3285
Technical Committee 210 + 201 /
Comité technique 210 + 201
For high ECRD, the seepage stability of gravelly soil
depends on many factors. Besides gradation, dry density, stress
level and downstream protection are all have impacts on the
internal stability of soil upon seepage flow. Normally, the
mixture of sand, gravel and fine grains with good gradation will
present good erosion resistance. For gravelly soil, if the content
of coarse grains (>5mm) below 50%, the content of clay grains
(<0.075mm) above 15%, and the material is well compacted,
the gradient for resisting seepage failure will be relatively high.
But in practice it should be aware that due to the variability of
gravelly soil, the result obtained by calculation must be checked
by filter test.
3.1.3 Rockfill material
Rockfill is the main construction material of rockfill dam. Its
strength properties are related with dam slope stability and its
stress-strain properties are related with dam deformation. From
the experience of modern rockfill dam construction,
deformation control is the most important issue to be
considered. For high rockfill dam, rockfill with high or medium
rock strength, i.e. the saturated uniaxial compressive strength is
30
∼
80MPa, should be the best choice. For getting high
compaction density, the rockfill should also have good
gradation. From the point of deformation control and
deformation coordination, rockfill for CFRD should have as
high compaction density as possible. The purpose is to reduce
the overall deformation quantities. For ECRD, the consideration
in rockfill selection is more emphasized on deformation
coordination between dam shell and earth core.
The particle shapes of rockfill material are usually
polyhedron. Most of the particles are contacted by point. The
compressibility of rockfill mainly depends on re-arrangement of
particles, and it is also affected by other factors such as rock
lithology, density, gradation, etc. Due to the granular
characteristic of rockfill material, grain breakage and particles
rearrangement is occurred at any moment during loading
process. That means the status of rockfill material will be
changed all the time. Therefore, the material properties will not
be a constant value. For low dam, as the relatively low stress
level of rockfill, the breakage of particles is not significant and
most of the deformations are occurred during the stage of
compaction. For high dam, due to the high stress level and
complicated stress paths, the breakage and rearrangement of
particles cannot be neglected. The process of the particles
breakage and particles movement will lead to a significant
increase of the post-construction deformation of rockfill. At
present, this post-construction deformation of rockfill cannot be
fully analyzed by existing models and methods. For correctly
describe the change of status of rockfill material that caused by
particles breakage and rearrangement, the properties of particles
breakage of rockfill material must be fullly studied, and the new
analysis models will be further developed.
For rockfill, another important characteristic is the wetting
deformation property of the material. The mechanism of wetting
deformation of rockfill is the inteneration and breakage of the
edge of rockfill particles under the action of water. Besides, the
lubricating action of water promotes the movement and
rearrangement of the particles. Thus, it leads to the additional
deformation. The wetting deformation of rockfill is directly
related with its lithology. Normally, soft rockfill has relatively
large wetting deformation. But it is noticed that even for the
hard rockfill, such as limestone and tuff, the wetting
deformation still cannot be neglected. The wetting deformation
of rockfill will be reduced with the increasing of its density. In
addition, the more of initial water content of rockfill, the less
wetting deformation. Therefore, adding water during rockfill
compaction will play an important role in speed up deformation
completion and reducing post-construction of rockfill.
Correctly predict deformation of rockfill dam depends on the
constitutive model used in numerical analysis. The paper
submitted by Y. Chen used an elasto-plastic model that takes
into account irreversible deformations of poorly or well-
compacted rockfill under deviatoric and isotropic loading of
rockfill, known as L&K-Enroch, developed by EDF-CIH (Chen
2013) to conduct 3D numerical analysis of Mohale CFRD in
South Africa.
3.2 Foundation treatment
Foundation or subsoil condition is very important to the safety
of dam. Before the construction of dam, the unfavorable layer in
foundation must be properly treated. The paper submitted by J.
