1028
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
appropriate the bentonite was stretched with rounded inert
quartz grains (washed Perth sand, d
50
= 0.24 mm, Cook
Industrial Minerals, Australia).
The pore water of the reconstituted samples was prepared
with a 0.01 mol/L CaCl
2
solution as standardised groundwater
equivalent.
Guanidinium solutions were prepared from analytical grade
guanidinium hydrochloride salt (C(NH
2
)
3
Cl, ≥99%, Fluka
Analytical, Switzerland) and demineralised water.
2.2
Investigations on particle scale
Homo-ionic bentonites were produced by saturation of Calcigel-
clay with 1.0 mol/L calcium and guanidinium solutions,
respectively. Images of the particles and aggregates were taken
with a scanning electron microscope. The grain size distribution
of the suspended material was measured with a Laser scattering
analyser (Partica LA-950, Horiba, Germany).
After saturation, the modified soils were washed in
suspension with demineralised water to remove excess ions and
to avoid salt precipitation in the inter-particle pore space.
Compacted samples were reconstituted from the washed
material at water contents slightly above to their liquid limit.
Mercury intrusion porosimetry (MIP, PASCAL 240/440,
Porotec, Germany) on dry samples was used to quantify the
alterations of the pores system due to guanidine treatment.
Crack-free pieces of the slowly dried clays were subjected to
vacuum evacuation for 2 h prior to mercury intrusion.
2.3
Macroscopic tests
The primary and intended soil improvement of chemically
enhanced drainage is the increase in hydraulic conductivity.
This increase was measured based on the evaluation of time
settlement curves on bentonite samples. For this purpose,
compacted samples of unmodified bentonite were reconstituted
and mounted into a standard oedometer cell. The chemical agent
was then delivered to the soil in the pore water by diffusion
from the top and bottom filter plates. Subsequent loading up to
800 kPa allowed deriving hydraulic conductivities at different
void ratios. Untreated samples served as reference for
comparison.
Oedometric tests on compacted mixtures of bentonite (40 %)
and quartz sand (60 %) were carried out to assess both the
increase in permeability and the effects on stiffness due to the
chemical treatment. Samples were reconstituted with different
chemical composition of the pore water - either artificial
groundwater or guanidinium solutions - and subsequently tested
according to the procedure given in ASTM D2435-04.
The same mixtures were used in constant head permeameter
tests, were the permeability was measured on both modified and
unmodified soil. Additionally, the temporal evolution of the
permeability during flow-through treatment with guanidinium
solutions was recorded for a sample with initially unmodified
soil.
Since chemically enhanced drainage is planned to be applied
in the context of stabilisation measures, the effects of the
chemical modification on the strength parameters of the soil
should not be neglected. Therefore, we assessed the influence
on the residual shear resistance of pure bentonite samples with a
ring shear apparatus. The samples were directly reconstituted
from homo-ionic calcium and guanidinium bentonites, as the
device used in this study did not allow for chemical
modification of the soil within the sample cell.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1
Modification of particles and pores
During sample preparation of modified bentonites, a granular,
non-plastic behaviour was observed. Images taken with a
scanning electron microscope (Figure 1) revealed that in
suspension the clay fraction aggregated upon addition of
guanidinium.
