366
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
water in the soil particles with a direct factor, but Aoyama and
Fukuda(1990) proved that it can be generated in the closed
system without water supply from under the ice layer.
In this study, Italian regulations that set the maximum and
minimum temperatures based on real weather, are considered
proper and applied to the test. In order to determine a proper
temperature range suitable for the domestic weather conditions,
the freezing and thawing temperatures are set based on the
comparison of 10 years' weather data on Seoul, Icheon,
Cheongju, Jeonju, Daegu, Milyang, Yeongju, Yeongwol,
Wonju, Jecheon, and Taebaek along with its resulting
temperature range of -21.1 to +26.5
℃
.
Therefore, the freezing and thawing temperatures to
reproduce real weather conditions are set at -20
℃
and +20
℃
respectively, and the temperature duration at 4 hours to carry
out a repetition test up to 200 times. For the water supply
method, a freezing-induced method by maintaining comparative
humidity rather than a flooding method is used, which is to
reproduce a general effect occurring under the temperature
condition below 0 not under special conditions such as rainfall
or underground water.
2.2. Repeat Drying and Wetting
To reproduce the weathering caused by weakened binding
power between the particles that compose soil when repeating
the flooding and drying process in pure water excluding the
effect of temperature, a drying and wetting repetition test was
conducted.
For fresh rock or high consolidation rock, deterioration due
to drying and wetting repetition does not occur significantly,
however weakening of binding power between the particles and
chemical weathering are promoted by the water permeated into
a gap in the earth and sand state. In other words, chemical
effects like reprecipitation of decomposed ions such as
dissolution, filteration, deformation and salification change the
characteristics of soil.
A method to copy rainfall is yet to be established that a total
flooding method is applied to make a continuous contact
between water and soil particles in this study. This is because
only the surface of the soil particles would be affected if a
periodic spraying method is applied.
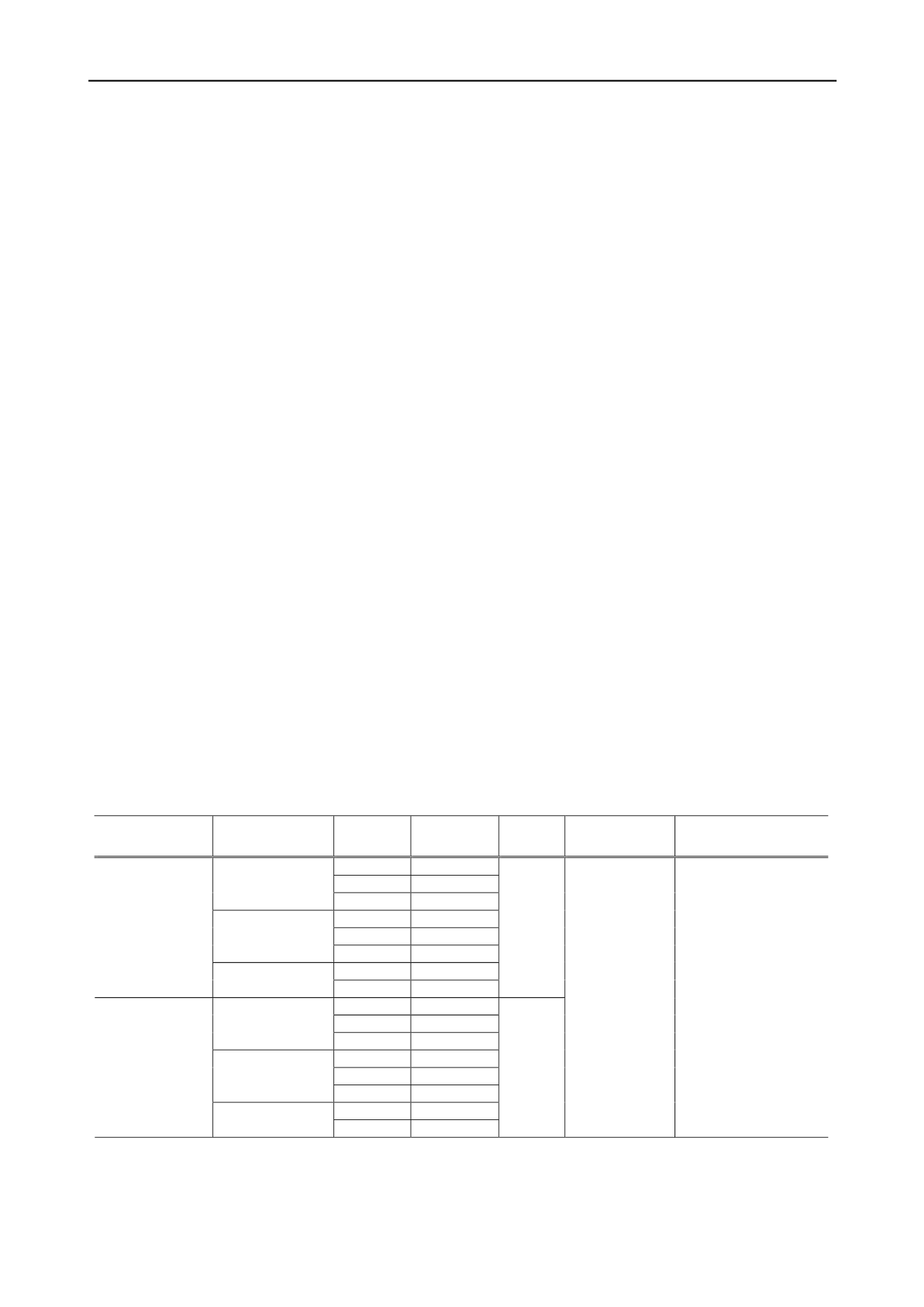
Table 1. Classification of strength test and test codes
After checking the change of water content by weight during
drying through a preparatory experiment, it turned out to have
deteriorated below the optimum level in about 24 hours, so the
repetition test of drying and wetting in this study has been
