2532
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
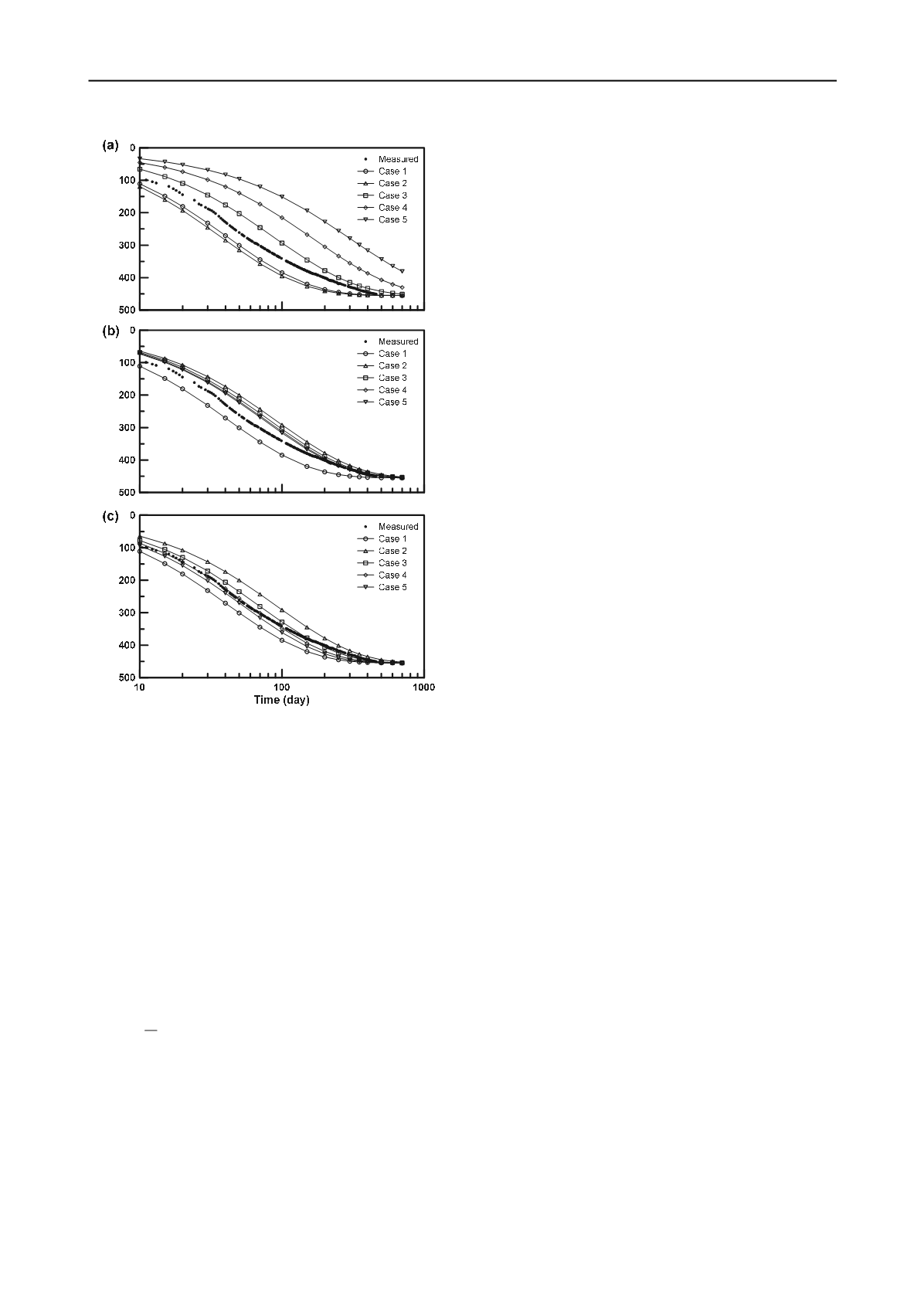
figure 5. measured and predicted settlement rate for the layer above el
-30m: (a) hansbo
’
s method, (b) proposed method with case a, (c)
proposed method with case b
the surcharge load is assumed to be applied all at once, while, in
the field, the surcharge load is applied incrementally.
