3170
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
These parameters included the effect of footing diameter (d) cm
where increasing rigid footing breadth caused increasing in
settlement in soil but the presence of EPS beads lead to decrease
the percent of the swelling and the settlement deformation. The
second parameter was the effect of beads density (
B
) kN/m
3
where increase beads density lead to decrease each of the
swelling and settlement on surface soil and circular footing. The
third parameter the effect of beads content in the sand
replacement layer (
)% which was the most important
parameter in this study where increasing this content lead to
significant decrease in swelling. The fourth parameter was the
effect of normalized replacement thickness (t
r
/t
s
) % where
increasing the replaced layer improved the resistance to the
swelling pressure and decrease the swelling deformation.
-5
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
-0.5
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
3.5
4.0
4.5
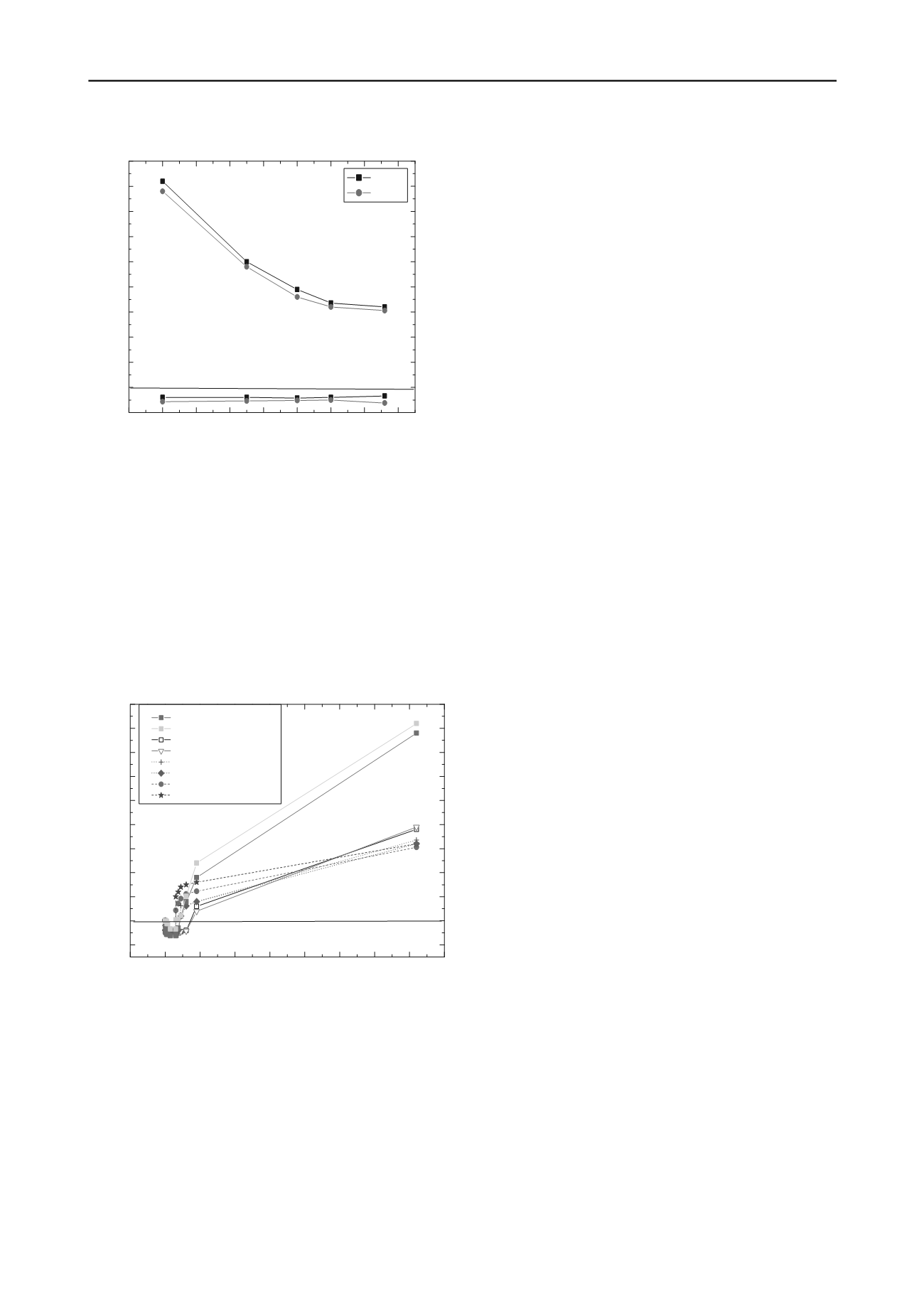
Replacement depth
Settlement(mm) Swelling (mm)
Normalized Replacement Thickness, t
r
/t
s
, %
soil
footing
Figure 5.Relationship between increasing normalized replacement
thickness (t
r
/t
s
) % on settlement and swelling for soil and footing
The innovative application of the recycled EPS beads mixed
with sand replacement layer at optimum moisture content, so as
to make a beneficial use of the waste EPS products, will offer a
sustainable solution for both the housing and EPS industries.