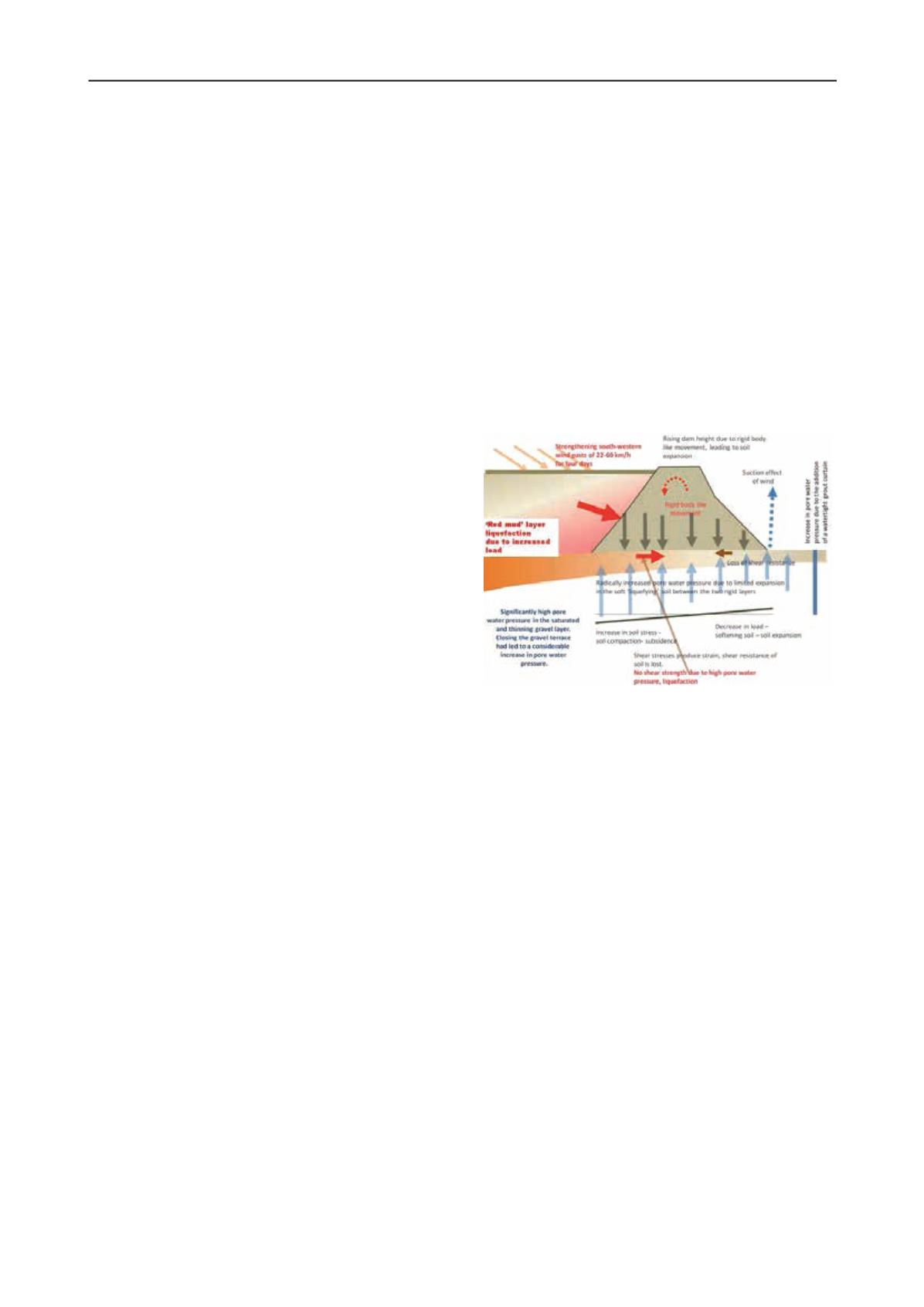
Mecsi presented a failure case of tailing dam in Hungary (Mecsi
2013). The foundation of the dam has a sand-silt layer that may
move under high water condition. Figure 4 is the summary of
some effects for the failure of the tailing dam. It shows the
impact of the unfavorable subsoil on the safety of the dam.
Figure 4 Summary of the effects for tailing dam failure
The foundation of high rockfill dam includes bedrock
foundation and alluvium foundation of sandy gravel deposit.
For the sandy gravel alluvium, if the alluvium has no soft, weak
clay layers or silt, fine sand layers, the bearing capacity and
stability of the foundation can be guaranteed. The main task of
foundation treatment is seepage control. If the lower part of
alluvium foundation exist sand layer, the possibility of sand
layer liquefaction should be carefully assessed.
For high rockfill dams, the commonly accepted seepage
control measure for foundation treatment is vertical cut off. It
could effectively block the seepage though pervious alluvium
foundation. With the measures of filter and drainage at
downstream seepage exit, the foundation and dam body will not
subject to seepage failure.
For high rockfill dam with deep alluvium foundation, the
most effective vertical seepage control measures are excavation
of all the alluvium layers under the impervious part of the dam
or using concrete diaphragm wall to cut the seepage though
foundation. Recently, concrete diaphragm wall is accepted for
most of the high CFRD constructed on deep alluvium
foundation. For this application, the diaphragm wall is
connected with plinth via concrete slabs (Xu 2010). For high
ECRD, both measures as alluvium excavation and concrete
diaphragm wall are applied.


