3122
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
Fig. 7. Organizing Committee Building under construction
.
Table 1. Soil conditions of the Organizing Committee Building site.
Soil element
Depth,
m
E,
MPa
φ,
deg
c,
kPa
Clay
0…4,5
6
13
22
Very soft clays
4,5…21
0,7
10,6 10,3
Coarse sand
21…23
27
29
0
Mixture of gravel
and pebbles
>23
53
35
0
Table 1 shows that application of spread footings is not
possible, as it would result in excessive settlement. Soil
improvement
such
as
strengthening,
reinforcement,
replacement, etc. are not applicable because of thick layers of
soft clays. Installation of drains for soil consolidation together
with preloading of soil mass could not be applied due to tight
project deadlines. Therefore, pile footing was the only
alternative. At the stage of pile type selection there were
considered prefabricated piles, bored cast piles, jet-piles, gravel
piles in geosynthetic shell, etc.
The condition that complicates pile foundation design is that
in order to ensure a footing seismic stability the piles shall bear
the total lateral seismic load. The soil stratum capable to
adequately resist to the lateral load usually occurs at over 21 m
depth. In conditions of the site in question pile design bearing
capacity to vertical load is times 40…60 greater that to the
lateral load. In order to bear the vertical load of the 9-storey
sector of the building 511 piles with 0.35x0.35 cm2 cross
section are required while it requires 2030 piles to resist to
lateral seismic load, i.e. times 4 as much.
Mass application of pile foundations with intermediary sand
layer has started in 1960s in seismic areas of the USSR. The
results of full-scale experiments demonstrated that in such
foundations the lateral seismic load does not practically apply to
the piles. Such foundation is recommended for practical
application on sites having magnitude 7…9 seismicity.
Application of pile foundation with intermediate cohesionless
soil layer is not recommended by construction codes for sites
with soils containing more than 10% of organic matter,
collapsible soils, on karstic terrains, etc. This ban comes from
possibility of collapse of loose soil and its disrupture that may
result in extra deformations of the building. In order to enable
application of such foundation a specific approach was required
for foundation analysis and design.
