3022
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
Figure 1. A concept of permeable reactive barriers.
1 MATERIALS AND TEST METHODS
Tests, result of which are presented in this paper, were carried
out on zeolite-sand mixtures with 50% - ZS50, 20% - ZS20
content of Na-form of Slovak zeolite having 0.5-1.0 mm
particle sizes. The mineral composition of the Slovak zeolite
is as follows:
(Ca;K
2
;Na
2
;Mg)
4
Al
8
Si
40
O
96
·24H
2
O
(2)
The zeolite-sand mixtures considered as a reactive materials
have specific surface areas from 3,65 m
2
/g for ZS20 to 29,04
m
2
/g for ZS50. The crystal structure of zeolite is presented
by 3-dimentional aluminosilicate framework with the developed
system of micropores and channels occupied by water
molecules and exchangeable cations. Crystal habits of zeolite
include blocky and thin-tabular crystals with good monoclinic
crystal forms (Sprynsky et al. 2004). According to the results
of scanning electron micrographs study unit cell parameters
of crystals are close to each other (Fig. 2).
To determine the effect of synthetic leachates (containing
360 mgNH
4
+
/L, 100 mgCa/L, 200 mgMg/L and 100 mgCu/L)
and landfill leachate on the hydraulic conductivity of ZS50 and
ZS20, constant-head permeability tests were performed using
flexible wall permeameter (Fig. 3). In the tests the natural
leachate from municipal landfill in Warsaw was used.
Chemical composition of leachate is listed in table 1.
Due to the character of these studies, it was necessary
to use equipment made from materials not reacting with
contaminated water. The hydraulic gradient of 2
was obtained by establishing an elevation difference between
the liquid surface of inflow and outflow ends. Before leachate
tests, specimens were pre-saturated with distilled water until
establishing the constant flow through the samples. Samples
Figure 2 Scanning electron micrograph of zeolite (Katzenbach et al.
2008)
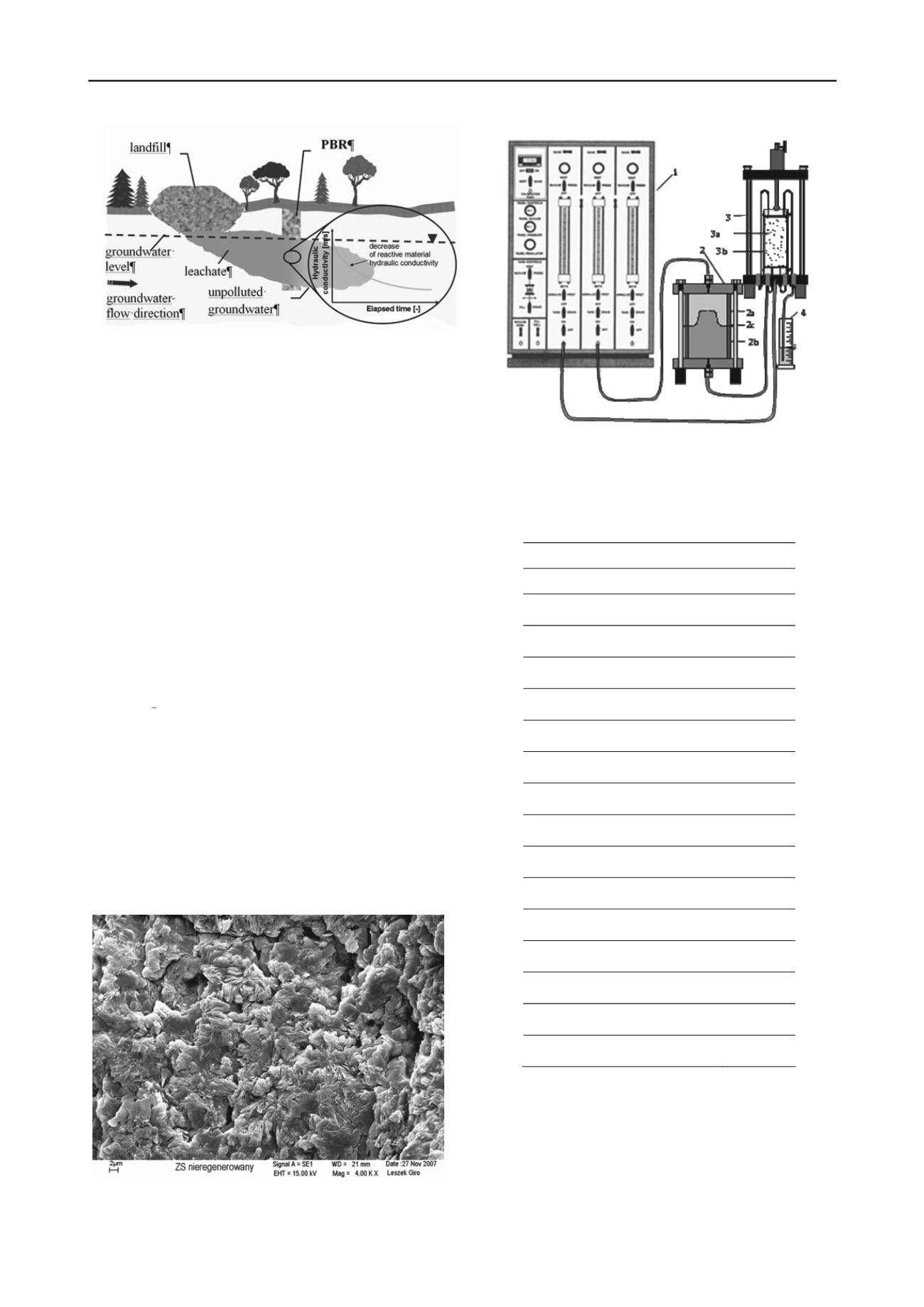
Figure 3. Scheme of a flexible-wall permeameter: 1-control panel,
2-bladder accumulator, 2a-water, 2b-liquid other than water, 2c-elastic
membrane, 3-chamber, 3a-sample, 3b-latex membrane, 4- measuring
cylinder (acc. to Trautwein Soil Testing Equipment Co.).
Table 1. Chemical composition of leachate from municipal landfill
in Warsaw.
Parameter
Value
BOD (mg/l)
127.0
COD (mg/l)
960.0
Ammonia – N (mg/l)
52.0
Total P (mg/l)
3.94
Chloride (mg/l)
1400.5
Sulfate (mg/l)
419.0
Sodium (mg/l)
917.0
Potassium (mg/l)
396.0
Calcium (mg/l)
81.2
Magnesium (mg/l)
88.8
Iron (mg/l)
1.28
Chromium (mg/l)
0.13
Zink (mg/l)
1.83
Copper (mg/l)
0.2
Conductivity (µS/cm)
6480
pH
8.21
were placed between two porous plates, that’s hydraulic
conductivity was more than 1.0E-3 m/s. The samples
were making with mixed materials having 10% of water
content. The specimens tested were 0,07 m in diameter
and 0,12 m in height. In this study specimens were compacted
to relative density equal 0.6. The confining pressure
was 50 kPa.


