2279
Technical Committee 208 /
Comité technique 208
was happened on 8 June shown in Figure 7, and this landslide
disaster caused the slope of observation point 2 inclined
gradually at the same time. As a result, there was almost two
day for taking refuge before the landslide happened.
1.1
Monitoring of a slope failure site for secondary disaster
prevention in Japan
Another field detection result of a slope failure site along a
national road in Kyushu of Japan is shown in Figure 8. This
slope consists of strongly weathered granite, and it was failed
due to a heavy rainfall in July of 2009. The slope was excavated
to have a gradient of 45 degrees for disaster relief work, and
was monitored with three sensor units. Heavy rainfall caused a
second failure, and a local part of slope including the sensor unit
fallen down. Figure 9 shows the records of tilt sensor of the
unit, in directions toward and laterals to the slope, respectively.
Specially, the tilting in Y-axis (lateral direction) showed
extraordinary behaviors 50 minutes before the second failure.
Its tilting rate was around 3 degrees per day (0.12 degrees
per hour). As this second failure took place adjacent to the
location of the sensor unit 2, the behaviors of the slope before
and after the failure was detected by the monitoring system. The
site manager got aware of the extraordinary behaviors of the
data from sensor unit 2, and he stopped the disaster relief work
and the road service to avoid large loss successfully.
Figure 7. New landslide on June 7, 2009.
1.2
Field evaluation for developed tilt sensors to traditional
extensometers based on in-site measuring
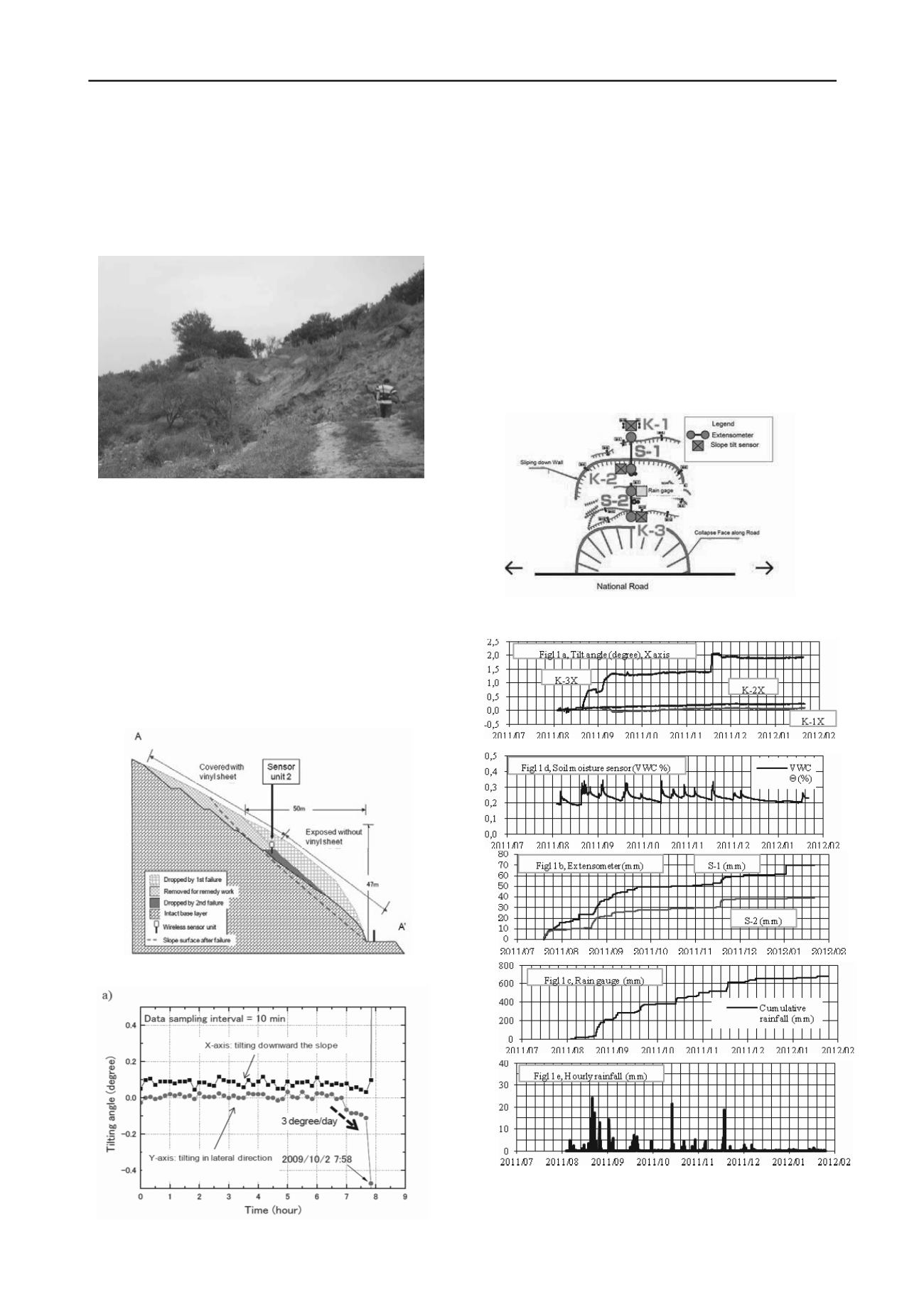
Another in-site measurement results were showed in Figure 10
to Figure 11a-e, a heavy rainfall on July 2011 caused a slope
failure alone local national road in Kyushu of Japan.
For the road earthwork construction, an emergency
monitoring system using multiple borehole inclinometers,
extensometers, tilt sensors and rain gauge has been set up at
Figure 10. A field site of failed slope along national road in Japan
Figure 8. Sketch of failed slope along highway
Figure 9. Tilt angle change just before the second failure.
Figure 11, Time histories vs. measuring values.
slope failure site. For validating developed tilt sensor with field
extensometers data, the three tilt sensors were installed nearby


