1012
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
Production of MH bearing sands and their shear tests were
conducted using the temperature-controlled high-stress triaxial
testing apparatus (Hyodo, et al.2008). For the simulation
material, MH was formed in these host sands with 50%, 30%
and 0% degree of MH saturation. From the results of density
tests on natural cores from Nankai Trough, the porosities of the
simulation materials were set as
n
=40% and 45%. In this paper,
only the results of
n
=45% are presented. The method of
formation of MH in the simulation materials is as follows.
Firstly, an initial water content equivalent to the desired degree
of MH saturation was prepared and then an unsaturated
specimen, with diameter 30mm and height 60mm, was made
using tamping to a given density. Next, the specimen was set in
the cell of the apparatus and methane gas was injected into the
specimen for 24hr at 10MPa pore water pressure, 13MPa cell
pressure and at a temperature of 5
℃
to form the MH. After
stopping the methane gas injection and confirming the
formation of MH, the specimen was filled with pure water in
order to saturate it. A given effective stress was then applied
and shear tests were performed under drained conditions with a
rate of shear of 0.1%/min. After the shear test, the pore pressure
was decreased to a level outside of the MH stability boundary in
order to dissociate the MH which had been produced. The
quantity of MH was measured and the degree of MH saturation
was calculated by this amount of dissociated gas. The triaxial
test results for host sands Ta, Tb, Tc and Td with an initial
porosity of
n
=45%, under an effective confining stress of
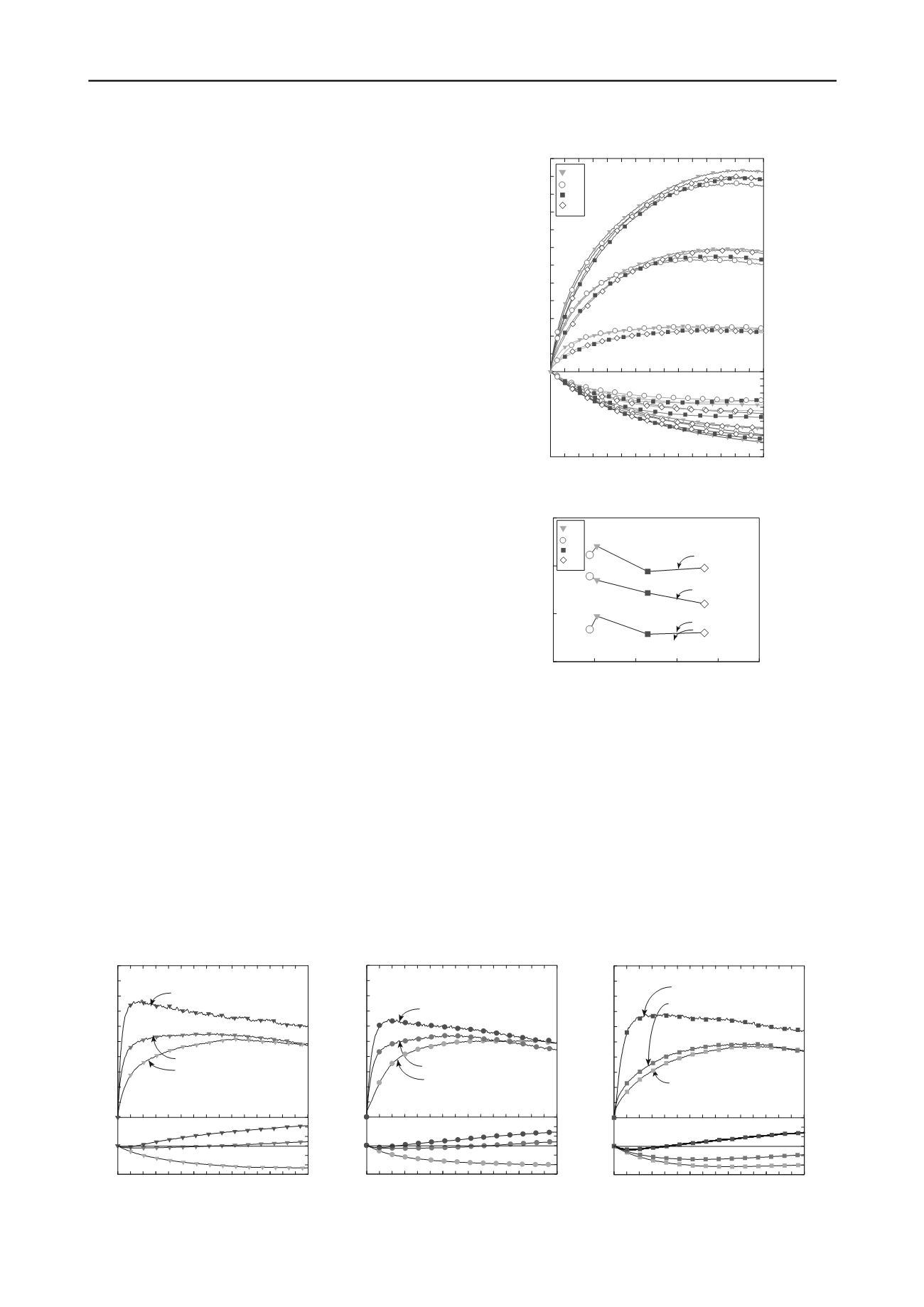
1MPa, 3MPa and 5MPa are presented in Figure 2. In the figure,
the initial stiffness and residual strength slightly decreases with
increasing fines content, however there is no marked difference.