performed with 24-hour cycle.
3 STRENGTH CHANGE CHARACTERISTIC
3.1. Target Sample
The weathering soil sample to identify the strength change is
classified into igneous rock, metamorphic rock, and
sedimentary rock, and the soil underground has been collected
after removing about 1.0m surface layer to exclude the effect of
vegetation.
Table 1 shows the test codes by strength test for weathering
degree change cycle.
3.2. Physical Characteristic Change
Weathering soil is a type of soil with a very high crushability
compared to other types of deposit soil. Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 are
representative results performed to know the effect of particle
crushing caused by weathering progress.
As shown in the figures above, the grain-size distribution
curves move to the left when repeating the freezing and thawing
and the drying and wetting compared to that of the test
beginning state, which means soil particles become finer and
signifies that the distribution effect of weathering soil is very
big because of the weathering caused by temperature and water.
The previous studies shows that the granulation of quartz and
feldspar by the particle change take the most cases of the
granulation.
The increase in fine-grained soil due to the 190 time
repetition of freezing and thawing and the 180 time repetition of
drying and wetting are compared with each other and shown in
Table 1. The report of Kim(2002) also pointed out that the
shape and feature of the surface among basic structural
characteristics have a huge impact on the physical and dynamic
features of soil, and among many factors for the change of
particle shape, the initial grain diameter, mineral composition of
particles, and features for weathering work as important factors
and the characteristics change according to the weathering
progress.
Artificial Weathering
Conditions
Estimated
Parent Rock
Sample
Type
Classification
Code
Cycle
Times
Direct shear Test
Condition
Uniaxial Compression Test
Condition
Seoul
FGS
Yuseong
FGY
Igneous rock
(G)
Jeonju
FGJ
Cheongdo
FSC
Goryeong
FSG
Sedimentary rock
(S)
Gwangju
FSK
Sabuk
FMS
Freezing
Thawing
(F)
Metamorphic Rock
(M)
Mungyeong
FMM
0
10
25
40
60
80
100
120
150
190
Seoul
DGS
Yuseong
DGY
Igneous rock
(G)
Jeonju
DGJ
Cheongdo
DSC
Goryeong
DSG
Sedimentary rock
(S)
Gwangju
DSK
Sabuk
DMS
Drying
Weting
(D)
Metamorphic rock
(M)
Mungyeong
DMM
0
10
40
60
100
150
180
- initial
condition
0.95Ydmax
-vertical
Stress
(kg/cm2)
0.35
0.69
1.04
1.39
-shear speed
0.5mm/min
-test code
(S)
- initial
condition
0.95Ydmax
-deformation
Speed
0.1%/min
-test code
(U)