Expanded pile caps together with cushion of cohesoinless
soil reinforced by two layers of geosynthetics were used.
Existing calculation method proposed by construction codes
was developed with regard to aforementioned additions. The
improved method took into account elasto-plastic properties of
soils of the base; pile group effect, geometric and stiffness
properties of deep footing (pile caps, reinforcement nets, etc.);
stiffness parameters of foundation rafts (pile rafts); seismic
conditions of construction site, etc.
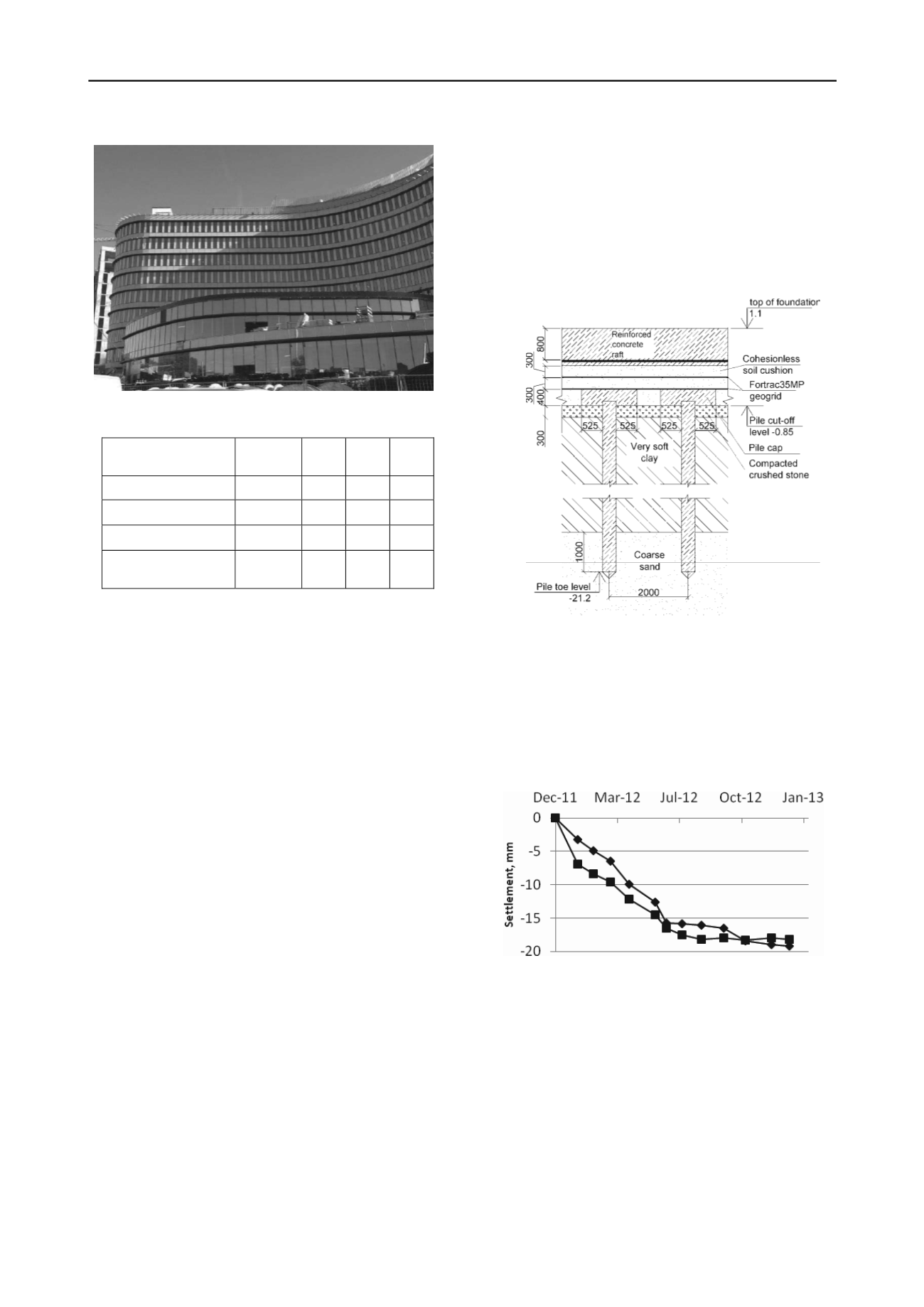
The foundation design approved for implementation is
shown on Fig. 8. Pile foundation below 9-th storey sector
consists of 0.35x0.35 m prefabricated piles spaced over 2x2 m
and for the 3-storey sector with 4x4 m square grid. The pile
cap dimensions are 1,4х1,4х0,4 m. The intermediate cushion is
600 mm thick, reinforced by two layers of Fortrac 35MP
geogrid. The raft thickness under 9-storey and 3-store sectors
800 and 600 мм respectively.
Fig. 8. Foundation cross-section for Organizing Committee
Building.
The most essential factors predominant for the effectiveness
of a such footing are: thickness of the intermediate layer above
pile heads; pile caps overview dimensions; pile-to-pile spacing;
pile cross sections; number of layers and stiffness of geogrid.
The building settlements monitoring data demonstrated that
the settlement is close to analytical value and is compatible with
actual standard pile footing settlements. Typical time-settlement
diagrams based on measured values are shown on Fig.9.
Figure 9. Time-settlement diagrams for Organizing Committee
Building
.
4
PLOT D1 AND PLOT 17.
Hotel complexes 3* and 4* are being constructed on plots 17
and D1.Plot D1 is located a slightly little closer to the shore.
Construction of 12 multistorey hotels (up to 8 floors) and
buildings of public entertainment area is planned on plot 17.
Each of the hotel building consists of two sections with
dimensions of 36 x 14.9 m. Dimensions of the plot 17 is 265 x
220 m. Overview of the complex is shown in Fig. 12. Soil
conditions of the site vary significantly due to its large area. The
typical cross section of the site top down consists of 4 m thick
fill, less frequent are peats, sludge and water-saturated silty
sands, underlain at different depths (3…11 m) by gravely sands
and gravel and pebble soils.


