3038
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
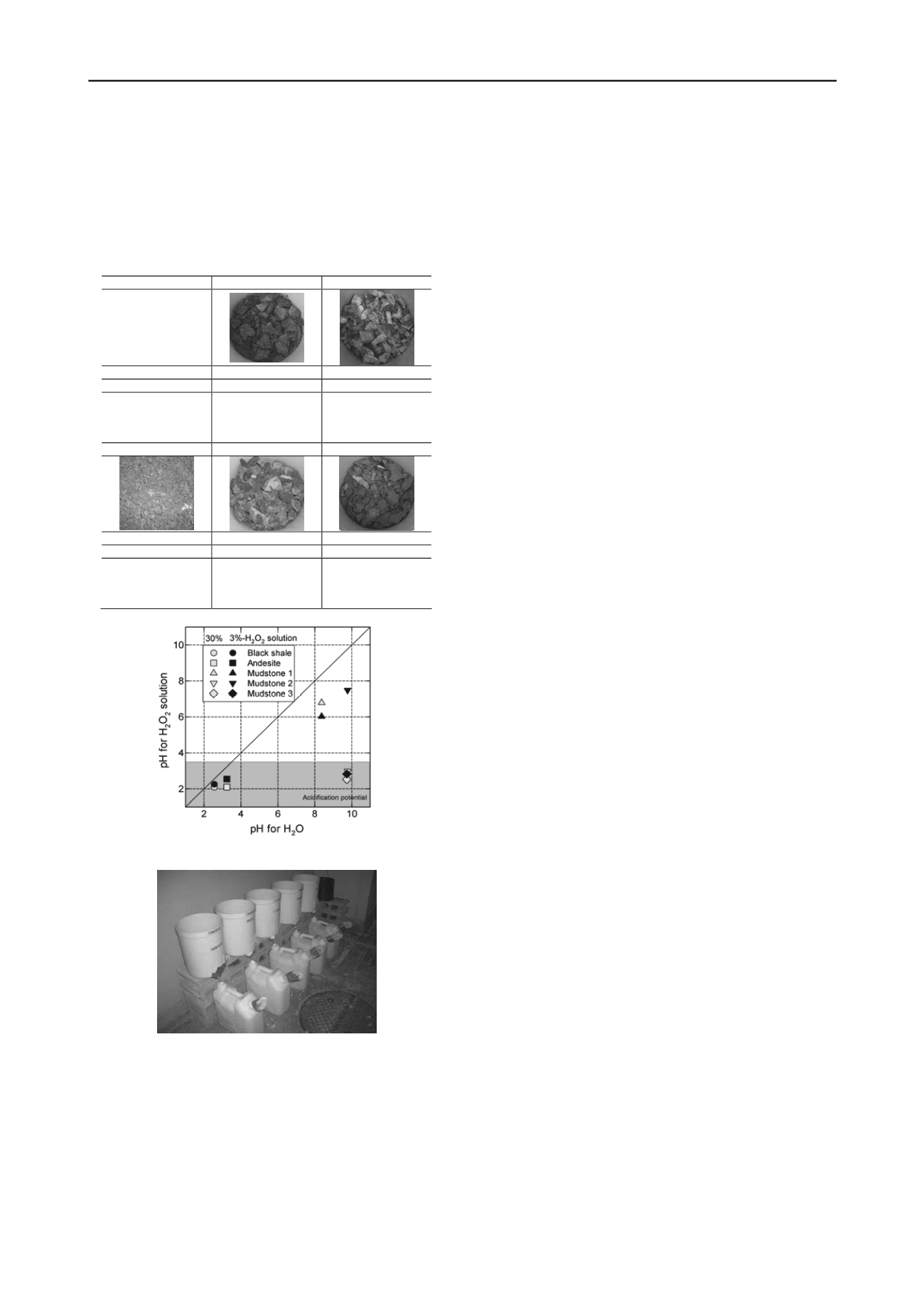
andesite are fundamentally acidic even for distilled water. Three
mudstone are considered to be alkaline rocks without
oxidization effects. However, pH value of MS-2 for 30% H
2
O
2
solutions were drastically reduced to 2-3, and pH values of MS-
3 for 3% and 30% H
2
O
2
solutions were lower than 3. These
results supported that MS-3 is most easily acidifying among
three mudstones.
Table 1. Chemical properties of rock samples used in this study
Sample ID
Black shale
Andesite
Appearance
As content (mg/kg)
28
26
Pb content (mg/kg)
23
5
Chemical composition
(% in mass)
SiO
2
: 43.6, Fe
2
O
3
: 21.4,
Al
2
O
3
: 4.6, CaO: 0.2,
K
2
O: 16.5, SO
3
: 8.8,
TiO
3
: 3.0, Others: 1.9
SiO
2
: 59.0, Fe
2
O
3
: 11.6.
