3117
Technical Committee 301 /
Comité technique 301
Gamma ray
source
shield lead
shield lead
photo-multiplier
and amplifier
Detector of Gamma ray
permeable spacer
supply
specimem
(soil)
test mold
pore water
pressure gauge
Marriotte siphon
Rainmaking
i
water tank
Marriott siphon
exhaust port of
the boundary flow
lower exhaust port
exhaust port of
the surface flow
Coarse particle soil
100
200
300
fine particle soil
1100
leakage sensor
Hypodermic needle
inclination angle
check box for
intensity of
Test Chamber
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
0.001
0.01
0.1
1
10
100
Particle size D
(
mm
)
100
Percent passing
(
%
)
coarse soil
fine soil
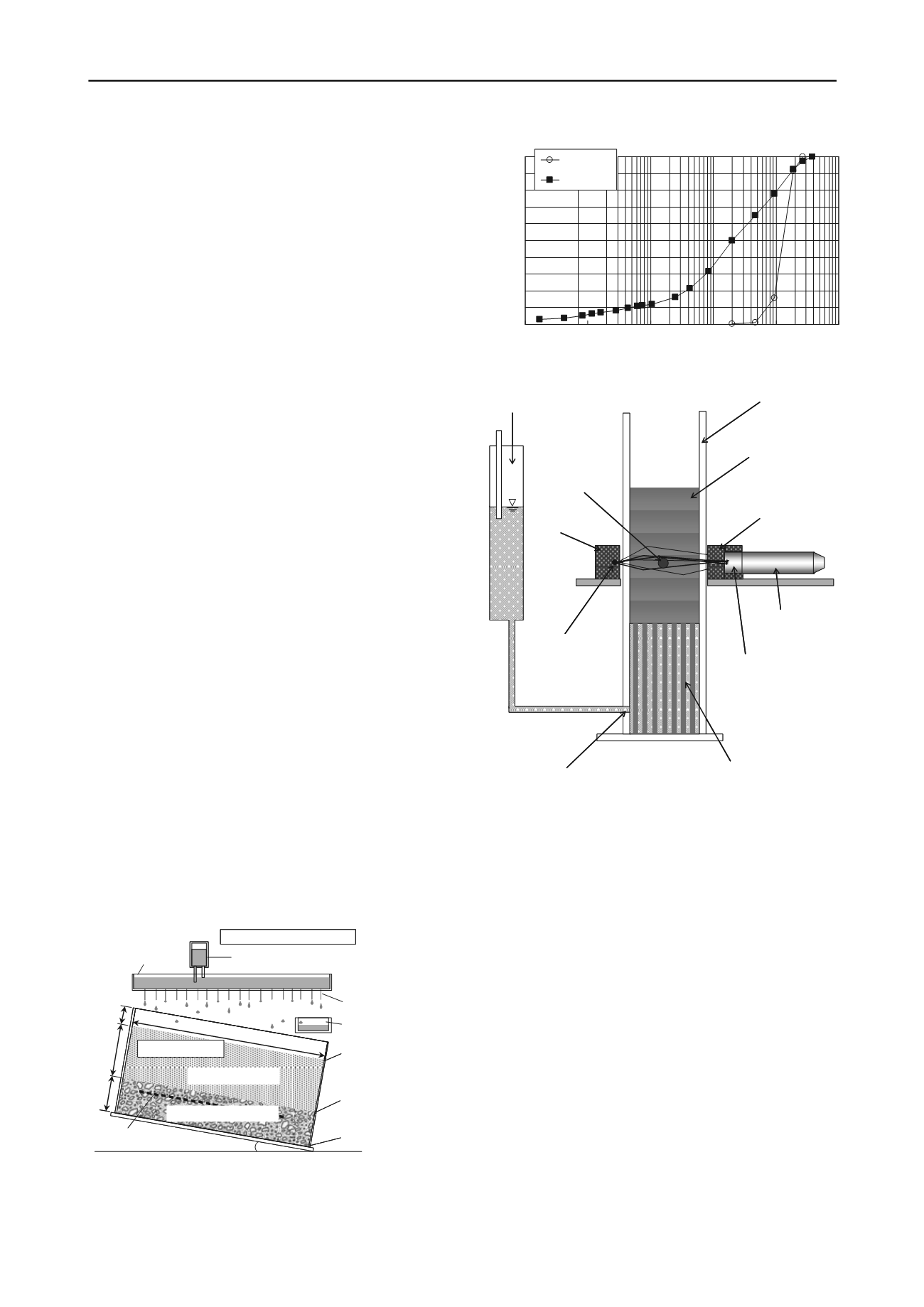
Figure 6 Grain size distribution curves of the candidate soils
100 % and when the underground water level lowers in the dry
season, the degree of saturation from G.L. -5.04 m to – 9.0 m
significantly drops to about 35%. On the contrary, the degree of
saturation above G.L. -5.04 m is about 60% in the rainy season,
and it is noteworthy that the degree of saturation in the layers
above the groundwater level of does not change at all
layer and the underlying
content equivalent to the one for the actual restoration. A series
of compaction tests is conducted with the different compaction
energy on the material under the natural water content. Based
on the experimental results, the density of the soil for the
chamber test is determined by supposing the compaction energy
at the construction of restored earth mound. The relation of the
moisture content by volume and the suction is separately
investigated from the unsaturated seepage test. The adopted
testing apparatus for the unsaturated seepage test with the
radioisotope system is shown in Figure 7.
