1270
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
cap,
s
x
and
s
y
(m) the centre-to-centre distance piles along and
across the road,
s
d
(m) the diagonal centre-to-centre distance
piles,
(kN/m
3
) the unit fill weight,
p
(kPa) the surcharge load
and
(
o
) the friction angle. Figure 7 also gives the minimum
embankment height as required in respectively EBGEO (2010)
and CUR226 (2010).
The figures, as well as most other comparisons in Van
Eekelen et al. (2013b), show that the concentric arch model
agrees best with the numerical calculations, and most
measurements in the scaled model tests. For the considered field
test, the model of Zaeske and the concentric arches model give
comparable good results.
0%
10%
20%
30%
40%
50%
60%
70%
80%
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5
2.0
2.5
load part A (percentage of total load, %)
H/(sd-d) (m
)
concentric arches
Le Hello et al. 2009
Hewlett and Randolph
EBGEO
EBGEO minimum H
CUR minimum H
a=0.6m, sx=sy=1.5m,
gamma=19 kN/m3,
p=0kPa, phi=29deg
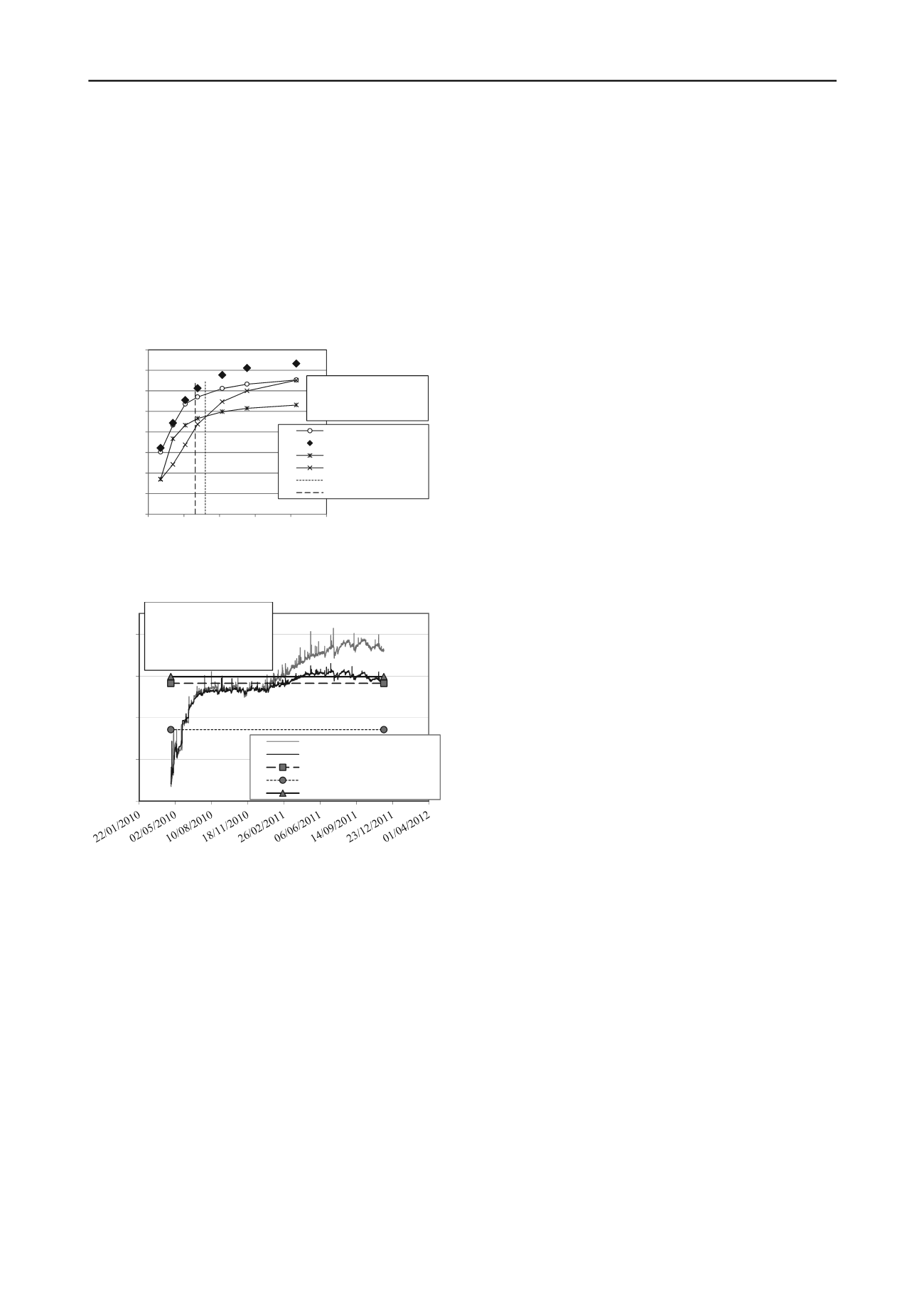
Figure 7. Variation of embankment height
H
, comparison analytical
models with numerical calculations of Le Hello et al. (2009).
