2682
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
n the figure is the
I
versus
t
plots
for homogeneous soil with shear modulus equal to
G
s
. As
ect of layering is predominant for
Similar plots can be obtained for
ent field is defined and the variational principles of
me
alent three dimensional finite
element analysis. A parametric study is performed for piles in
lay red soil profile. It is found that soil layering does have an
effect on the pile response, particularly for short, stubby piles
ith low slenderness ratio.
les in three-layer soil.
Randolph, M. F. (1981). Piles subjected to torsion. Journal of
Geotechnical Engineering, 107(8), 1095–1111.
0.01
0.1
1
10
100
Relative Pile-Soil Stiffness,
t
0.01
0.1
1
10
100
1000
10000
Torsional Influence factor,
I
Homogeeous Soil
3 Layer Case I
3 Layer Case II
3 Layer Case III
G
s
1
G
s
2
L
p
/
3
G
p
L
p
/
3
L
p
/
3
G
s
3
Layering Cases
0.23
G
s
0.69
G
s
2.08
G
s
I
II
0.69
G
s
0.23
G
s
2.08
G
s
III
2.08
G
s
0.69
G
s
0.23
G
s
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1
H
1
/
L
p
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
I
I
,homogeneous
L
p
/
r
p
= 20;
I
homogeneous
= 0.56
L
p
/
r
p
= 100;
I
homogeneous
= 0.11
G
p
/
G
s
1
= 1000
G
s
2
/
G
s
1
= 0.25
0.50
4.0
2.0
G
s
1
G
s
2
L
p
H
1
G
p
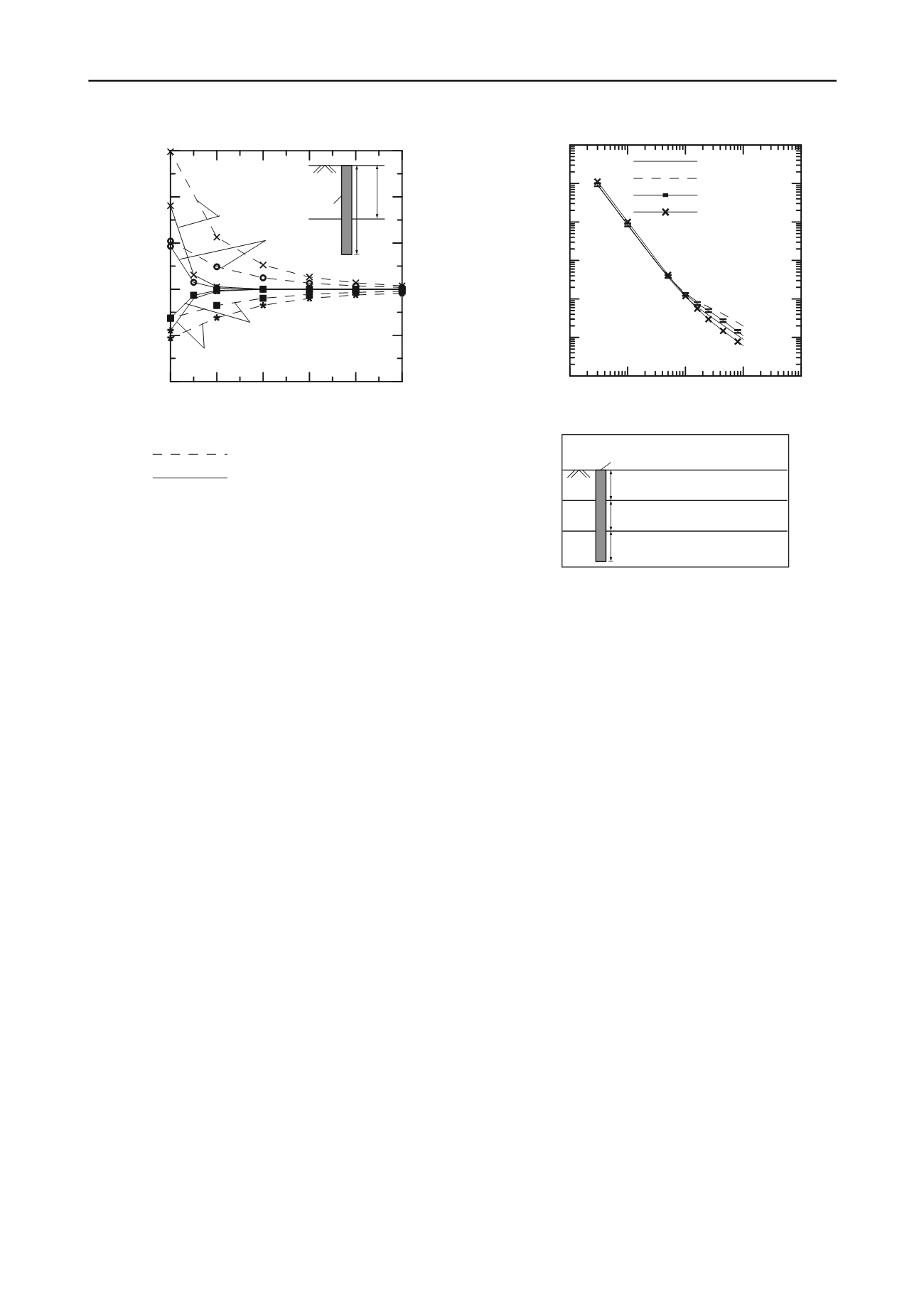
Figure 4. Angle of twist versus depth of a 10 m long pile in a 2-layer
soil deposit.
