3112
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
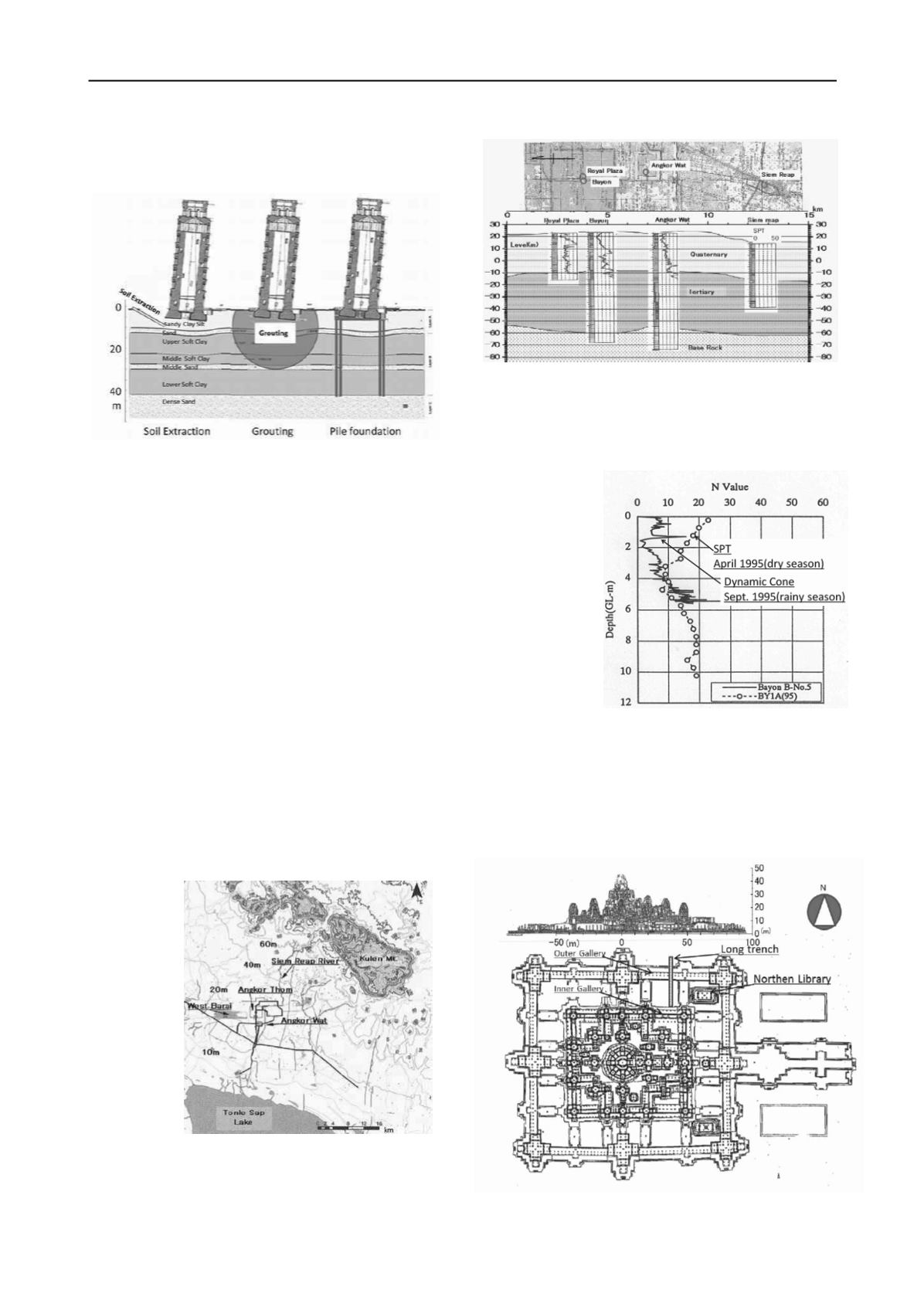
extract upper soft clay of the northen side by boring was
adapted in 1998 as a trial test. The soil extraction was succefully
applied and completed in 2001 (Burland,2009).
Figure 1. Possible contermeasures for restoration
Figure 1 shows three possible methods to restore the Pisa
Tower. During the selection of possible various methods,
discusions had been focussed upon the keeping the specific
character of the Tower and the structural safety of the upper
strcture. There was a choice to restore the tower at upright
condition without any inclination. However, the state of being
inclined is the specific value of the Pisa Tower, the
characteristic element of the authenticity, the restoring method
is only valid to keep the inclined state within some safety
margine.
We could compare other methods of grouing or pile
foundation to the soil extraction on the base of the authenticity
as follows.
The inclination of the Tower is one of the characteristic
element of the authenticity as an essential factor of the heritage.
There are also important geotechnical factors to have caused the
inclination of the characteristic of the heritage. These are thick
soft clay ground and direct shalllow foundation that also
constitute the characteristic elements of the authenticity.
3.2 Stone masonry in Angkor
Angkor monuments are distributed in a wide region of ancient
Khmer Empire whose basic activities was in a Angkor plain
from Kulen Mountains Ton le Sap Lake in Cambodia as shown
in Figure 2.
Figure 2. Angkor Plain
Figure 3. Geological section in Angkor plain N-S direction
Figure 3 shows geological section of the central part of the
Angkor plain. Angkor plain consists of surface soil layers of
Quaternary with 30-40meters in thickness followed by tertiary
deposit and base rock.
Figure 4.
Seasonal change
of N value in
Angkor
Angkor belongs to monsoon region and shows distinctive
climate of rainy season from May to October and dry season
from November to April in a year.
Figure 4 shows changes of strength of SPT N-values at the
same site in Bayon for dry and rainy season. The soil is silty
fine sand and shows the STP value of about N=20 at the surface
in dry season but drops to about N=5 during rainy season.
Figure 5. Bayon temple plan and section


