2884
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
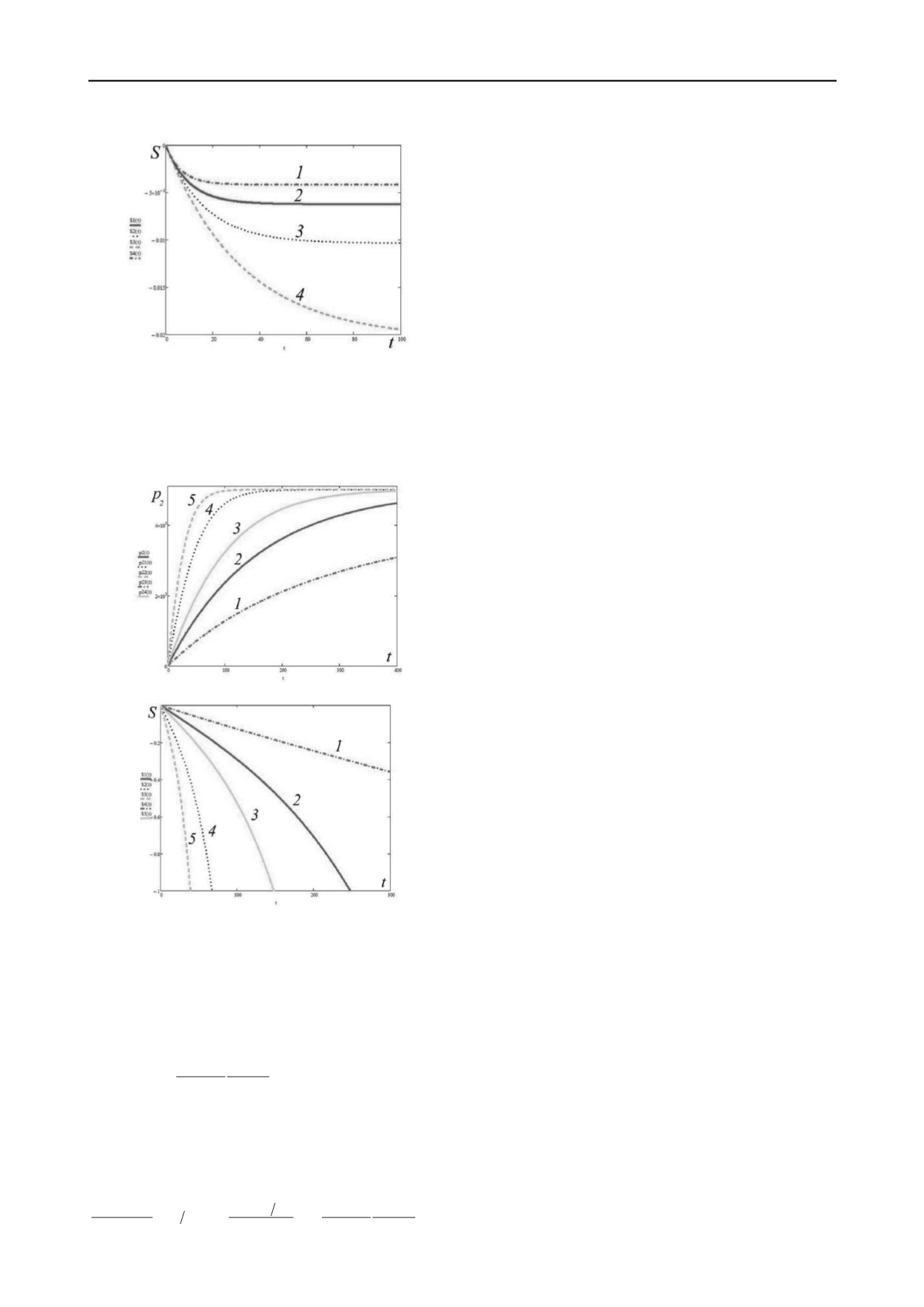
Analysis of solution (19) showed that
decays versus
time at different rates and tends to constant values (Fig. 7) while
the settlement can decay or not decay, depending on the
intensity of applied load
(Fig. 7b).
2
p
2
1
/
aN p
6 CONCLUSIONS
1. A rheological equation is proposed to describe soil shear,
based on the modified Maxwell model, having clay
strengthening and softening parameters.
2. Analysis of the equations has shown that for the case of
constant loading it describes decaying, non-decaying and
progressing soil creep as well as stress and shear strain
relaxation processes in kinematic loading mode.
(b)
Fig. 6. Here
p
2
(t)
(kPa) - t (hours)(а) and
s(
in meters
)
(b) curves from (16) and (14) respectively with input parameters
from (15)
3. In the pile-soil interaction problem solution the distribution
of applied force between the side surface and the lower tip
is time-related, and it can result either in decaying or in non-
decaying pile settlements, depending on the parameters of
soil around the pile and under its tip.
5.2
Elasto-plastic bed under pile tip
7 REFERENCES
Vyalov S.S. 1978. Rheological bases of soil mechanics.[in Russian],
Vysshajashkola, Moscow.
ZaretskiyYu.K. 1988. Visco-elastic behavior of soil and calculations of
structurers. [in Russian], Stroiizdat, Moscow.
Osipov V.I. 1979. Nature of strength of clay soil.[in Russian] Moscow
State University, Moscow.
Ter-Martirosyan Z.G. 2010.Soil Mechanics. [in Russian], ASV,
Moscow.
Ter-Martirosyan A.Z. 2010. Interaction between foundations and
rheological soil under cyclic and vibration loads.[in Russian]
Author's abstract of dissertation for Ph.D. degree
, Moscow.
Skempton A.W. 1964. Long-term stability of clay slopes.
“Geotechnique”.Vol. 14.- №2. - P.p. 77-101.
(a)
Murajama S. and Sibata T.1961.Reological properties of clay. // Proc. 5-
th ICSMFE. Paris, Vol. I. - P.p. 269-173.
(b)
Fig. 7.
p
2
(kPa) - t (hours) (а) according (19) and
s(meters) - t(hours)
(b) according (18) plots for different
viscosity and elasticity parameters of soil around pile and
different elasto-plastic parameters of soil under pile tip.
The settlement rate of soils under pile tip is roughly
approximated as:
2
*
2
*
2
2
2
2
4
1
p p
p
G
a p S
r
(18)
With as limit load on soil bed, determined from
known solutions [11].
*
2
p
Eq. (1) yields that
if
*
2 2
p p
S
Comparison ofeqs. (4) and (18) according (11) yields a
differential equation versus
p
2
:
2
*
2
*
2
2
2
2
1
0 0
2
0
2 0 0
1
2 1
2
0
4
1
2
ln
ln
2
p p
p
G
a p
lG
ab a p ab
t l
p p a
(19)