Figure 8 shows the experimental results between the tangent of
the inclination angle of the foundation and the limit length
L
that denotes the resistant distance for the capillary barrier under
the prescribed intensity of precipitation of 3.6 mm/hr. In the
present study, the thickness of the compacted earth mound is
300mm. A set of electric sensors to detect water is put at the top
of the underlying coarse gravel layer. When infiltrated water
leaks to the gravel layer, we can detect the location of the
breaking point of capillary barrier by the occurrence of short-
circuit. As shown in the figure, there is a definite linear
relationship between the limit length
L
and the inclination angle
of the foundation in terms of tan
. It is found that the water
resistant structure with capillary barrier at the border of the
layered earth mound is expected to function under the condition
of the inclined foundation such as tumulus mound.
Figure.5 Schematic view of the model chamber of the test for capillary
barrier
Figure 7 Schematic view of the unsaturated seepage test device
irrespective of the underground water level. From these results,
the seepage of the water to the layers above the groundwater
level due to suction can be ruled out. It is hence not necessary to
consider the problem of exudation of the underground water
into the stone chamber from its base.
4 ASSESSMENT OF WATER RESISTANT STRUCTURE
The shelter building is planned to be constructed for the
conservation of the naked stone chamber of the Garandoya
Tumulus. It is true the intruded rain water is intercepted by the
shelter building but it is preferable that the intruded water does
not reach the surface of the shelter building to avoid possible
leakage due to loss of function of the waterproof processing
equipped among the concrete panels of the shelter building. The
earth mound has been selected to cover the shelter building to
reproduce the original shape of the tumulus together with the
consideration of the adiabatic effect. The layered structure,
namely the well compacted soil underlain by the well permeable
coarse gravel has been adopted for the restored earth mound in
order to provide a good drainage function. The adopted layered
earth mound structure consequently give a possible function of
a capillary barrier at the border of the compacted soil and gravel
layers due to the different capacity of suction in those layers.
A series of the chamber tests on the layered foundation is
carried out to confirm the occurrence of capillary barrier at the
border of the upper compacted soil
coa se gravel layer. The model chamber is shown in Figure 5.
The selected parameters for this chamber test are the inclination
r
angle of the foundations and the intensity if precipitation. The
size of the model chamber is 1100 mm in length, 600 mm in
height, and 120 mm in width. The equipment for precipitation
has eight hypodermic needles per 100 cm
2
at the bottom of the
tank, and can give the raindrop from the needle tip to the
surface of the model foundation. Intensity of precipitation is
adjusted by the hydrostatic pressure in terms of the level of
water in the tank that can be controlled by the Marriott siphon.
The soil with which the present experiment is conducted is the
candidate material of the tumulus restoration that is the graded
grain material extracted from the quarry in the proximity of the
tumulus. The coarse gravel is also extracted from the same
quarry. The particle size distribution of the materials is shown
in Figure 6. The candidate material is a well-graded sandy soil.
The initial water content of soil was adjusted as natural water


