2350
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
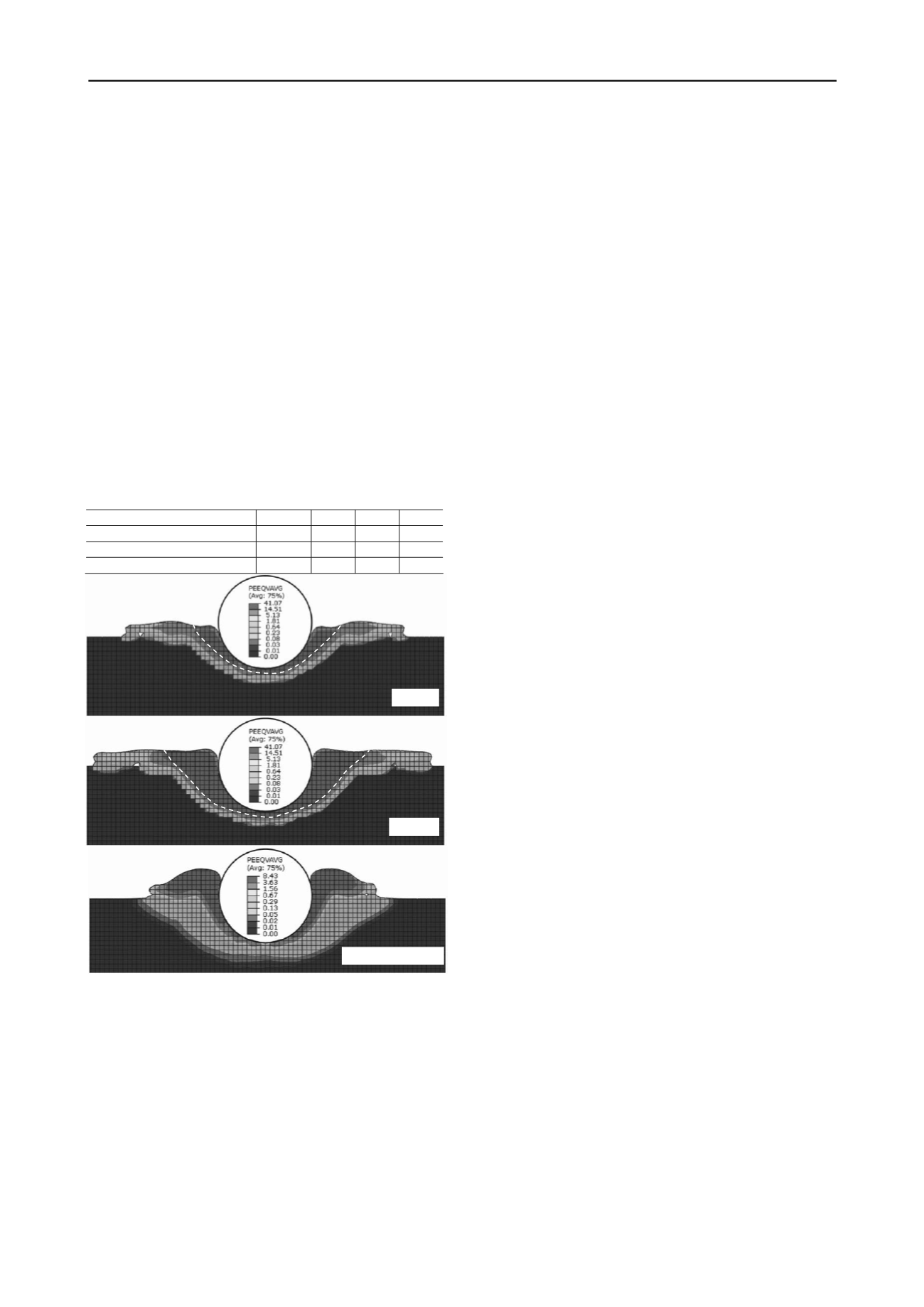
than 95%. The softening has a significant effect on the shape of
the berm and soil movement around the pipe. the highly
softened displaced soil mass formed flat berms on the top of the
seabed extended over a large distance in cyclic loading. In
addition, the soil is in contact with the pipe almost up to the top
of the berm. However, for monotonic loading the displaced soil
mass formed a berm mainly near the pipe and the berm height is
more than that of in cyclic loading. That means, the soil
deformation in monotonic and cyclic loading is significantly
dif
ning behaviour of soil will provide more
accurate results.
able 3. Dynamic embedment facto
K K
H
ferent.
In a parametric study Dutta et al. (2012 b) showed that the
effect of softening on the vertical penetration resistance in
monotonic loading is not very significant, which is because of
less plastic strain developed near the pipe. However, for cyclic
loading huge plastic strain is developed in a zone near the pipe
which causes significant reduction in undrained shear strength.
That means, the zone of considerable softening is higher in
cyclic loading. As in offshore the small amplitude lateral cyclic
loading near the touchdown zone is commonly encountered
from the motion of the vessel, the analyses for cyclic motion
with strain softe
T
r,
f
dyn
.