4 conclUsion
in this study, the radial consolidation enhanced by the vertical
drain is discussed with the analytical method existed, and the
modified solution is suggested. through parametric study and
comparison between the calculated and measured settlement
rates, the results are summarized as follows.
as the degree of disturbance increases, hansbo
’
s analysis
shows that the time factor t
h
increases for a certain degree of
radial consolidation. however, the time factor for proposed
analysis (t
hs
), which corresponds to a certain degree of radial
consolidation, slightly decreases as the degree of disturbance
increases. furthermore, proposed analysis gives the almost
identical
hs
r
T U
'
curves when the k
h
/k
s
value becomes larger
than 20.
for Busan new-port site, the extent of the disturbed zone is
evaluated using two possible void ratio variations within the
disturbed zone. When a constant permeability or void ratio
within the disturbed zone is assumed, the extent of the disturbed
zone r
s
is estimated to be 2.7r
m
. for the linear spatial variation
within the disturbed zone, the extent of the transition zone r
t
is
estimated to be 4.1r
m
with the same equivalent radius between
fully disturbed zone and mandrel (r
f
= 1.0r
m
).
the settlement rate predicted by the proposed analysis is
well matched with the measured field settlement when the k
h
/k
f
ratio is 2.5 with a linear spatial distribution of the permeability
within the disturbed zone. the proposed method has advantages
to evaluate the extent of disturbed zone and it is less influenced
by the disturbance effect than hansbo
’
s method.
5 references
Basu d., Basu p., and prezzi m. 2006. analytical solutions for
consolidation aided by vertical drains.
Geomechanics and
Geoengineering: An International Journal
1(1), 63-71.
Basu d. and prezzi m. 2007. effect of the smear and transition zones
around prefabricated vertical drains installed in a triangular pattern
on the rate of soil consolidation.
Journal of Geomechanics
7(1), 34-
43.
Bergado d.t., asakami h., alfaro m.c., and Balasubramaniam a.s.
1991. smear effects of vertical drains on soft Bangkok clay.
Journal of Geotechnical Engineering
117(10), 1509-1530.
Burland J.G. 1990. on compressibility and shear strength of natural
clay.
Geotechnique
40(3), 329-378.
carillo n. 1942. simple two and three dimensional cases in the theory
of consolidation of soils.
Journal of Mathematics and Physics
21(1), 11-18.
chai J.c. and miura n. 1999. investigation of factors affecting vertical
drain behavior.
Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental
Engineering
125(3), 216-226.
hansbo s. 1981. consolidation of fine-grained soils by prefabricated
drains.
Proceedings of 10th International Conference on Soil
Mechanics and Foundation Engineering
, stockholm,sweden,
Vol.3, 677-682.
hird c.c. and moseley V.J. 2000. model study of seepage in smear
zones around vertical drains in layered soil.
Geotechnique
50(1),
89-97.
holtz r.d., Jamiolkowski m.B., lancellotta r., and pedroni s. 1987.
Performance of prefabricated band-shaped drains
. construction
industry research and information association (ciria) report,
research project 364.
hong s.J. 2011.
Evaluation of geotechnical properties of Busan
Newport clay
, doctoral thesis, Korea University.
indraratna B. and redana i.W. 1998. laboratory determination of smear
zone due to vertical drain installation.
Journal of Geotechnical and
Geoenvironmental Engineering
124(2), 180-184.
lo d.o.K. 1991.
Soil improvement by vertical drains
, doctoral thesis,
University of illinois at Urbana-champaign.
onoue a. 1988. consolidation by vertical drains taking well resistance
and smear into consideration.
Soils and Foundation
28(4), 165-174.
onoue a., ting n.h., Germaine, J.t., and Whitman, r.V. 1991.
permeability of disturbed zone around vertical drains.
Proceedings
of 1991 ASCE Geotechnical Engineering Congress
, Boulder,
colorado, Vol. 2, 879-890.
sathananthan i. and indraratna B. 2006. laboratory evaluation of smear
zone and correlation between permeability and moisture content.
Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering
132(7), 942-945.
sharma J.s. and Xiao d. 2000. characterization of a smear zone around
vertical drains by large-scale laboratory tests.
Canadian
Geotechnical Journal
37(6),1265-1271.
shin d.h., lee c., lee J.s., and lee W. 2009. detection of smear zone
using micro-cone and electrical resistance probe.
Canadian
Geotechnical Journal
46(6),719-726.
tavenas f., Jean p., leblond p., and leroueil s. 1983. the permeability
of natural soft clays. part ii: permeability characteristics.
Canadian
Geotechnical Journal
20(4), 645-660.
Zeng G.X. and Xie K.h. 1989. new development of the vertical drain
theories.
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Soil
Mechanics and Foundation Engineering
, rio de Janeiro, Brazil,
Vol.2, 1435-1438.