The effect of soil layering is further studied with three-layer
profiles for three different cases. For all the cases, the three
layers divide the pile shaft into three equal parts of length
L
p
/3
and the pile base rests within the third layer, which extends
down to great depth (Figure 5). Moreover, the shear moduli
G
s
1
,
G
s
2
and
G
s
3
of the top, middle and bottom layers are so chosen
that (
G
s
1
+
G
s
2
+
G
s
3
)/3 =
G
s
for all the cases. Case I represents
a soil profile in which the soil stiffness increases with depth
the top, middle and bottom (third) layer have a shear moduli
equal to 0.23
G
s
, 0.69
G
s
and 2.08
G
s
, respectively. Note that, for
this case,
G
s
3
= 3
G
s
2
and
G
s
2
= 3
G
s
1
. For Case II,
G
s
1
= 0.69
G
s
,
G
s
2
= 0.23
G
s
and
G
s
3
= 2.08
G
s
. For case III, the soil stiffness
decreases as depth increases with
G
s
1
= 2.08
G
s
,
G
s
2
= 0.69
G
s
and
G
s
3
= 0.23
G
s
. Figure 7 shows the
I
versus
t
plots for these
cases. The parameter
t
is calculated using the average shear
modulus
G
s
. Also plotted i
Figure 5. Response of pi
5 REFERENCES
ile, F. (2010). Torsional response of pile gr
Bas
oups. Proc. 11th DFI and
EFFC Int. Conf. on Geotechnical Challenges in Urban
Regeneration, June 26-28, London.
kowsk
Bud
a, B. B. and Szymczak, C. (1993). Sensitivity analysis of
piles undergoing torsion. Computers and Structures, 48(5), 827-
834.
Chow, Y. K. (1985). Torsional response of piles in nonhomogeneous
soil. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 111(7), 942–947.
t, R. N. and O’Neill, M. W.
Dut
(1983). Torsional behavior of model
piles in sand. Geotechnical Practice in Offshore Engineering,
ASCE, New York, 315–334.
evident from Figure 5, the eff
t
> 1.0 for which
I
< 1.0.
cases with multiple layers.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The paper presents a method for analyzing piles in multi-
layered elastic soil subject to a torque at the head. The analysis
is based on a continuum approach in which a rational
displacem
Guo, W. D. and Randolph, M. F. (1996). Torsional piles in non-
homogeneous media. Computers and Geotechnics, 19(4), 265-287.
, W., Chow, Y. K. and Randolph,
Guo
M. F. (2007). Torsional piles in
two-layered nonhomogeneous soil. International Journal of
Geomechanics, 7(6), 410–422.
he, R. A. G. and V
Hac
alsangkar, A. J. (1988). Torsional resistance of
single piles in layered soil. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,
114(2), 216–220.
chanics are used to develop the governing differential
equations. The equations are solved analytically using which
the pile response can be obtained using an iterative solution
scheme.
The new method predicts the pile response quite accurately,
as established by comparing the results of the present analysis
with those obtained in previous studies by different researchers
and with the results of equiv
Poulos, H. G. (1975). Torsional response of piles. Journal of
Geotechnical Engineering, 101(10), 1019–1035.
apakse, R.K.N.D. (1988). A torsion loa
Raj
d transfer problem for a class
of non-homogeneous elastic solids. International Journal of Solids
and Structures, 24(2), 139-151.
e
w


