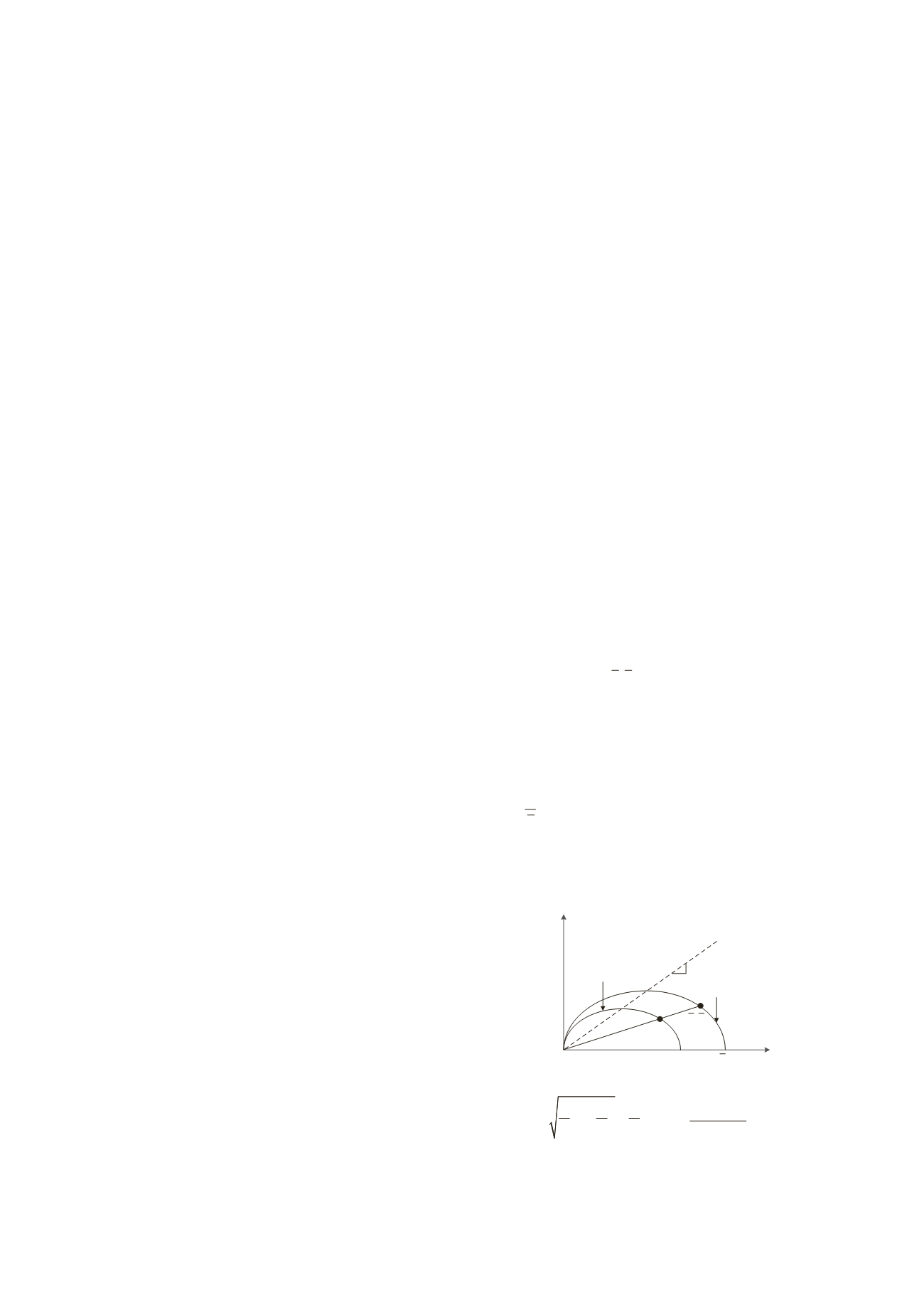
845
An elastic-viscous-plastic modeling of time-dependent behaviors of
overconsolidated clays
Un modèle élasto-visco-plastique pour les argiles surconsolidés
Yao Y.P., Kong L.M.
