1266
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
The correlation between P-FWD results and dry density
values showed significant scatter. However, the same tendency
was verified for
E
P-FWD
, which increases with dry density
increase, as happened with the values obtained with the
geogauge equipment.
Similarly to the case of the
K
GG
, the variation of
E
P-FWD
with
dry density was negligible, thus restraining the conclusions
about the sensitivity of the elastic stiffness modulus to water
content variation.
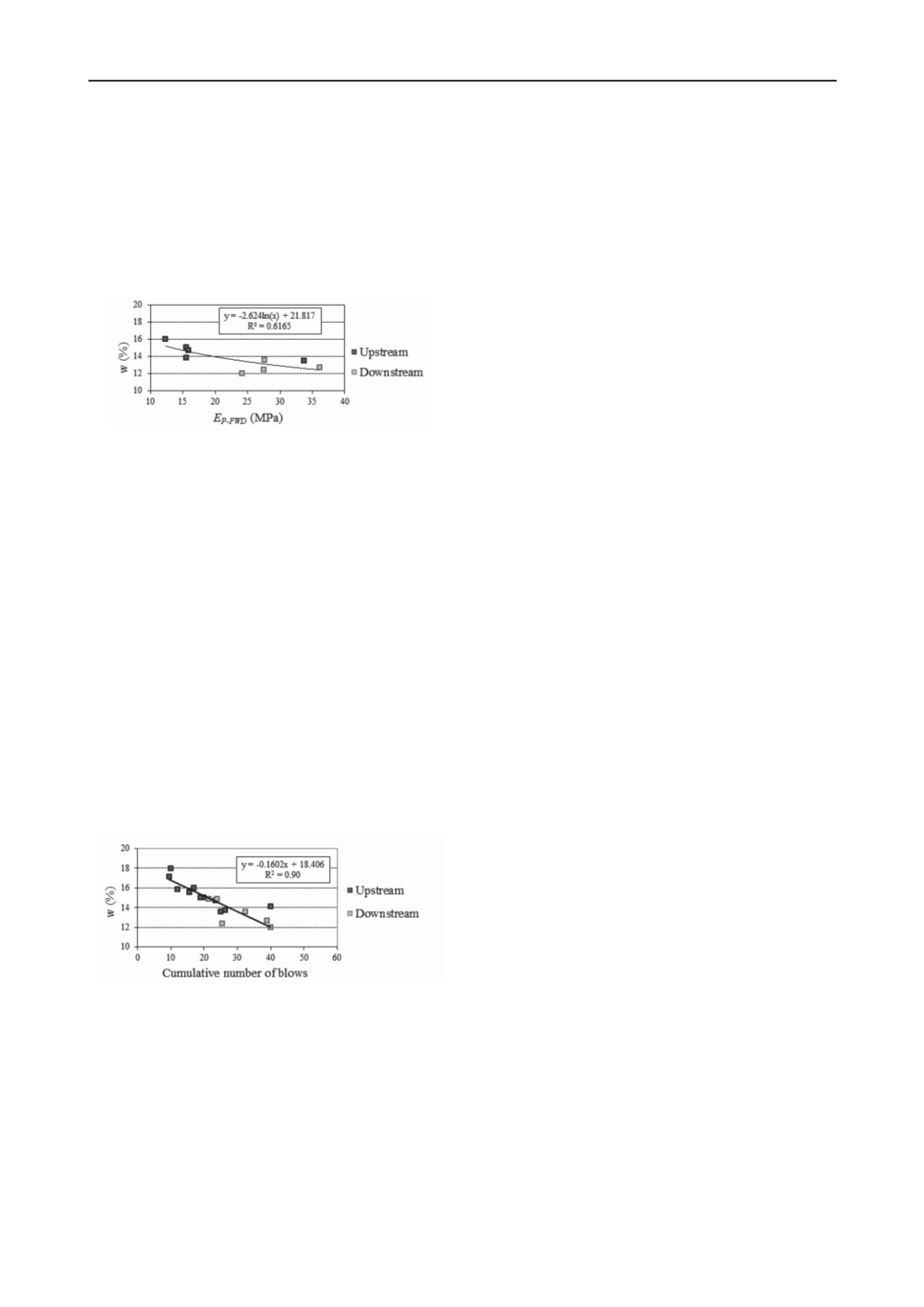
Figure 10. Relation between elastic stiffness modulus, E
P-FWD
, and water
content, w.
3.3
DCP results
DCP tests were carried out with penetration through the layer
thickness, i.e. 40 cm. The cumulative number of blows was
calculated by adding N
10
for each 10 cm of penetration
successively. Given the reduction of N
10
in the last 10 cm
penetration, lower compaction efficiency at the lower of the
layer was identified in some test points. As the vibrating roller
with smoth drum transmits energy to the layer from the surface
to the base, deficiency in compaction energy is prone to occur at
the base of the compaction layer. The decrease in N
10
between
30 and 40 cm depth occurred mainly in the downstream shell
compacted at the dry side of optimum water content.