6 REFERENCES
Abdelrahman G. E. 2009. Lightweight Mixture Using Clay, EPS-Beads
and Cement.
Seventeen International Conference in Soil
Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering
, 17ICSMGE, Alex.,
Egypt.
4.3.6 Effect of normalized replacement thickness (t
r
/t
s
) % at
beads content (B) = 0.6%, footing diameter (d) = 7cm and of
beads density
(
B
) = 0.16 kN/m
3
-200 0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600
-0.5
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
3.5
4.0
4.5
Beads,0.6%-Footing,7cm-Beads size(4-5mm)
Depth of replacement layer to soil depth, t
r
/t
s
%
Settlement (mm) Swelling(mm)
Time (min)
0% Replacement-Footing
0% Replacement-Soil
20% Replacement-Footing
20% Replacement-soil
25% Replacement-Footing
25% Replacement-soil
33% Replacement-Footing
33% Replacement-soil
Figure 6 shows the detailed measurments for footing and
replaced soil surrounded the footing during 24 hours. It obvious
that at replaced soil with sand and EPS beads decreased the
swilling more than 60% , also no big difference in settlement
before adding water between different replacement ratios.
Adding water after one hour to the model to saturate the soil
caused swelling which increases with time. Increasing
replacement layer thickness decreases the swelling.
Chen, F.H. 1988. Foundations on Expansive Soils.
Developments in
Geotechnical Engineering
Vol.54, Amsterdam: Elsevier Science
Publishing.
Illuri, H.K. and Nataatmadja, A. 2007.
Reduction of Shrink-Swell
Potential With EPS Inclusion
. Proceedings 10th Australia New
Zealand Conference on Geomechanics: Common Ground,
Brisbane, Australia, pp. 90-95.
Illuri, H. K. 2007. Development of Soil EPS Mixes for Geotechnical
Applications.
Ph.D. Disseration, School of Urban Development
Centre for Built Environment and Engineering Research,
Queensland University of technology
, Australia, 334p.
Nataatmadja, A. and Illuri, H. K. 2009. Sustainable Backfill Materials
Made of Clay and Recycled EPS.
3rd CIB International
Conference on Smart and Sustainable Built Environments
, Delft,
Netherland.
Nelson, J.D and Miller, D.J. 1992. Expansive Soils Problems and
Practice in Foundation and Pavement Engineering.
John Willey &
Sons, Inc
, USA.
PPW Directive 2005. Directive 2005/20/E6 of the European Partiament
and the Council of 9 March 2005 Amending Directive 94/62/EC
on Packaging and Packaging Waste.
(OJL70 of 2005.03.16).
United Nations Environment Program (UNEP) 2000. The Montreal
Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer.
United
Nations Environment Programme,
Nairobi, 47.
Figure 6 .Relationship between time (min) and settlement and swelling
in (mm) for different normalized replacement thickness (t
r
/t
s
) % at
beads content (B) = 0.6%, footing diameter (d) = 7cm and of beads
density (
B
) = 0.16 kN/m
3
5 CONCLUSIONS
The results of a study on the potential use of sand –EPS mix as
soil replacement layer to reduce swelling of expansive soils
below structure foundation have been presented. Different
parameters affecting the swelling of structure foundation have
been studied.


