3176
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
with water in the capillary state. The most suitable state for
pellet formation is the capillary state.
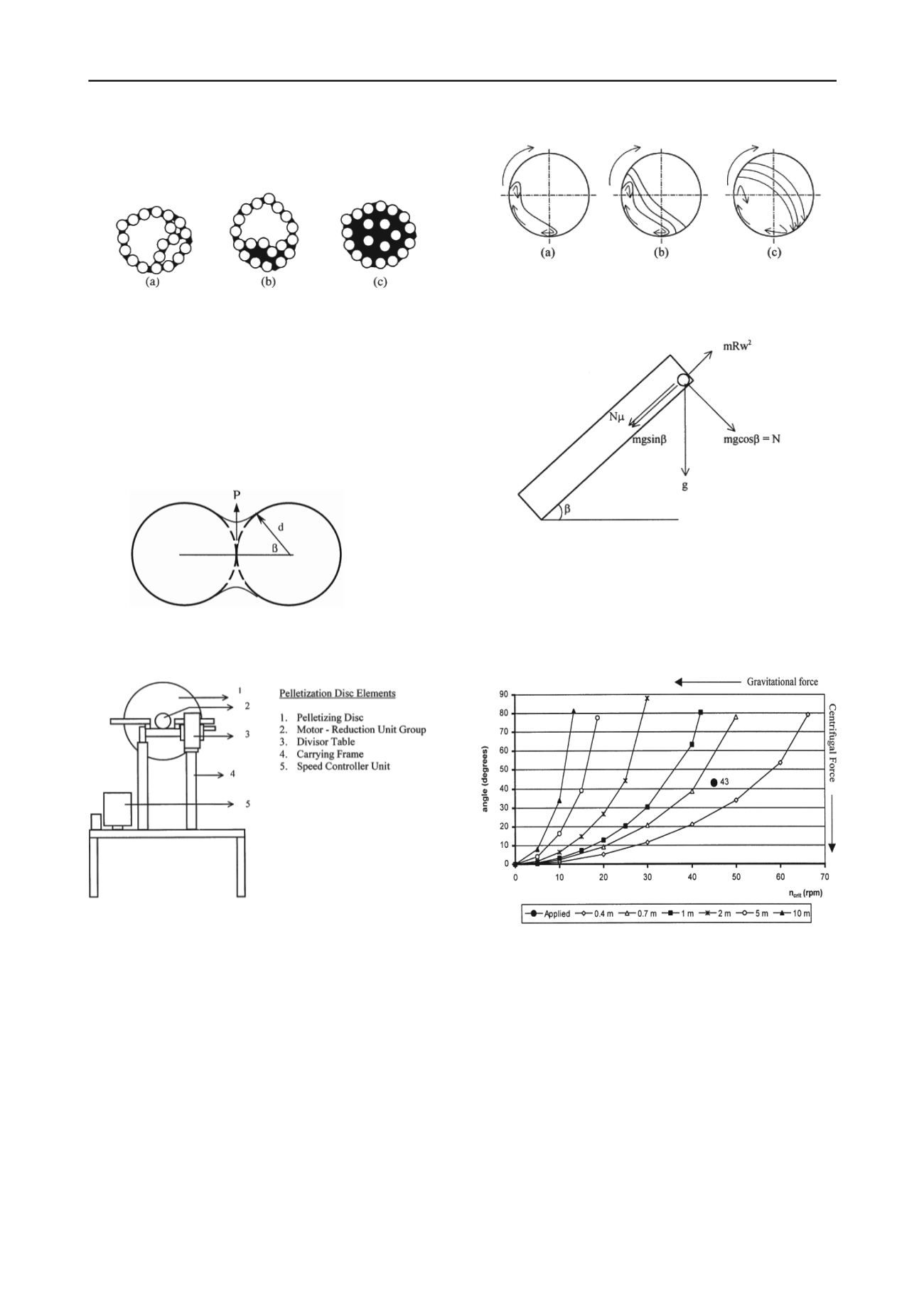
Figure 1. Mechanism of pellet formation; a) the pendular state; b) the
funicular state; c) the capillary state.
The formation of capillary force between two grains is
presented in Figure 2. The grain diameter of the powder
material influences the magnitude of the surface tension force;
small grain diameter is necessary to create enough pulling force
to initiate agglomeration. Agglomeration can be achieved by
drum or disc pelletizers. A typical disc pelletizer designed and
manufactured for this study is presented in Figure 3 (Doven
1998).
Figure 2.. Surface tension force created by water bridge between two
particles
.
Figure 3. The sketch of disc pelletizer (back view).
The revolution speed of the disc can be controlled between 0
and 70 rpm and the angle of the disc plane to the normal can be
adjusted between 0 and 90 degrees. The diameter of the disc is
0.40 meters and scraping blades are placed from center to one
edge at 0.06 m intervals. During the revolution of the disc the
grains pulled by surface tension are compacted further. The
agglomerated grains hit to the scraping blades, falling free to the
bottom section of the disc. This free fall action compacts the
agglomerated product more. This repeated revolving and free
fall action densifies and makes the agglomerated product
stronger for handling. The motion of the grains in the disc is
presented in Figure 4. The forces applied to the grains during
pellet formation are presented in Figure 5. To achieve the most
suitable pelletization process; the revolution speed and the angle
of disc plane to the normal should be set in a manner to avoid
the dominancy of gravitational or centrifugal forces (Figure 6).
Figure 4. Motion of material in disc pelletizer revolving at various
speeds.
Figure 5. Forces acting on an individual pellet during pelletization
process.
When the gravitational and centrifugal forces are in
equilibrium then the normal force exerted by the pellet
converges to zero and the following equation prevails.
m x g x sin β = m x R x W
2
(1)
Figure 6. Variation of operation angle with respect to diameter of
pelletization disc and critical revolution speed.
For various disc diameters the effect of operating angle and
revolution speed on centrifugal and gravitational forces are
presented in Figure 6.
2 PHYSICAL AND ENGINEERING PROPERTIES OF THE
MANUFACTURED PELLETS
Turkey produces more than 17 million tons of fly ash annually.
The fly ash used in the presented studies is obtained from Soma
Coal Burning Thermal Power Plant in the west part of Turkey.
The typical chemical composition of Soma fly ash is given in
Table 1. The physical properties of manufactured fly ash pellets
are presented in Table 2. The water absorption of the produced
ellets is high.
p
Table 1. The chemical composition of Soma Fly Ash.


