3109
Technical Committee 301 /
Comité technique 301
is required to prevent the sphere rebounding over the
embankment crest on the first impact.
The maximum width of the activated embankment body
is 5 to 6 times the sphere diameter.
In the tests it was found that the failure planes from the
second impact onwards tended increasingly to form in
an upward direction.
The pictures taken with the high-speed camera clearly
show quite significant elastic deformations during the
period of impact.
45
70
=10°
D
v
v
=20°
b=4,5cm
e
h
a
„Uphill face"
„Downhill face"
Extensometer
Extensometer
a , a , a , a
o
2 3
1
b
o
Figure 2. Model embankment with rip-rap facing
=10°
D
v
v
=20°
e
h
a
"Uphill face"
„Downhill face"
Extensometer
Extensometer
a , a , a , a
o
2 3
1
b
o
Activated embankment area A
a
b
Figure 3. Model embankment system
3.2.3 Lessons from trials with rip rap facing and without
geosynthetics
The following additional observations were made on
embankments with rip rap facing:
Slope angles ≥ 50° require a freeboard of at least 1 x the
diameter of the sphere.
After the impact, the sphere scarcely changes its height,
whereas in the case of pure soil embankments, and
reinforced structures, it tends to jump or roll in the
direction of the crest.
3.2.4 Lessons learned from the tests with geosynthetics
The model tests with the geosynthetics all showed a
significantly larger lateral distribution (influence width)
of the displacements. An influence width of at least 8 - 9
times the diameter of the sphere can be estimated from
the measurements and the pictures taken with the high-
speed camera.
Very slim constructions with uphill and downhill slope
angles of 70° and 60° were also investigated. These
exhibited a noticeably more elastic behaviour than pure
soil embankments.
However, they require a markedly greater freeboard than
embankments with rip rap facing. For geogrid-
reinforced structures, a freeboard of 1.5 times the sphere
diameter can be considered as being on the safe side.
4 DESIGN MODEL FOR ROCKFALL-PROTECTION
EMBANKMENTS
4
.1
Principles
A characteristic failure body for different structures was derived
from the 1g model tests. An important and consistent parameter
was the activated width of the embankment in the direction normal
to the impact. The basic concept of the proposed design method is
to derive a non-dimensional relationship between the penetration
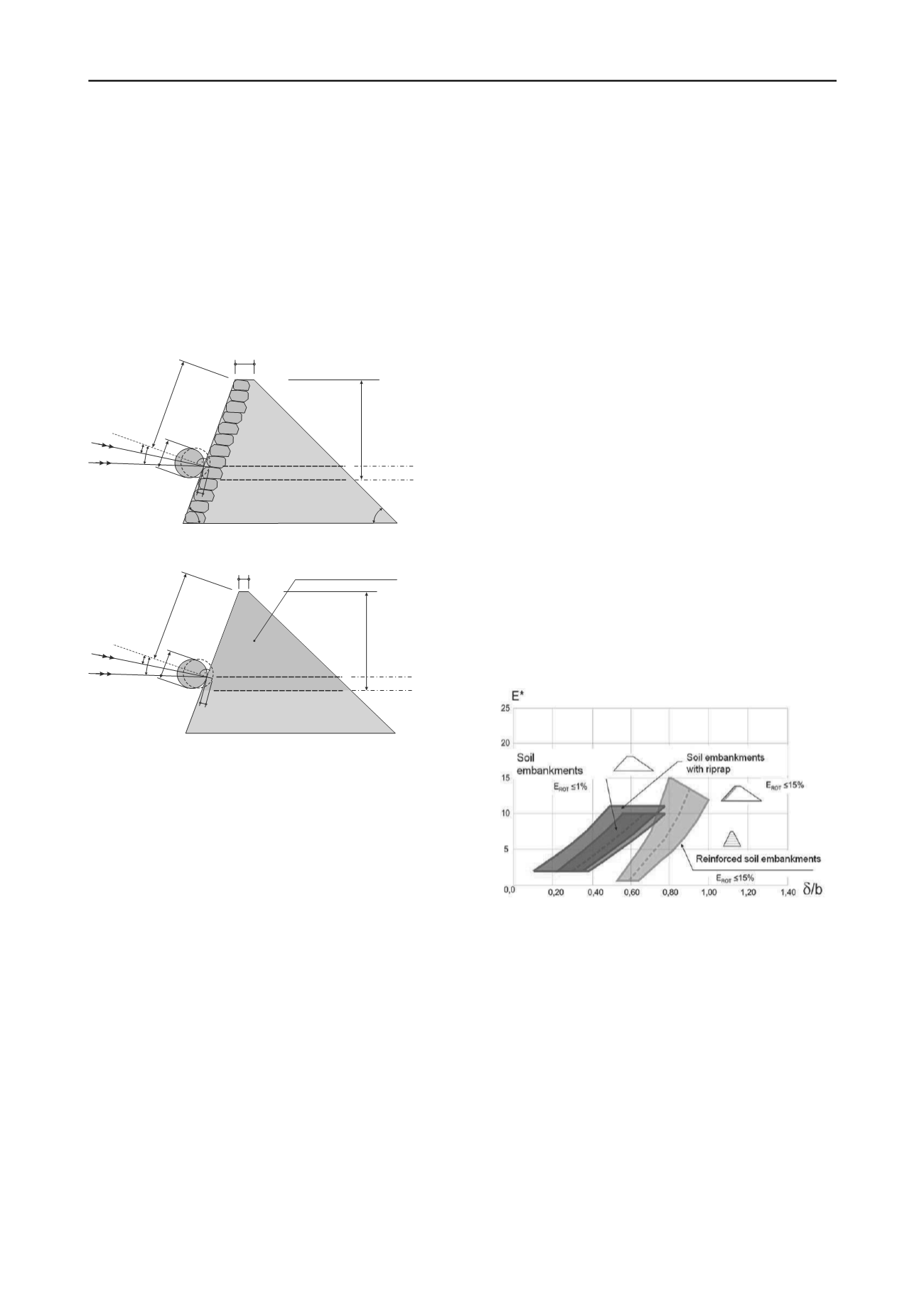
depth and the crest width (δ/b) using the relative impact energy
E*, Hofmann & Mölk (2012).
4.2
Activated failure body
Normal to the impact direction, the size of the activated failure
body is a function of the embankment structure. Whereas the
width of the failure body in unreinforced embankments (both with
and without rip rap facing) is at least 5 to 6 times the diameter of
the block (the sphere in the model), this value increases to 8 to 9
times the diameter of the block for reinforced structures.
4.3
Required freeboard
Freeboard is defined here as the distance between the upper
surface of the block and the upper surface of the embankment,
measured along the slope (Section 3.2)
Figure 4. Comparison of the different structures
4.4
Estimate of the equivalent static force
An estimate of the equivalent static force is made using equation
(5), on the assumption that the force initially increases, and then
decreases, in a linear manner, and that the velocity decreases in a
linear manner according to Blovsky (2002) (Figure 5). The
equivalent static force is then distributed over the activated
embankment width involved.
F = v² m / δ
(5)
F = 2 v m / Δt
(6)
Δt = 2 δ/ v
(7)
δ = (0,8 bis 0,85) m v²/ F
(8)


