3308
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
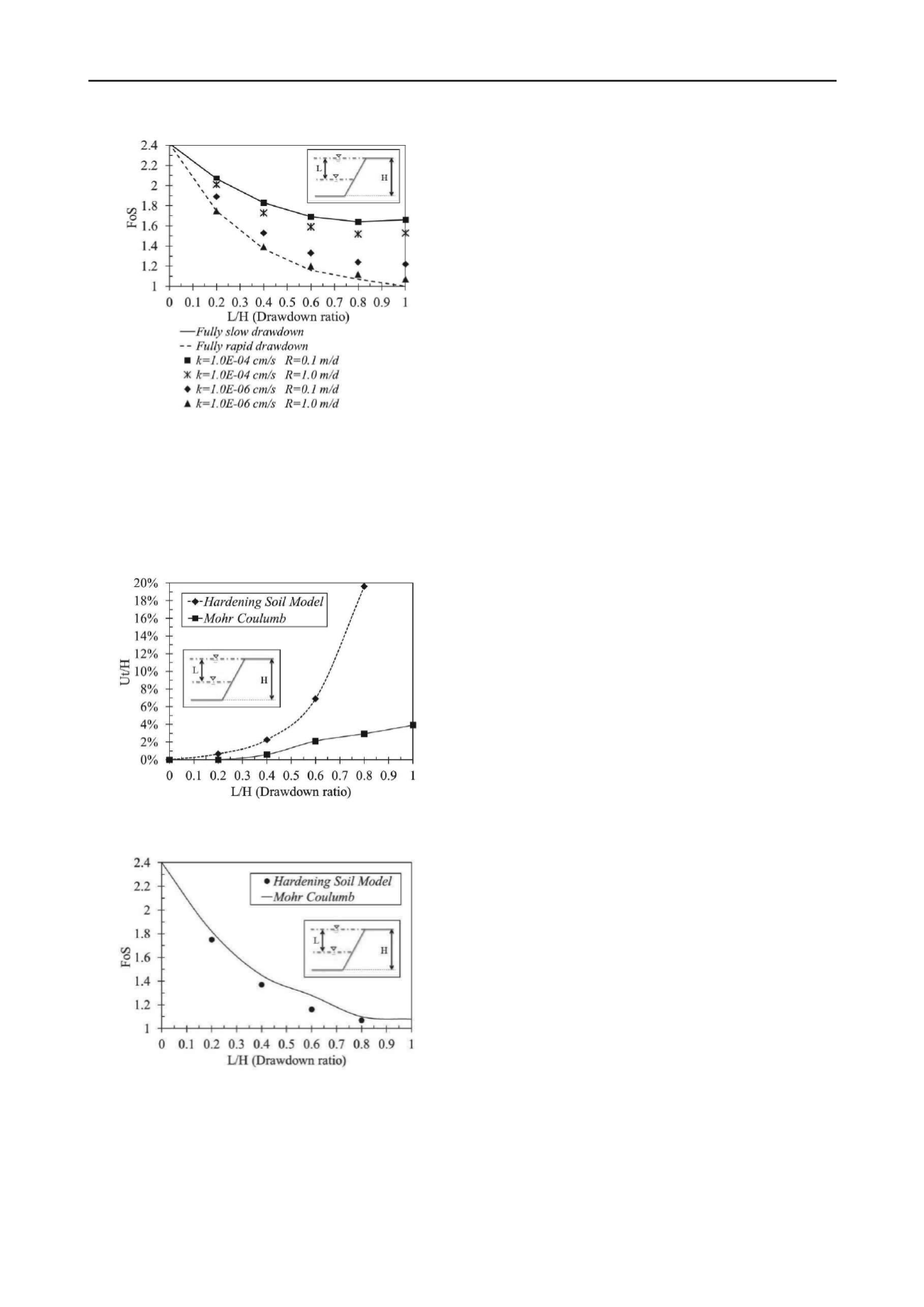
Figure 4. Variation of F○S with drawdown ratio (L/H) for H=6 m height
and 2:1 slope.
Finally, the influence of varying the constitutive model and
its parameters for predicting horizontal displacements was
studied (Fig. 5). The safety factors in the analysis of the
analyzed levee were also computed (Fig. 6). For these purposes,
two constitutive models were assumed in analyses: Mohr
Coulomb (MC) and Hardening Soil Model (HSM).
Figure 5. Horizontal displacements at the toe of the slope obtained by
MC and HS constitutive models (k=1×10
-6
cm/s and R=1.0 m/d).