Volumetric strain induced by shear appears on the contractive
side and increases with increasing fines content and confining
stress. Figure 3 shows the variation of the secant modulus at 1%
axial strain against fines content for each material with each
confining stress. It can be seen that there is a trend for the secant
modulus to decrease with increasing fines content at all
confining stresses. However, this is not true for Ta and Tb, due
to the effect of their mean particle size. Fig.4(a)-(c) show the
shear testing results for MH bearing sands by using Ta, Tb and
Tc as host sands. Tests were performed at a porosity of
n
=45%
with effective confining stress of 1MPa at various degrees of
MH saturation. From the figures it can be observed that initial
stiffness and peak residual strengths increased as the degree of
MH saturation increased. Corresponding volumetric strain
increases and behaves in a more dilative manner with increasing
degrees of MH saturation. In Figure 5, the difference between
the peak strength of MH bearing sand and the strengths of the
host sands, at an axial strain corresponding to the peak value of
MH bearing sand, are normalized by effective confining stress
and then plotted against the degree of MH saturation. It can be
observed that the strength increased rapidly when the degree of
MH saturation passed 30%, and the rate of increase decreases in
order of Ta, Tb and Tc. It is therefore obvious that the grain size
distribution affects the cementation effect of MH.
4 SHEAR CHARACTERISTICS OF MH BEARING SANDS
BY HIGH-STRESS PLANE STRAIN SHEAR TESTING
An overview of the testing equipment (Yoneda et al. 2011) is
shown in Figure 6. This apparatus can control temperatures and
pressures equivalent to an MH reservoir in deep seabeds.
Additionally, observation windows are installed in front of and
behind the specimen in order to allow the local deformation of
the specimen during shear tests to be measured. The specimen is
a cuboid with 80mm width, 60mm thickness and 160mm height.
A 5mm
x
5mm mesh was drawn on the membrane in front of
the observation window. The observation was performed using
a digital camera(g), which took pictures according to a timer
controlled by a remote system. An LED(h) was installed to
brighten the pressure cell(i), which allowed the specimen(e) to
Figure 2 Variation of deviator stress and volumetric
s
train
against axial strain for host sands
0
10 20 30 40 50
0
1
2
3
T
a
T
b
T
c
T
d
Secant modulus
E
(
(MPa)
Fines content
F
c
(%)
n
=45%
c
'=1MPa
c
'=3MPa
c
'=5MPa
Figure 4 Variation of deviator stress and volumetric
s
train against axial strain for methane hydrate bearing sands
(b) T
b
(a)T
a
(c) T
c
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
0
-6
0
10
20
30
Volumetric strain
v
(%)
Axial strain
a
(%)
Deviator stress
q
(MPa)
T
b
c
'=1MPa
S
MH
=0%
n
=45.5%
S
MH
=31.1%
n
=45.5%
S
MH
=47.4%
n
=45.3%
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
0
-6
0
10
20
30
Volumetric strain
v
(%)
Axial strain
a
(%)
Deviator stress
q
(MPa)
T
c
c
'=1MPa
S
MH
=0%
n
=45.0%
S
MH
=24.3%
n
=45.2%
S
MH
=58.6%
n
=44.9%
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
0
-6
0
10
20
30
Volumetric strain
v
(%)
Axial strain
a
(%)
Deviator stress
q
(MPa)
T
a
c
'=1MPa
S
MH
=0%
n
=45.1%
S
MH
=24.6%
n
=45.5%
S
MH
=43.7%
n
=44.8%
Figure 3 Relationship between secant modulus
and fines content
0
4
8
12
12
6
0
0
10
20
30
Volumetric strain
v
(%)
Axial strain
a
(%)
Deviator stress
q
(MPa)
S
MH
=0%
n
=45%
a
=30%
T
a
T
b
T
c
T
d


