2355
Centrifuge test and numerical modeling for a suction bucket monopod foundation
Essai en centrifugeuse et la modélisation numérique d'une fondation de type : caisson
à succion
Kim D.J., Youn J.U., Jee S.H., Choi J.
Hyundai Engineering and Construction, Seoul, Korea
Choo Y.W., Kim S., Kim J.H., Kim D.S.
Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, KAIST, Daejeon, Korea
Lee J.S.
Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Wonkwang University, Iksan, Korea
ABSTRACT: A centrifuge load test for a preliminary design of a monopod suction bucket foundation was performed. The target
site was the Yellow Sea of Korea and the prototype foundation was a steel monopod caisson with a diameter of 15.5m for a 3MW
turbine. The seabed conditions comprised of a dense silty sand above layers of sandy silt were reproduced to a model soil profile
using soil samples collected at nearby seashores. Horizontal load and overturning moment were applied and monitored in the test,
with vertical load being simulated by self-weight of the bucket model. Series of numerical analysis were performed in order to
validate test conditions and compare the effects of soil parameters.
RÉSUMÉ : Un test de chargement en centrifugeuse pour étudier le design préliminaire d'une fondation de type « caisson à
succion » a été réalisé. Le site cible était la mer Jaune de Corée et la fondation prototype était un caisson unique en acier caisson de
15.5 m de diamètre pour une éolienne de 3 MW. La stratigraphie du fond marin, sable limoneux dense et limon sableux, a été
reproduite pour faire un profil de sol modèle en utilisant des échantillons de sol prélevés sur le rivage à proximité. Un chargement
horizontal et un moment de renversement ont été appliqués et contrôlés pendant l'essai, le chargement vertical était simulé en
utilisant le poids propre du modèle. La modélisation numérique a été réalisée afin de valider les conditions d'essai et de comparer
les effets du choix des paramètres de sol.
KEYWORDS: Suction bucket foundation, Monopod bucket foundation, Offshore wind, Centrifuge Test, Numerical Modeling
MOTS-CLÉS : Caisson à succion, Caisson de fondation, Éolienne Offshore, centrifugeuse, modélisation numérique
1 INTRODUCTION
Suciton bucket (also termed as suction caisson or suction pile)
has been considered as a viable alternative to conventional
foundations for offshore wind turbines, becuase it has features
appropriate for installing large foundations in offshore
environment with minimal environmental problems (Byrne and
Houlsby 2003, Houlsby et al. 2005, Villalobos 2006, LeBlanc et
al. 2009, Hung and Kim 2012, Oh et al. 2012). In Korea, major
offshore wind farm projects are planned in the Yellow Sea near
the south western coast of Korea. The soil profiles are mainly
composed of layers of silty sand and sandy silt.
A preliminary design was performed for field testing of suction
bucket foundations, and centrifuge load tests were performed to
verify and compare alternative designs. In this paper, a
centrifuge test for a steel monopod with a diameter of 15.5 m
and a length of 10.5 m is described. Expected horizontal load
combined with moment load was applied in the test.
Numerical analyses were performed to validate the centrifuge
test model conditions such as model weight and soil boundary
distance. In addition, the effects of soil parameters such as
elastic modulus, internal friction angle, dilation angle, cohesion
and wall interface friction angle, on foundation behaviour were
evaluated.
2 CENTRIFUGE MODELING
A centrifuge test was performed with a geotechnical centrifuge
at KAIST (Korea Advanced Institute of Science and
Technology) in South Korea. It has a maximum capacity of 240
g-ton and 5 m radius (Kim et al. 2012). Detailed description of
the centrifuge test for this study can be found in Choo et al.
(2012) and Kim et al (2013). The procedures and results are
briefly described here.