Figure 6. F○S as a function of drawdown ratio (L/H) computed by MC
and HS models (k=1×10
-6
cm/s and R=1.0 m/d).
From results presented in Figures 5 and 6 it can be drawn the
following concluding comments:
- During the consolidation phase the MC model exhibits
unrealistic horizontal deformations and lower than those
obtained by the HSM model, due to: a) the HSM shows a plastic
behavior at stress levels lower than the MC (Gens, 2012), b) in
the loading and unloading process horizontal stresses in the
HSM are larger than in the MC model, and c) the HSM has
major peaks values of excess pore water pressure generated
during loading or unloading process (Berilgen, 2007).
- When using the phi-c reduction method in combination
with advanced constitutive models, these models behave such as
the Mohr-Coulomb model, since stresses dependent on rigidity
and the behavior obtained due to hardening effects are excluded
from the analysis. In this case, the stiffness is calculated at the
beginning of the calculation stage and remains constant until the
calculation phase is completed.
4 GENERAL CONCLUSIONS
As demonstrated in this paper, the stability of a submerged
slope under drawdown conditions (partial or total) is mainly
affected by the properties of the material constituting the levee
and the drawdown rate and drawdown ratio.
From results of parametric analyses it was observed that the
fully rapid drawdown
condition occurs when the water level of
the reservoir descends more quickly than the remaining pore
water pressures (
p
seepage
and
p
excess
) are dissipated within the
levee precisely caused by the drawdown, and no necessarily due
to a total decrease of the water surface in a given period of time
(minutes, hours or days). Finally, from slope stability analyses
the safety factor was observed to decrease when the drawdown
ratio (L/H) increases.
5 REFERENCES
Alonso E.E. and Pinyol N.M. 2008. Unsaturated soil mechanics in earth
and rockfill dam engineering.
First European Conference on
Unsaturated Soils
. Durham, Balkema.
Berilgen M. 2007. Investigation of stability of slopes under drawdown
condition.
Computers and Geotechnics
Vol. 34, 81-91.
Duncan J.M., Wrigth S.G. and Wong K.S. 1990. Slope stability during
rapid drawdown.
Proceedings of the H. Bolton Seed Memorial
Symposium
Vol. 2, 253-272.
Gens A. 2012. Advanced Course on Computational Geotechnics 2D and
3D (PLAXIS and PLAXFLOW Users), Consolidation Section.
UAQ, Santiago de Querétaro, Qro., México.
Griffiths D.V. and Lane P.A. 1999. Slope stability analysis by finite
elements.
Geotechnique
49(3), 387-403.
Huang M.S. and Jia C.Q. 2009. Strength reduction FEM instability
analysis of soil slopes subjected to transient unsaturated seepage.
Computers and Geotechnics
36(2), 93-101.
Lane P.A. and Griffiths D.V. 2000. Assessment of stability of slopes
under drawdown conditions.
Journal of Geotechnical and
Geoenvironmental Engineering
126(5), 443–50.
Nian T., Jiang J., Wan S. and Luan M. 2011. Strength Reduction FE
Analysis of the Stability of Bank Slopes Subjected to Transient
Unsaturated Seepage.
Electronic Journal of Geotechnical
Engineering
. Vol. 16, 165-177.
Nagtegaal J.C., Parks D.M. and Rice J.R. 1974. On numerically
accurate finite element solutions in the fully plastic range.
Comp.
Meth. Appl. Mech. Engng
. Vol. 4, 153-177.
PLAXFLOW Version 1.6 2008. Scientific Manual, Edited by R.B.J.
Brinkgreve.
Delft University of Technology and Plaxis bv
. R. Al-
Khoury, Plaxis bv and J.M. van Esch, GeoDelft. The Netherlands.
PLAXIS 2D Version 9.0 2008. Scientific Manual, Edited by R.B.J.
Brinkgreve, W. Broere and D. Waterman,
Delft University of
Technology and Plaxis bv
; The Netherlands.
Sloan S.W. 1981. Numerical analysis of incompressible and plastic
solids using finite elements. Ph.D. Thesis. University of
Cambridge, U.K.
Sloan S.W. and Randolph M.F. 1982. Numerical prediction of collapse
loads using finite element methods.
Int. J. Num. Analyt. Meth. in
Geomech.
Vol. 6, 47-76.
Terzaghi K. 1943. Theoretical soil mechanics. Art. 122: Effect of
drainage on earth pressure and stability. pp. 338. John Wiley.
Van Genuchten MTh. 1980. A closed-form equation for predicting the
hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils.
Soil Sci Am J
44(5),
892-898.


