2066
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
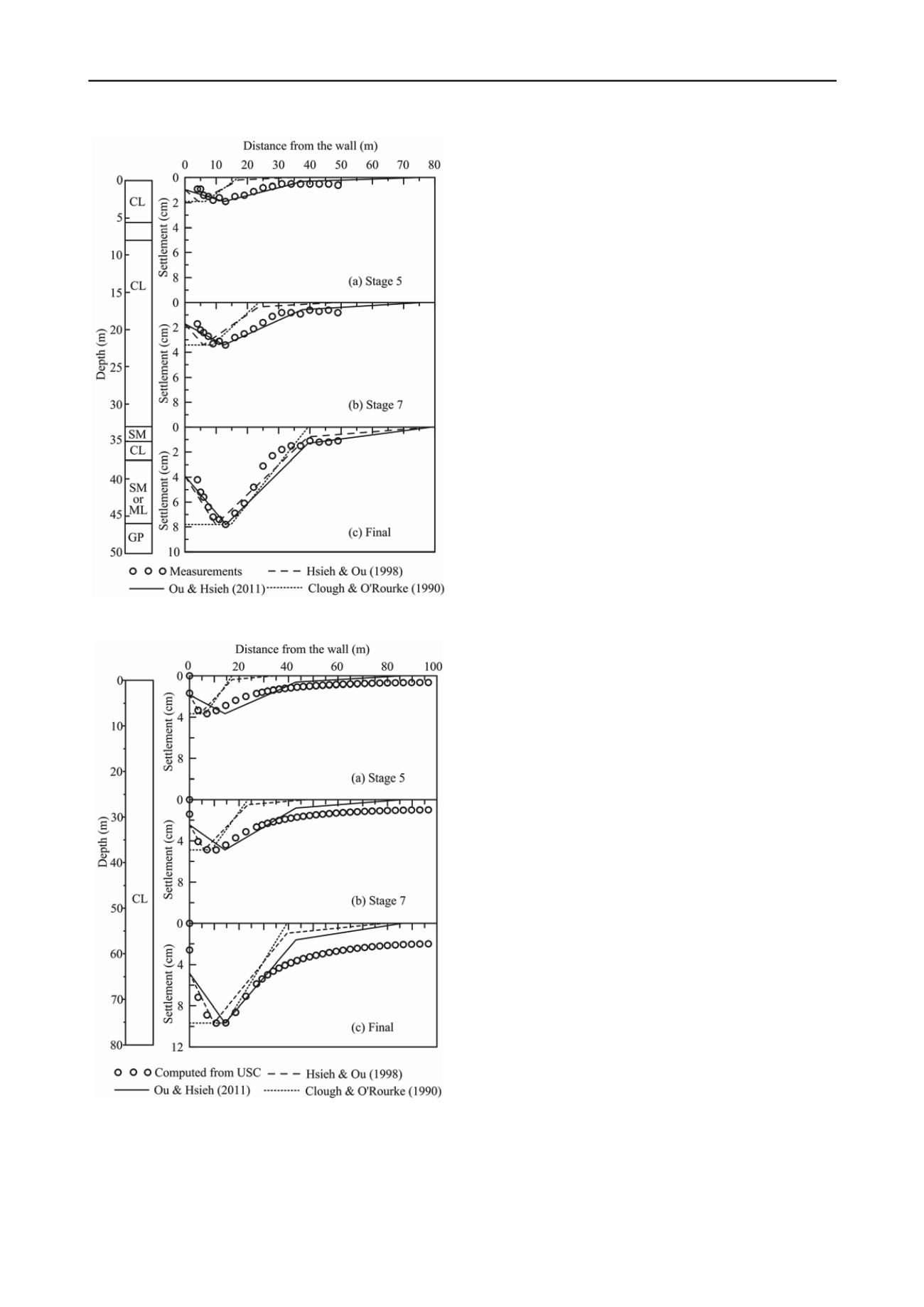
Figure 8. Verification of the proposed method for TNEC excavation.
Figure 9. Verification of the proposed method for the hypothetical
excavation with the 80 m thick soft clay.
5 CONCLUSION
The objective of this paper is to investigate the mechanism of
ground settlement induced by deep excavation under the plane
strain condition through finite element analysis. The study
focuses on the settlement under the normal excavation condition,
that is, no dewatering induced settlement, no excessively long
construction duration causing the occurrence of creep, and no
serious construction defects. The USC model was selected to
perform parametric studies to find the dominating factors
affecting settlement influence zone based on the calibration of a
well-documented case history and a hypothetical excavation
with 80 m thick soft clay using various soil models. It is found
that the primary influence zone is mainly the active failure zone
or the potential failure zone due to basal heave. A method is
then proposed to estimate the primary influence zone from the
relevant parameters such as two times excavation depth,
excavation width, depth to rock-like soil layer and depth of the
bottom of the soft clay. Case studies reveals that the proposed
method improves the prediction of settlement for excavations
whose twice the excavation depth are very different than
excavation width, depth to rock-like soil layer and depth of the
bottom of the soft clay. The methods of Clough and O’Rourke
and Hiseh and Ou only yield moderately good prediction results
for the settlement at the final stage for most of the cases and
largely poor predictions at the intermediate stages, which can be
treated as single case histories because the excavation depth is
the only parameter used in the formula.
6 REFERENCES
Clough G.W. and O'Rourke T.D. 1990. Construction-induced
movements of in situ walls. Proceedings of the Design and
Performance of Earth Retaining Structures, ASCE Special
Publication, 439–470.
Hsieh P.G. and Ou C.Y. 1998. Shape of ground surface settlement
profiles caused by excavation. Canadian Geotechnical Journal 35(6),
1004-1017.
Hsieh, P.G. and Ou, C.Y. 2011, Analysis of nonlinear stress and strain
in clay under the undrained condition, Journal of Mechanics, 27 (2),
201-213.
Lim, A., Ou, C.Y. and Hsieh, P.G. 2010. Evaluation of clay constitutive
models for analysis of deep excavation under undrained conditions,
Journal of GeoEngineering, 5(1), 9-20.
Ou, C.Y. and Hsieh, P.G. 2011. A simplified method for predicting
ground settlement profiles induced by excavation in soft clay,
Computers and Geotechnics 38(12), 987-997.
Ou, C.Y., Liao, J.T. and Lin, H.D. 1998. Performance of diaphragm
wall constructed using top-down method, Journal of Geotechnical
and Geoenvironmental Engineering, ASCE, 124(9), 798-808.


