3098
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
Table 2. The specification of Geotextile
items
contents
type
KJV-6000
base texture
high-strength vinylon
width
2,000mm
weight
320g/m
2
tensile strength
59.0kN/m
reduction coefficient
0.6
On the other hand, when the curing time of treated soil is
short, it is considered that the strength of base ground is
insufficient for the bearing capacity. The base ground, which is
composed of tamping layers and Geo-textile, may not have
uniformly mechanical behaviors. It is supposed that only Geo-
textile resists the overturning moment, which generates from the
tower’s load. As a result, it is simulated that Geo
-textile will be
able to share 26 percent of the total overturning moment. When
converting this value to the settlement, it is estimated 40cm.
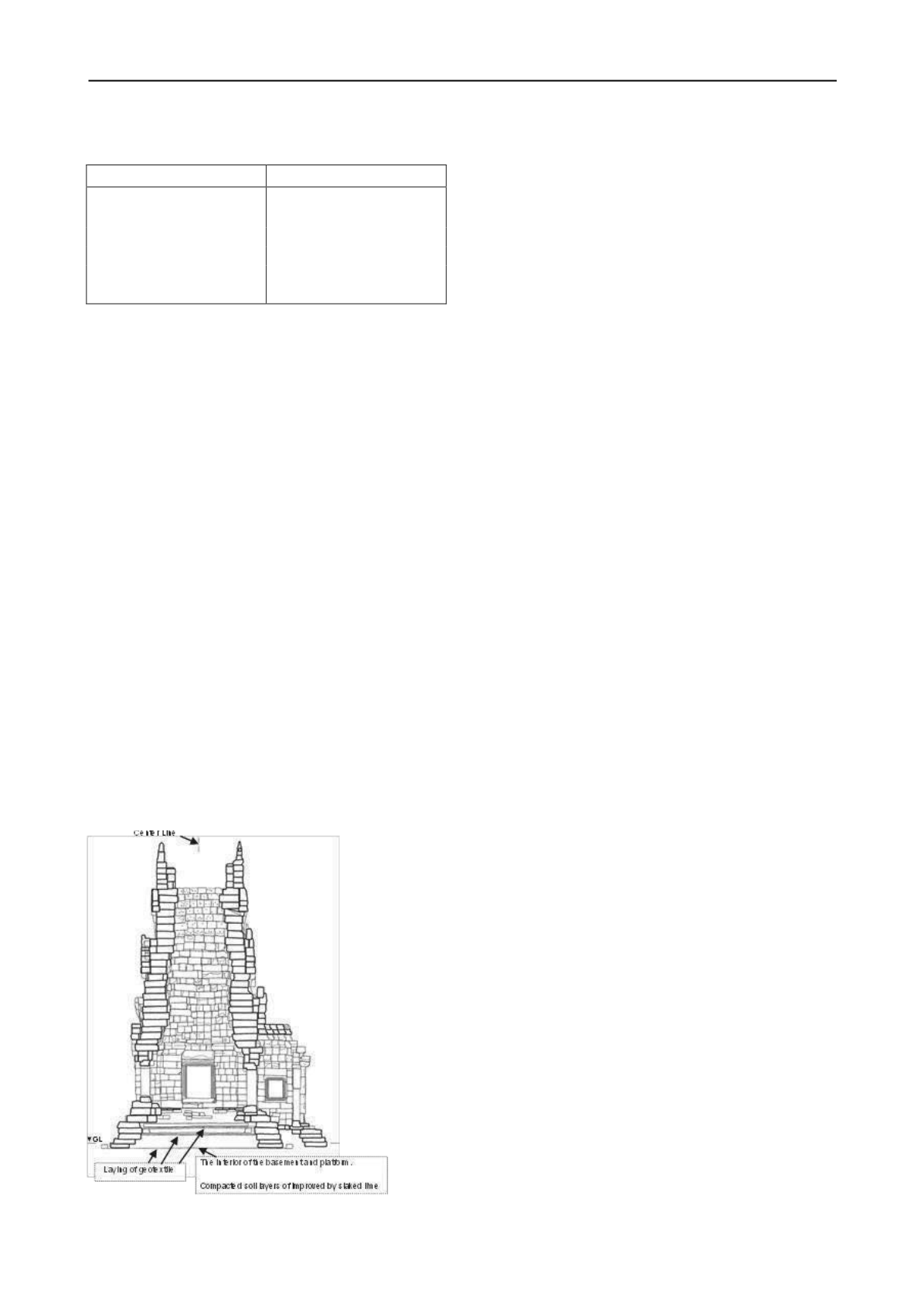
Based on above-mentioned result, Figure 7 shows a decided
section for reconstitution of the foundation platform.
7CONCLUSION
This project has been achieved in May, 2005. After that,
monitoring for these structures is being done. Until present after
the reconstitution, there is no trouble on them.
A consensus, which cultural heritages should be conserved
and saved from various collapsing factors, is changing in recent.
If modern materials and modern methods will be applied for
restoration works of heritages, the historic value on it may be
spoiled. Therefore it is demanded that materials and methods
for restoration works will not spoil the historic values of
heritages. From these viewpoints, a concept about “authenticity
and heritage” is discussi
ng now, especially on consideration of
designing and working for heritage geo-technology. The
authors desire for this paper to become a reference for the same
purpose.
Figure 7. Decided section for reconstitution of the foundation platform
8ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to express their sincere thanks to
Professor Takeshi Nakagawa of Waseda University. The
project, on which this paper is based, was supervised and
promoted by him responsible the entire.
9REFERENCES
Nakagawa T. (Supervisor) 1996-2005. Annual Report on the Technical
Survey of Angkor Monument 1995-2004, Japanese Government
Team for Safeguarding Angkor (JSA), Japan International
Cooperation Center
Nakagawa T. (Supervisor). 2005. Report on the Conservation and
Restoration Work of the Prasat Suor Prat Tower, Royal Plaza of
Angkor Thom, Kingdom of Cambodia, Japanese Government Team
for Safeguarding Angkor (JSA), Japan International Cooperation
Center.
Akazawa Y, Nakagawa T, Mizoguchi A, Nakazawa J, Iwasaki Y,
Fukuda M. 2009. Development and reserch of the restoration
methods for basement and platform of Prasat Suor Prat Tower N1,
AIJ Journal of Technology and Design vol. 30, 567-572.
Iwasaki Y, Akazawa Y, Fukuda M, Nakazawa J, Nakagawa K, Shimoda
I, and Nakagawa T. 2013. Dismantling for Reconstitution of N1
Tower of Prasat Suor Prat, Angkor Thom, Cambodia (TC 301- IS
NAPOLI 2013, Currently, submitted).