Al
2
O
3
: 13.5, CaO: N.D.,
K
2
O: 8.9, SO
3
: 5.4,
TiO
3
: 1.0, Others: 0.6
MS-1
MS-2
MS-3
23
15
23
13
6
1
SiO
2
: 54.2,Fe
2
O
3
: 15.3,
Al
2
O
3
: 10.4, CaO: 7.9,
K
2
O: 5.2, SO
3
: 4.0,
TiO
3
: 1.4, Others: 1.5
SiO
2
: 54.2, Fe
2
O
3
: 18.7,
Al
2
O
3
: 12.3, CaO: 2.7,
K
2
O: 7.2, SO
3
: 2.5,
TiO
3
: 1.9, Others: 0.5
SiO
2
: 64.6, Fe
2
O
3
: 11.6,
Al
2
O
3
: 9.9, CaO: 1.1,
K
2
O: 5.2, SO
3
: 3.9,
TiO
3
: 1.5, Others: 0.5
Figure 1. pH of each rock sample for distilled water and H
2
O
2
solutions.
Photo 1. View of outdoor exposure test
2.2
Outdoor exposure test
Outdoor exposure tests have been conducted for five rock
samples since October 2009. This paper presents the
experimental results obtained until February 2012 (about 27
months). Each sample was crushed into 9.5 to 37.5 mm in grain
size (2.0 to 9.5 mm in diameter for mudstone 1 due to its
crushability). 4000g of rock sample with natural moisture
content was stored in a cylindrical plastic container with a cross
section of 0.05 m
2
with the dry density of 2.0 Mg/m
3
for black
shale, 1.1 Mg/m
3
for andesite, 1.2 Mg/m
3
for mudstone 1 and
1.6 Mg/m
3
for mudstone 2 & 3, and exposed to the rainfall and
air throughout the test (Photo 1). Rainfall intensity and
percolation volume were continuously monitored. The leachate
was periodically collected and subjected to chemical analyses.
2.3
Laboratory leaching tests
Leaching concentrations of As and Pb were analyzed according
to the batch leaching test method for the soil quality regulated
by the Notification No.46 of Japanese Ministry of the
Environment in 1991. In the batch test, air-dried rock samples
were crushed until its parcentage passing at 2 mm became 100%.
In addition, for black shale, the sample subjected to accelerated
oxidation was also prepared. Accelerated oxidation was
promoted by storing the crushed sample in an incubator under
80% O
2
and 100% humidity condition in 200 days.
As and Pb leaching concentations during the aforementioned
pH measurement using H
2
O
2
solutions were analysed to
evaluate the effects of accelerated acidification on the leaching
behavior.
Tank leaching tests were conducted for monolithic rock
samples with approximately 400 g in dry mass by submerging
into distilled water for 28 days. The liquid to solid ratio (mL/g)
of 10 was employed. Column leaching tests were performed for
about 750 g rock samples, which were crushed until its
percentage passing at 4.75 mm became 100%. A cylindrical
specimen was prepared by vibratory compaction in an acrylic
column (55 mm in inner diamete) and then permeated with the
permeant by maintaining the constant water head (24 mL/hour
in flow rate). The permeant was distilled water after its pH was
adjusted to 4.7 using the nitric acid.
An atomic absorption spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, AA-
6800) with a hydride generator and an electrothermal
atomization system was used to determine the concentration of
As and Pb in the solution. Chemical parameters of the solution
(pH, Eh, Electrical conductivity (EC)) were also monitored.
3 RESULTS OF OUTDOOR EXPOSURE TESTS
Figure 2 show profiles of percolation volume, pH, EC, Eh,
temperature and concentrations of As and Pb of the leachate
sample with time. This paper describes the results for black
shale and andesite rock samples only. Cumulative flow volumes
ranged from 16 to 19 in the liquid to solid ratio (mL/g) after 27
months since due to the difference in permeability.
The leachate from the black shale was acidic, and pH values
ranged between 2.1 and 2.5 (Figure 2(a)). As concentrations
were higher than 0.1 mg/L in the first three months, then
decreased with time and reached 0.02 mg/L. Temperature rising
during summer (July-September) were followed by slight
decrease in pH and increase in EC and leaching concentrations.
This is because the rock samples were subjected to wet and
higher temperaure conditions in summer and dissolution of the
minerals
was
promoted
due
to
the
oxidization
produces.Leaching of Pb was also detected but with much lower
concentrations than As.
Testing results for the andesite (Figure 2(b)) had similarities
with those for the black shale. pH values were ranging from 2.4
to 4.0. At the initial stage, EC values and As leaching
concentrations were relatively high and then gradually
decreasing and stabilized. However, 10 months after, with
gradual lowering of pH values, the values of both parameters
were getting larger particularly in summer as same as black
shale. These profiles of pH, As leaching concentrations and EC
were well explained well by the results of the accelerated
oxidation test using H
2
O
2
solutions (see Figure 1). Obvious pH
drops were observed against the oxidization by H
2
O
2
solutions.
The andesite sample was gradually oxidized during the outdoor
exposure test, and leaching of As and other minerals were
promoted accordingly. Pb leaching higher than 0.01 mg/L were
rarely observed throughout the test.