C-04 C-05 HP-06 P-07
Initial static embedment (
w
in
/
D
)
0.08
0.12
0.10
0.22
Final embedment (
w
/
D
)
0.34
0.50
0.48
0.77
f
dyn
4.25
4.16
4.8
3.5
Figure 6. Equivalent plastic strain.
ated. The following conclusions can be drawn from this
BAQUS FE software can simulate the pipeline
oading is
ipe in
c loading.
Forty cycles of small amplitude lateral loading increased the
initial static embedment. The
cycles.
The work has been funded by C-CORE, MITACS and NSERC
h is greatly acknowledged.
9
Bru
Che
Geotechncial Journal
(accepted).
Zhou, H. and Randolph, M. F. (2009). Numerical investigations into
cycling of full-flow penetrometers in soft clay. Géotechnique, 59
(10), 801-812.
The shape of the berm depends on type of loading; spread
over a large area in cyclic and mounted near the p
monotonic loading.
The softening of soil in a zone near the pipe is significantly
higher in cyclic loading compared to monotoni
embedment by a factor of 4-5 of
embedment is higher in initial loading
8 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Discovery grant whic
REFERENCES
ton, D., White, D., Cheuk, C. And Bolton, M. (2006). Pipe/soil
interaction behaviour during lateral buckling, including large
amplitude cyclic displacement tests by the Safebuck JIP.
Proc.
Offshore Technology Conference
, Houston, Texas, USA. OTC
17944.
neiro, D. Gouveia, J. and Par
Car
rilha, R. 2010. Feedback analysis of
pipeline embedment over as-laid survey results.
Proc. Int. Conf. on
Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering,
Shanghai, China.
OMAE2010-20410.
ola, F., El-chayeb, A., Greco, S. and Carluc
Cas
ci, A. 2011.
Characterization of pipe soil interaction and influence on HP/HT
pipeline design.
Proc. Int. Conf. on Offshore and Polar
Engineering Conference,
Hawaii,USA,pg:111-121.
Cheuk, Y.C. and White, J.D. 2008. Centrifuge modelling of pipe
penetration due to dynamic lay effects.
Proc. Int. Conf. on Offshore
Mechanics and Arctic Engineering,
Estoril, Portugal. OMAE2008-
57923.
uk, Y.C. and White, J.D. 2011. Modelling the dynamic embedment
of seabed pipelines.
Géotechnique
61 (1), 39-57.
ta, S., Hawlader, B. and Phillips, R. 2012a. Finite elem
Dut
ent modeling
of vertical penetration of offshore pipelines using Coupled Eulerian
Lagrangian approach.
Proc. Int. Conf. on Offshore and Polar
Engineering Conference,
Rhodes,Greece,pg:343-348.
ta, S., Hawlader, B
(a)KC-04
Dut
. and Phillips, R. 2012b. Strain softening and rate
effects on soil shear strength in modeling of vertical penetration of
offshore pipelines.
Proc. Int. Pipeline Conference,
Alberta, Canada.
IPC2012-90233.
Einav, I. and Randolph, F.M. 2005. Combining upper bound and strain
path methods for evaluating penetration resistance.
Int. J. Numer.
Meth. Engng.,
63:1991-2016.
(b)KC-05
Lund, K.H. 2000. Effect of increase in pipeline soil penetration from
installation.
Proc. Int. Conf. on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic
Engineering,
New orleans, USA. OMAE2000-PIPE5047.
Oliphant, J. and Yun, J.G. 2011. Pipeline embedment prediction using
as-laid data.
Proc. Int. Conf. on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic
Engineering,
Rotterdam, The Netherlands. OMAE2011-50095.
Randolph F.M. and White J.D. 2008. Pipeline embedment in deep
water: Processes and quantitative assesment.
Proc. Offshore
Technology Conference
, Houston, Texas, USA. OTC 19128.
ng, D., White, J.D. and Rand
7 CONCLUSION
Large deformation finite element analyses are conducted to
assess the embedment of as-laid offshore pipelines in clay. The
effects of small amplitude cyclic lateral loading are
investig
Wa
olph, F.M. 2009. Numerical simulations
of dynamic embedment during pipe laying on soft clay.
Proc. Int.
Conf. on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering,
Hawaii,
USA. OMAE2009-79199.
stgate, J.Z., White, J.D. and Randolp
(c) Monotonic loading
We
h, F.M. 2010. Pipeline laying
and embedment in soft fine-grained soils: Field observations and
numerical simulations.
Proc. Offshore Technology Conference
,
Houston, Texas, USA. OTC 20407.
Westgate, J.Z., White, J.D. and Randolph, F.M. 2012. Modelling the
embedment process during offshore pipe laying on fine-grained
soils.
Canadian
study.
The Coupled Eulerian Lagrangian (CEL) method currently
available in A
embedment.
The plastic shear strain near the pipeline in cyclic l
significantly higher than that of in monotonic loading.