0
40
80
120
160
arching A (kN/pile)
A pile 692
A pile 693
EBGEO/CUR A (phi=43)
BS8006 A (phi=43)
conc arches var 2 (phi=43)
=43
o
, average values
geometry: sx=sy=2.25 m,
H=1.86 m, 17 m soft soil:
k=0 kN/m
3
Figure 8. Comparison measured and calculated arching A in highway
exit Woerden, the Netherlands, described in Van Eekelen et al., 2012c
7 CONCLUSIONS
It is important to make a distinction between models for piled
embankments with or without geosynthetic basal reinforced
(GR). In the case with GR, the load is concentrated on the GR
strips between the piles (and the piles), and the load on the GR
strips is inversed triangular distributed. This paper deals with
the situation with GR.
The paper summarizes three equilibrium models describing
arching in GR basal reinforced piled embankments, namely the
models of Hewlett and Randolph (1988), Zaeske (2001) and the
concentric arches model of Van Eekelen (2013b).
It is shown how the three models obtain their load
distribution. Hewlett and Randolph (1988) as well as Zaeske
(2001) find an equally distribution load on the GR between the
piles. The concentric arches model (Van Eekelen et al. 2013b)
finds a load concentration on the GR strips, and approximately
an inversed triangular load distribution on those GR strips. This
is more in accordance with observations in scaled model tests,
numerical analysis and field measurements. The considered
numerical calculations agree best with the concentric arches
model. Measurements in the field agree equally well with the
concentric arches model and the model of Zaeske (2001).
8 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The financial support of Deltares and the financial support and
fruitful discussions with manufacturers Naue, TenCate and
Huesker for the research is greatly appreciated.
9 REFERENCES
ASIRI, 2012.
Recommandations pour la conception, le
dimensionnement, l'exécution et le contrôle de l'amélioration des
sols de fondation par inclusions rigides
, ISBN: 978-2-85978-462-1
(in French with in the appendix a digital version in English).
BS8006-1:2010.
Code of practice for strengthened/reinforced soils and
other fills
, BSI 2010, ISBN 978-0-580-53842-1.
CUR 226, 2010.
Ontwerprichtlijn paalmatrassystemen (Design
Guideline Piled Embankments
), ISBN 978-90-376-0518-1 (in
Dutch).
EBGEO, 2010 Empfehlungen für den Entwurf und die Berechnung von
Erdkörpern mit Bewehrungen aus Geokunststoffen e EBGEO, vol.
2. German Geotechnical Society, Auflage, ISBN 978-3-433-02950-
3. (in German, also available in English): Recommendations for
Design and Analysis of Earth Structures using Geosynthetic
Reinforcements EBGEO, 2011. ISBN 978-3-433-02983-1 and
digital in English ISBN 978-3-433-60093-1.
Hewlet, W.J., Randolph, M.F. Aust, M.I.E., 1988. Analysis of piled
embankments.
Ground Engineering
, April 1988, Volume 22,
Number 3, 12-18.
Kempfert, H.-G., Göbel, C., Alexiew, D., Heitz, C., 2004. German
recommendations for reinforced embankments on pile-similar
elements. In:
Proceedings of EuroGeo 3
, Munich, pp. 279-284.
Le Hello, B., Villard, P., 2009. Embankments reinforced by piles and
geosynthetics – Numerical and experimental studies with the
transfer of load on the soil embankment.
Engineering Geology
106
(2009) pp. 78 – 91.
Nadukuru, S.S., Michalowski, R.L., 2012. Arching in Distribution of
active Load on Retaining Walls.
Journal of geotechnical and
geoenvironmental engineering
, May 2012. 575-584.
Van Eekelen, S.J.M., Bezuijen, A., Lodder, H.J., van Tol, A.F., 2012a.
Model experiments on piled embankments Part I.
Geotextiles and
Geomembranes
32: 69-81.
Van Eekelen, S.J.M., Bezuijen, A., Lodder, H.J., van Tol, A.F., 2012b.
Model experiments on piled embankments. Part II.
Geotextiles and
Geomembranes
32: 82-94 including its corrigendum: Van Eekelen,
S.J.M., Bezuijen, A., Lodder, H.J., van Tol, A.F., 2012b2.
Corrigendum to ‘Model experiments on piled embankments. Part
II’ [Geotextiles and Geomembranes volume 32 (2012) pp. 82e94].
Geotextiles and Geomembranes 35: 119.
Van Eekelen, S.J.M., Bezuijen, A., 2012c. Does a piled embankment
‘feel’ the passage of a heavy truck? High frequency field
measurements. In:
proceedings of the 5th European Geosynthetics
Congress
. Valencia. Vol 5. Pp. 162-166.
Van Eekelen, S.J.M. and Bezuijen, A., 2013a, Dutch research on piled
embankments,
Proceedings of Geo-Congres, California
, March
2013.
Van Eekelen, S.J.M., Bezuijen, A., Lodder, H.J., van Tol, A.F., 2013b.
Analytical model for arching in piled embankments. To be
published in
Geotextiles and Geomembranes
.
Vermeer, P.A., Punlor, A., Ruse, N., 2001. Arching effects behind a
soldier pile wall.
Computers and Geotechnics
28 (2001) 379–396.
Zaeske, D., 2001.
Zur Wirkungsweise von unbewehrten und bewehrten
mineralischen
Tragschichten
über
pfahlartigen
Gründungselementen
. Schriftenreihe Geotechnik, Uni Kassel, Heft
10, February 2001 (in German).