Whenever a relatively homogeneous condition was
identified, equivalent conclusions were obtained based on the
commulative number of blows or on average penetration rate
(Conde
et al
. 2012). Otherwise, it was decided to select the most
representative deph for data processing. In these cases the best
quality correlation between water content and cumulative
number of blows were obtained at 30 cm depth, as ilustrated at
Figure 11. The determination coefficient is here much higher
than those obtained with the previous equipments, showing is
adequacy for compaction control.
Figure 11. Relationship between cumulative number of blows at 30 cm
depth and water content, w
.
Alike to the results of the other two equipments, the
relationship between DCP cumulative number of blows and dry
density had a significant dispersion, and it
wasn’t possible to
establish a correlation. Nevertheless, the downstream shoulder
penetration was observed to be higer than that of the upstream
one.
4 CONCLUSION
In order to assess the applicability of geogauge, portable falling
weight deflectometer and dynamic cone penetrometer devices
as compaction control tools, they were used during the
construction of an earth dam in southern Portugal to control the
compaction of the upstream and downstream shells. The
following conclusions and remarks may be drawn from the
current research :
P-FWD results can be affected by an inadequate
configuration choice.
Stiffness values by geogauge tests and stiffness modulus by
P-FWD tests, despite some dispersion, showed an
exponential negative correlation with water content. Higher
correlation to water content was apparent on downstream
shell, i.e. at dry compaction conditions.
A good quality linear correlation between DCP results and
water content was found. As a remark, in the presence of
heterogeneous conditions within the compaction layer
carefull choice of the reference testing depth is needed.
In all testing points, only a small variation in dry density
was observed (RC between 98 and 100%), thus putting this
experimental program off as a data base provider for the
assessment of the applicability of geogauge, P-FWD and
DCP to relative compaction control. Further research is
necessary with significant variation of dry density between
tests in order to clarify the correlation of the readings to
compaction.
Among the equipments used in this study the DCP
equipment showed greater suitability as a compaction
control tool, due to the strong negative correlation with
water content values.
5 ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors gratefully acknowledge the dam owner EDIA for
the permission for testing and the dam contractor MONTE
ADRIANO for the in situ assistance. Also thanks are due to
LNEC technicians Mr. Joaquim Timóteo da Silva, Mr. Rui
Coelho and Mr. António Cardoso.
6 REFERENCES
Abu-Farsakh, M. Y.; Alshibli, K.; Nazzal, M. and Seyman, E. 2004.
Assessment of In-Situ Test Technology For Construction Control of
Base Courses and Embankments
.
Technical
Report
nºFHWA/LA.04/385, Louisiana Transportation Research Center,
Baton Rouge, LA. USA. 126p.
Alshibli, K. A.; Abu-Farsakh, M. and Seyman, E. 2005. Laboratory
Evaluation of the Geogauge and Light Falling Weight
Deflectometer as Construction Control Tools.
Journal of Materials
in Civil Engineering
, 17 (5), 560-569.
American Society for Testing and Material. ASTM D4643 - 2000.
“Standard Test Method for Determination of Water (Moisture)
Content of Soil by the Microwave Oven Method”, ASTM
International, USA.
American Society for Testing and Material. ASTM D1556 - 2007.
“Standard Test
Method for Density and Unit Weight of Soil in
Place by the Sand-
Cone Method”, ASTM International, USA.
American Society for Testing and Material. ASTM D5080 - 2008.
“
Standard Test Method for Rapid Determination of Percent
Compaction
”, ASTM International,
USA.
Conde, M. C.; Caldeira, L. and Lopes, M. G. 2010. Study of application
conditions of the geogauge and the portable falling weight
deflectometer in compaction control. in Portuguese
Proceedings of
the XII Congresso Nacional de Geotecnia
, Guimarães, Portugal.
Conde, M. C.; Lopes, M. G. and Caldeira, L. 2009. Stiffness methods
for compaction control: the P-FWD device.
Proceedings of the 17
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical
Engineering
, Cairo, Egypt.
Conde, M. C; Caldeira, L.; Bilé Serra, J. and Lopes, M. G. 2012. Study
of dynamic cone penetrometer performance for soil compaction
control. in Portuguese
Proceedings of the XIII Congresso Nacional
de Geotecnia
, Lisbon, Portugal.
EN ISO 22476-2. 2005. Geotechnical investigation and testing
–
Field
testing
–
Part 2: Dynamic probing.


