3177
Technical Committee 307 /
Comité technique 307
Per cent
SiO
2
50.5
Al
2
O
3
23.7
Fe
2
O
3
5.8
CaO
9.3
MgO
2.6
SO
3
1.4
Loss on Ignition
2.2
Soma fly ash is self cementitious and it will harden without
the need of another binder. The physical properties of the
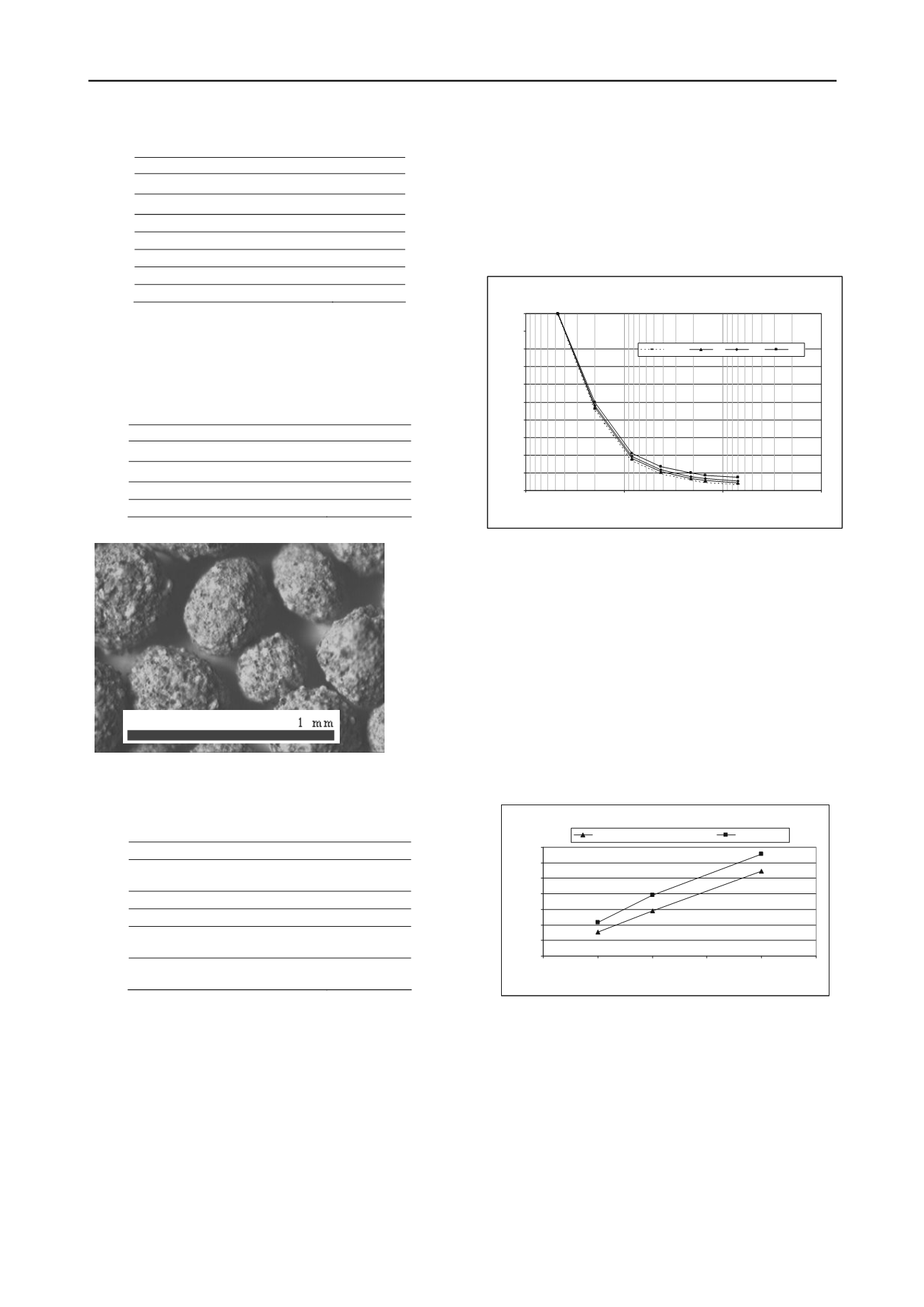
manufactured fly ash pellets are given in Table 2. The typical
fly ash pellets are given in Figure 7.
Table 2. Physical properties of the fly ash pellets.
Unit weight
9.6 kN/m
3
Water absorption
31.4 %
Specific gravity
2.17
Bulk specific gravity
1.29
Figure 7. Manufactured fly ash pellets.
Table 3. Engineering properties of the fly ash pellets.
Optimum moisture content
Dry unit weight (Standard Proct)
34.4 %
11.96 kN/m
3
Angle of internal friction
29.4°
California Bearing Ratio
58 %
Soundness loss of weight
9.5- 4.75 mm
9.0 %
Soundness loss of weight
19- 9.5 mm
7.9 %
Tables 1 through 3 show that fly ash pellets formed with
cold bonding technique have similar engineering properties to
that of soils. With no additional binder like lime or cement, self
cementitious fly ash pellets have acceptable engineering
properties. The soundness tests were conducted using sodium
sulphate. Less than 12 percent weight loss after sodium sulphate
treatment is allowable for concrete applications. The durability
performance of the manufactured aggregates is adequate even
for more demanding applications like concrete production.
From geotechnical point of view, the manufactured pellet
aggregates have properties similar to those of granular soils
except high water absorption value.
3 CRUSHING BEHAVIOR OF MANUFACTURED
PELLETS
To demonstrate the effect of aggregate crushing sieve analyses
were performed before and after direct shear testing of fly ash
pellets at 50, 100 and 200 kPa normal stress. The change in
grain size distributions before and after execution of the direct
shear tests are given in Figure 8 (Danyldz 2007).
FA
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
0,010
0,100
1,000
10,000
Grain diameter (mm)
Percent finer
Before
50
100
200
Figure 8. The grain size distribution of fly ash pellets before and
after the conduction of direct shear test at a normal stress of 50, 100
and 200 kPa.
The fly ash pellets crushing behavior is similar to calcerous
sands. The measured crushing behavior does not pose a threat
for the engineering performance of the fly ash pellets for most
geotechnical applications.
4 SHEAR STRENGTH OF FLY ASH PELLETS
Direct shear tests are conducted on manufactured fly ash pellet
aggregates under 50,100 and 200 kPa normal stress
applications. Interface tests are conducted on split samples of
fly ash pellets and concrete. The internal friction angle and
interface friction angle plots are presented in Figure 9.
FA
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
0
50
100
150
200
250
Normal Stress (kPa)
Interface or internal Stress (kPa)
interface frcition between concrete
internal friction
Figure 9. Internal and interface friction angles of fly ash pellets and
pellet concrete interface.
product
e disc is
ns during
the most
the angle
to avoid
gure 6).
Turkey produces more than 17 million tons of fly ash annually.
The fly ash used in the presented studies is obtained from Soma
Coal Burning Thermal Power Plant in th west part f Turkey.
The typical chemical composition of Soma fly ash is given in
Table 1. The physical properties of manufactured fly ash pellets
are presented in Table 2. The water absorption of the produced
ellets is high.
p
Table 1. The chemical composition of Soma Fly Ash.