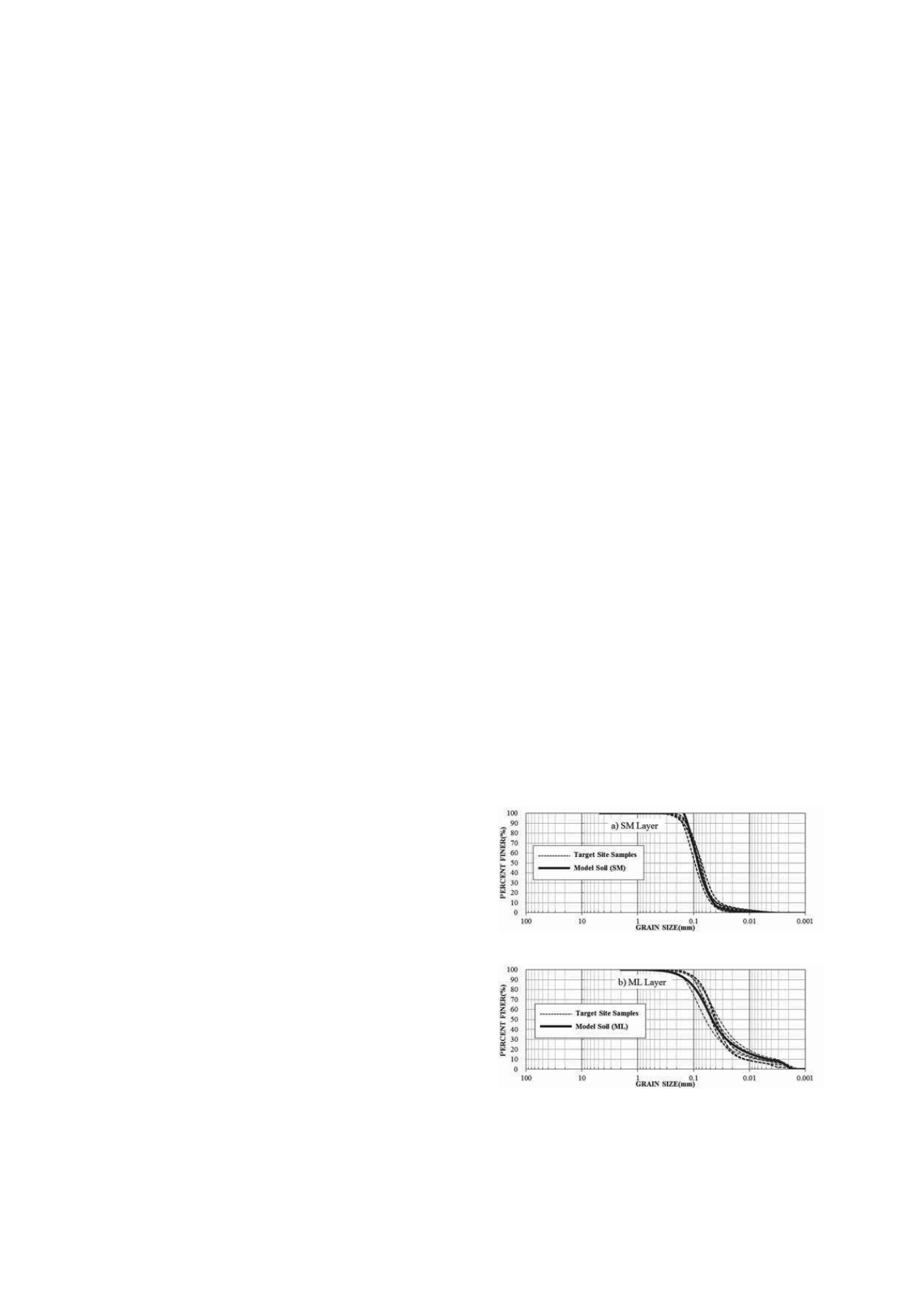
The soil conditions at the target site were replicated in the
model soil container for the centrifuge test. Natural soil samples
collected at the Western coastal areas near the target site were
used after verifying that the properties of model materials were
comparable the soil samples from the target site (Figure 2). The
model profile was formed in two layers of dense silty sand and
medium dense sandy silt up to the depth of 32 m, which was
about two times the diameter of the foundation.
(a) Silty Sand (SM) Layer
(b) Sandy Silt (ML) Layer
Figure 1. Comparison of grain size distributions between target site
samples and model soil
A 1/70 scaled model was used for the test. Horizontal load
by a displacement controlled actuator was applied and


