3272
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
mechanical bridging of flocculating agent: polyaluminum
chloride is frequently used in Japan. Some hydrophilic parts of
flocculating agent remain and bind clods as second binding,
then more than 10
-5
m diameter clods presumably form DWS’s
porous structure as shown in Fig. 1.
In this study, DWS was sampled in Ibaraki, Japan.
Approximate organic matter content of DWS was determined
by ignition loss tests. The ignition loss and fundamental
properties were listed in Table 1. Ignition loss of DWS was
17.6%
―
27.3%. The amount of humic and fulvic acids were
determind by alkaline and acid isolation (Ohkubo et al., 1998).
Specifically, humic acid content was dominant for DWS. It is
indicated that organic matter exists in as a solid part and a
bonding as well as the mechanical bridging. A main constituent
of polyaluminum chloride is Al
2
O
3
. Previous study has been
already confirmed Al leaching by column leaching tests in Fig.
3 (Watanabe et al., 2009). Organic matter decomposition at 30
degrees has been confirmed in Fig. 4 (Watanabe et al., 2011),
which means the loss of DWS particles and binders.
Consequently, engineering properties of DWS after the
decomposition mentioned above are interest on a discussion of
DWS durability.
Table 1. Fundamental properties of DWS.
DWS
3 RELATION BETWEEN SHEAR STRENGTH AND
DECOMPOSITION
Shear characteristics of DWS after decomposition were
investigated to elucidate the necessity of the mechanical
bridging and organic matter on DWS’s structure. The DWS
which was mainly decomposed by H
2
O
2
solution was used in
triaxial compression tests.
3.1 Experimental procedure
Triaxial compression tests were executed using the DWS for
which the mechanical bridging and organic matter had been
decomposed by the H
2
O
2
solution. The apparatus for the triaxial
compression tests is portrayed in Fig. 5. The specimen had 100-
mm height and 50-mm diameter. Specimens were produced by
dynamic compaction using DWS-A. The dry density in CASES
1–4 was 0.815–0.825 Mg/m
3
which corresponds to compaction
degree 76%. First, the specimen was isotropically confined by
10 kPa. Then the H
2
O
2
solution (6%, 9%, 15%) was percolated
through the specimen by 10 kPa of water pressure. Specimens
in CASES 2, 3 and 4 were decomposed by the H
2
O
2
solution.
During H
2
O
2
percolation, CO
2
was generated by oxidation. The
CO
2
continuously flow into the sealed desiccator, and the CO
2
concentration was measured using a wireless CO
2
sensor. The
completion of oxidation was confirmed as the CO
2
concentration converged, which prevented partial saturation of
the specimen during shearing. The decrease in organic matter by
H
2
O
2
has been investigated in Table 2. The discharged water
was collected, and Al concentration was measured. The distilled
water was percolated after H
2
O
2
percolation, and more than
0.95 of the B-value was confirmed for specimen saturation. The
isotropic consolidation pressure was 50 kPa or 100 kPa. The
triaxial tests were executed in the drainage condition with
0.1%/min of the strain rate.
Particle density of soil (Mg/m
3
)
Liquid limit (%)
Plastic limit (%)
Ignition loss(%)
Fulvic acid (%)
Humic acid (%)
A
2.58
224
145
17.6
0.039
3.14
B
2.61
178
104
18.8
0.032
2.39
C
2.52
269
151
26.6
0.034
9.27
D
2.45
113
91
27.3
0.040
4.31
E
2.54
17.1
0.016
1.20
F
2.65
22.1
0.049
3.90
G
2.45
19.1
0.036
5.14
0
0.02
0.04
0.06
0.08
0.1
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
[1] compaction degree: 92.1%
[2] compaction degree: 87.2%
[3] compaction degree: 77.2%
Al saturated concentration [1]
Al saturated concentration [2]
Al saturated concentration [3]
concentraiotn (mg/L)
Liquid per soild ratio (L/kg)
Al
Figure 3. Al concentration in column leaching tests (Watanabe et
al., 2009).
16
18
20
22
24
26
28
30
32
0
50
100
150
200
DWS-F (clod size: 9-19mm)
DWS-F (clod size: less than 2mm)
DWS-G (clod size: 2-19mm)
DWS-S (clod size: 2-19mm)
DWS-S (clod size: less than 2mm)
Ignition loss (%)
Elapsed time (d)
Figure 4. Changes of ignition loss of DWS at 30 deg. (Watanabe et
al., 2011).