School of Transportation Science and Engineering, Beihang University
ABSTRACT: The instant normal compression line is proposed by analyzing the existing theories and experimental results. Based on
the creep law, the relationship between the aging time and the overconsolidation parameter is built. With the reloading equation of the
UH model used to calculate the instant compression deformation, a one-dimensional stress-strain-time relationship is proposed.
Furthermore, the characteristic rate that is a function of the overconsolidation parameter is defined. Then a three-dimensional elastic-
viscous-plastic constitutive model is suggested by incorporating the equivalent time into the current yield function of the UH model.
The proposed model can describe not only creep, rate effect and other viscous phenomena, but also shear dilatancy, strain softening
and other behaviors of overconsolidated clays. Besides, it needs only one additional parameter (the coefficient of secondary
compression) to consider the creep law compared with the modified Cam-clay model.
RÉSUMÉ : Une ligne de compression normale instantanée est proposée en se basant sur les théories existantes et sur les résultats
expérimentaux. Basée sur la loi de fluage, la relation entre le temps de vieillissement et le paramètre de surconsolidation est établie.
En utilisant l'équation de rechargement du modèle UH pour calculer la déformation de compression instantanée, on propose une
relation contrainte-déformation-temps unidimensionnelle. Par ailleurs, on définit le taux caractéristique qui est fonction du paramètre
de surconsolidation. Ensuite, un modèle tridimensionnel visco-élasto-plastique est proposé en intégrant un temps équivalent dans la
fonction de charge actuelle du modèle UH. Le nouveau modèle peut décrire non seulement l'effet de fluage, l’effet de taux et d'autres
phénomènes visqueux, mais également dilatance, adoucissement et d'autres comportements d'argiles surconsolidés. En outre, il n’y a
besoin que d'un seul paramètre supplémentaire (le coefficient de compression secondaire) dans la loi de fluage par rapport au modèle
Cam-clay modifié.
KEYWORDS: creep, viscoplasticity, stress-strain, overconsolidation, three-dimensional.
1 INTRODUCTION
Viscosity refers to the time-dependency of stress-strain
relationship of clays. The phenomena related to viscosity
include creep and rate effect which would change the
engineering properties of clays and result in such engineering
problems as ground settlements and landslides. Therefore,
numerous studies on viscosity have been conducted and large
numbers of constitutive models have been developed. The
models considering viscosity could be built with the empirical
method, the viscoelastic method or the viscoplastic method.
However, the empirical models are strictly limited to the
specific boundary and loading conditions, and the linear
viscoelastic models are not well valid for the behaviors in the
range of large strains. Hence, more and more studies are
focusing on the viscoplastic models (e.g., Kutter and
Sathialingam 1992, Yin and Graham 2002, Yin et al. 2010).
Nevertheless, most of the models proposed so far are only
applicable to normally consolidated (NC) and slightly
overconsolidated (OC) clays. Although a few viscoplastic
models have been extended to describe viscosity of OC clays
(e.g., Kutter and Sathialingam 1992), they are all complex and
have plethoric parameters. Hence it is necessary to build a new
elastic viscoplastic model for OC clays.
2 UH MODEL
The UH model (Yao et al. 2009) is a constitutive model for OC
clays based on the modified Cam-clay model (MCC). As shown
in Figure 1, there are two yield surfaces in the UH model, i.e.,
the current yield surface and the reference yield surface. The
current yield surface is the one where the current stress point (
p
,
q
) lies.
p
is the mean effective stress and
q
the generalized
deviatoric stress. The reference yield surface passes the
reference stress point
( , )
p q
which is the corresponding point of
(
p
,
q
) at the same stress ratio
η
(
η
=
q
/
p
). The UH model defines
the overconsolidation parameter
R
to reflect the degree of
overconsolidation of clays.
R
is the ratio of the current stress to
its corresponding reference stress. A smaller value of
R
corresponds to a larger OCR (overconsolidation ratio). The
expression of
R
is
p R
p
(1)
In the UH model, the potential failure stress ratio M
f
is
suggested to reflect the strength of OC clays. M
f
is expressed as
follows (Yao et al. 2012).
,
p q
,
p q
x
p
x
p
Figure 1. Current and reference yield surfaces of the UH model.
f
M 6 1
R R R
2
M =
12(3 M)
(2)
where M is the stress ratio at the critical state. Based on the
concept of the potential failure ratio, the UH model changes the