1446
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
effect of download. The soil compaction occurs only during
excess of stress of the structure strength. At irreversible soil
compaction the deformation is with the deformation module,
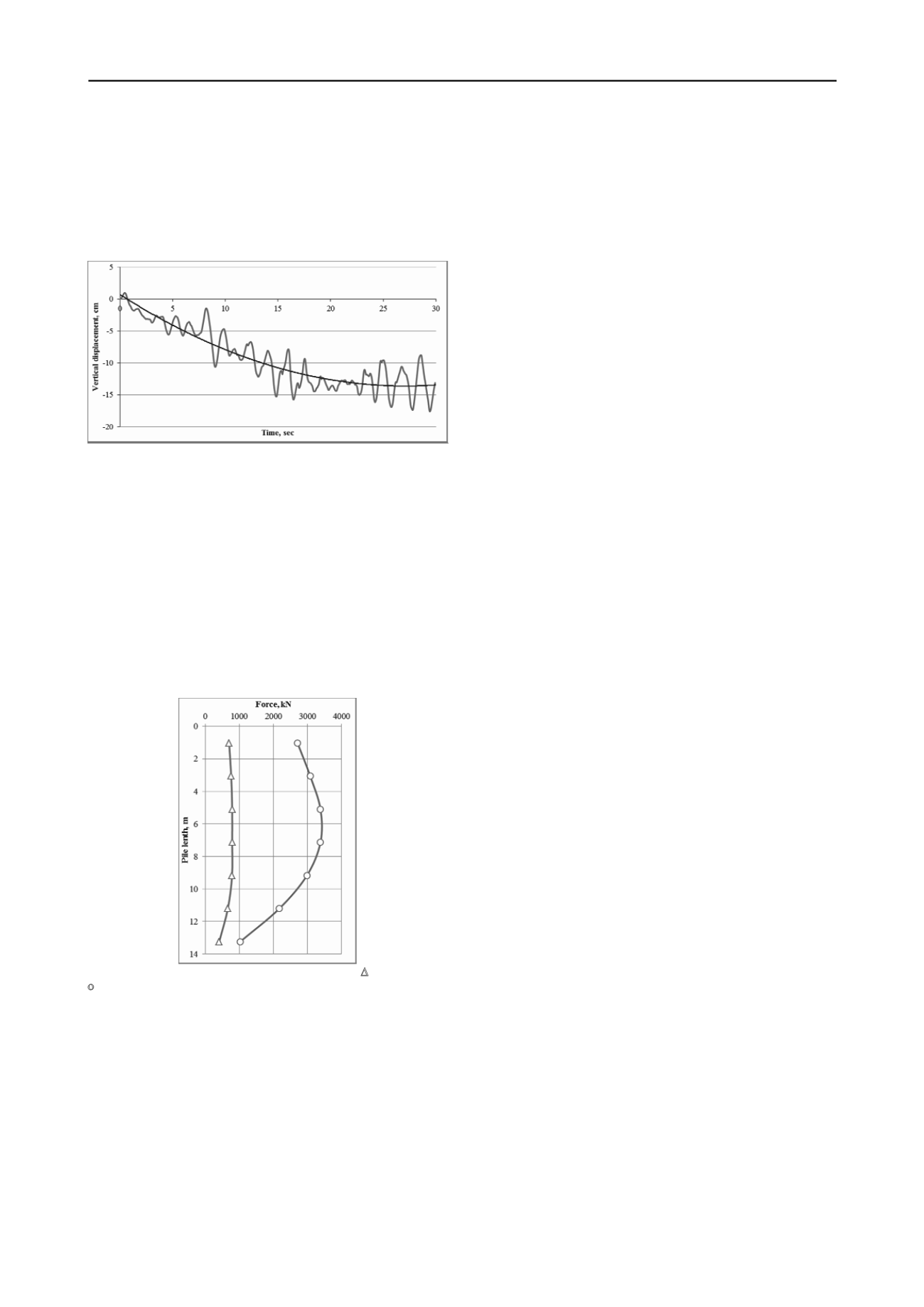
which corresponds to the real soil’s work. As it can be seen
from the diagram (Fig. 8), the process was developed to 20 s of
load, after which the settlement became stable and at least
exceeded the value of ~13 cm.
Figure 8. The diagram of the foundation settlement at the action of the
seismic load
The stress state in the foundation constructions was
decreased. At the top plate the moments became mostly 500-
800 kN
m/m, but in the areas of stress concentrations in the
zones of the elevator shaft, diaphragms and columns the local
values of moments were near 4.5
10
3
kN
m/m. In grillage slab –
to 3.3
10
3
kN
m/m.
At visco- elastoplastic formulation, the compressive forces in
piles decreased ~40 % and changed from 1.7
10
3
kN to
4
10
3
kN at the head level. During stretching, the maximal
efforts were from 0.5
10
3
kN to 3.5
10
3
kN in various zones.
Notice that in this variant the piles are in homogeneous soil.
But, despite of this, the significant stretching efforts have
maximum tensile values below the head of the pile (Fig. 9).
Figure 9. The diagrams of the vertical forces in piles (
– central zone,
– contur zone)
2 CONCLUSIONS
It has been shown that while solving problems of seismic
load influences on buildings and other structures it is necessary
to consider the inertial mass forces of the soil base and the
corresponding oscillation attenuation processes in the soil and
constructions.
It has been found that under the influence of seismic loads,
predominantly from inertial forces in the soil, zones of
significant tensile forces can appear in the piles. These zones
are located below the pile heads and must be taken into account
when designing grillage for the structure.
It has been determined that the utilization of piles during
seismic loads in layered soil bases with various deformation
properties leads to the appearance of forces within these piles
that can exceed the forces at the pile heads by as much as a
factor of two.
The maximum forces within the structure can occur at
various times and do not necessarily coincide with the periods
of maximum amplitude of the accelerogram.
The method of solving dynamic problems for the “soil base
– foundation – overhead construction” system presented and
implemented in ASSR “VESNA” allows more precise modeling
and therefore more efficient engineering designs for buildings
by taking into consideration the specifics of dynamic
interactions within such structures.
3 REFERENCES
Бойко І.П., Сахаров В.О. Моделювання нелінійного деформування
ґрунтів основи з урахуванням структурної міцності в умовах
прибудови. // Будівельні конструкції. Міжвідомчий науково-
технічний збірник. К.: НДІБК, 2004. – Вип.61, т.1. – с.27-33.
Сахаров В.О. Математична модель нелінійної ґрунтової основи для
досліджень задач прибудови // Основи і фундаменти: випуск.
Міжвідомчий науково-технічний збірник. – К.: КНУБА, 2005 –
вип.№29. 8-19.
Метод конечных элементов в механике твердых тел. / Под
редакцией А.С. Сахарова, И. Альтенбаха – К.: Вища Школа,
1982; Лейпциг: ФЕБ Файхбухферлаг, 1982. – 80с.
John Lysmer and R.L. Kuhlemeyer, Finite Dynamic Model for Infinite
Media, Proc. ASCE, Vol. 95, No.EM4, 1969, August
Vladimir Sakharov, Modelling of multistory building on nonlinear base
in an annex conditions. Active geotechnical design in infrastructure
development. – Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2006 – Vol.2. 693-698
I. Boyko, O. Sakharov & Yu. Nemchynov . The peculiarities ofstress-
strain state at interaction ofhigh-rise buildings and structures with
the base / Proceedings of the 16-th International Conference on Soil
Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2005, 1447-1450.
ДБН В.1.1-12-2006. Будівництво у сейсмічних районах.
ASCE Standard 4-98, 1999