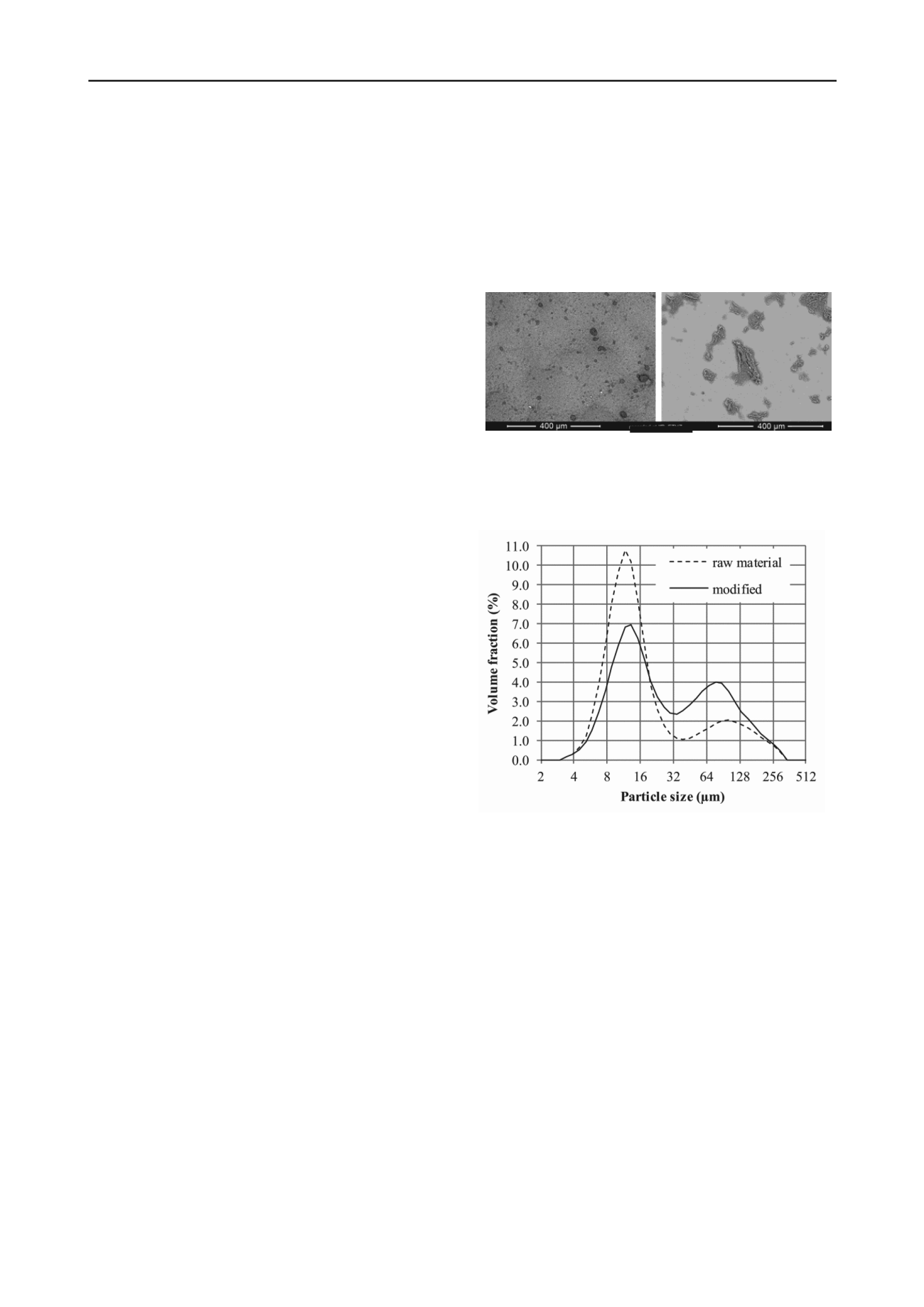
The measurement of the particle size distribution supported
this observation. Both calcium and guanidinium bentonites
feature a bimodal distribution. However, figure 2 shows that the
total volume fraction of the larger mode – containing the
aggregates – is almost doubled for the guanidinium samples
(42.4 %) compared to the calcium clay (22.4 %).
Figure 1. SEM-images of bentonite grains after washing in suspension
with demineralised water. The calcium form remains finely dispersed
(left), whereas the exposure to guanidinium ions (right) leads to the
formation aggregates.
Figure 2. Bimodal particle size distribution measured with laser
diffraction. The volume fraction of the larger mode (aggregates) is
significantly increased by the chemical modification.
Compacted samples were analysed with MIP in order to
examine whether these aggregates were capable of maintaining
an open pore structure. Considerable changes in the pore system
were detected. Even though the unmodified soil was prepared at
a higher water content (w
L,Ca
= 102%) the modified bentonite
(w
L,Gnd
= 64%) features a larger accessible pore volume
(Figure 3). The largest contribution to the additional pore
volume stems from pores with average radii of 2 µm. The total
pore volume of these larger pores had increased, the volume in
the smaller pore fraction (radius < 0.1 µm) however was slightly
reduced compared to the reference material.