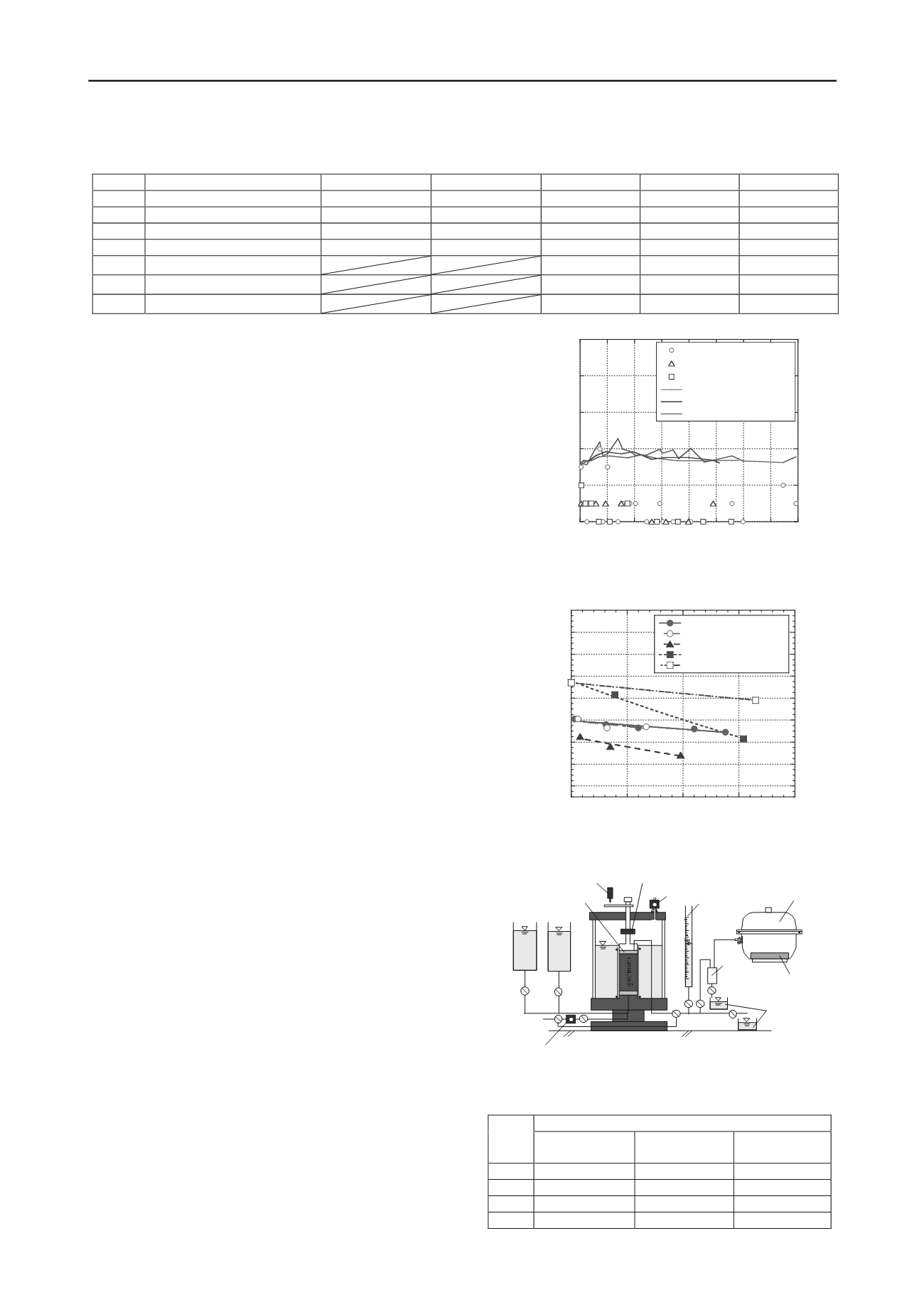
desiccator
wireless CO
2
sensor
outlet of water
water
trap
burette
pore water pressure gauge
displacement gauge
load cell
airpressure gauge
distilled
water
hydro
peroxide
solution
porous stone
Figure 5. Apparatus for triaxial compression test.
Table 2. Decomposition rate of organic matter by 6% hydrogen
peroxide solution for 24 h.
Decomposition rate (%)
DWS
Fulvic acid
Humic acid
Humin and soil
particles
B
77.1
44.9
3.1
C
86.5
43.2
8.1
D
88.0
46.6
10.3
E
73.4
42.5
6.6


