Figure1 shows the concept of the equivalent raft method. In
this figure,
H
1
is defined as the improvement depth. As shown
in this figure, Tomlinson et al. (2008) suggested that the pile
group transfers the load to the bearing layer at the elevation of
the pile tips by an end-bearing-type mechanism. He also
suggested that the pile group transfers the load to the soft soil
layer at an elevation corresponding to 2/3 the pile length below
the top of the piles. However, this method is still experimental
and has not been sufficiently validated.
H
1
H
1
/3
Bearing layer
α
H
1
Floating type
End bearing type
Equivalent
raft
Figure 1. Equivalent raft method
In this study, in order to investigate the group effect of this
improved ground in the consolidating ground, consolidation
settlement behavior was observed by using two types of model
tests. From the test results, the influence of improvement
conditions on the consolidation settlement and skin friction was
discussed. Secondly, ground behavior was observed through the
rubber membrane of transparent plate. By using image analysis,
several strain distributions of the model ground were clarified.
Based on the model tests, group effects during consolidation
were discussed. In particular, skin friction under different
improvement conditions were formulated.
Finally, in order to consider the equivalent raft elevation in
relation to the improvement conditions, full scale FEM analysis
were performed in the consolidating ground using the different
pile skin friction resistance. From the results, equivalent raft
elevations were discussed in the consolidation process.


