1044
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
equivalent water pressure vertical to the surface. The
(smoothed) internal force caused by the water pressure on any
section of the grain is equivalent to the water pressure.
Similarly, the average value of the stress of the soil skeleton
grains resulting from the pore fluid pressure
w
on grain contact
point (surface) shall be equivalent to
w
u
, as indicated in Figure
1(a). Therefore, whatever the shape and property of the soil
grain contacting surface are, to investigate the effect of the fluid
pressure, each soil skeleton grain may be considered to be an
isolated grain in the fluid. Furthermore, the average stress
caused by the pore fluid pressure on any section of the soil
skeleton grain is equal to
w
u
, as indicated in Figure 1 (b). Thus,
to take the soil skeleton as the free body, the average stress on
the section caused by the pore fluid pressure is equal to the pore
fluid pressure at the point, as indicated in Figure 1 (c).
u
In case of the pore fluid pressure, including pore water
pressure or matrix suction acts on partial surface of the grain not
on the whole surface of the grain, the skeleton grain still is in
balance
.
(a) (b) (c)
(a) stress on grain contact surface
(b) stress on the section of the soil grain
(c) stress on the section of the soil skeleton
Fig. 1 Stress of skeleton resulting from pore fluid pressure
The pore water pressure, pore air pressure and arising inter-
grain action force of the grain system are in balance, without
effect on the internal force of the internal force of the skeleton
system. Meanwhile, the balance force system shall not affect the
shearing strength and deformation of the skeleton system.
3 DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION OF EQUILIBRIUM AND
SOIL SKELETON STRESS EQUATION OF SATURATED
SOIL
The soil skeleton stress is defined to be the internal force
resulting from the external forces excluding the pore fluid
pressure acting on the soil skeleton of a unit area. Suppose the
soil is homogeneous, to select the soil skeleton and pore water
of the saturated soil as the free body of the independent analysis
object for the internal force balance analysis with a group of
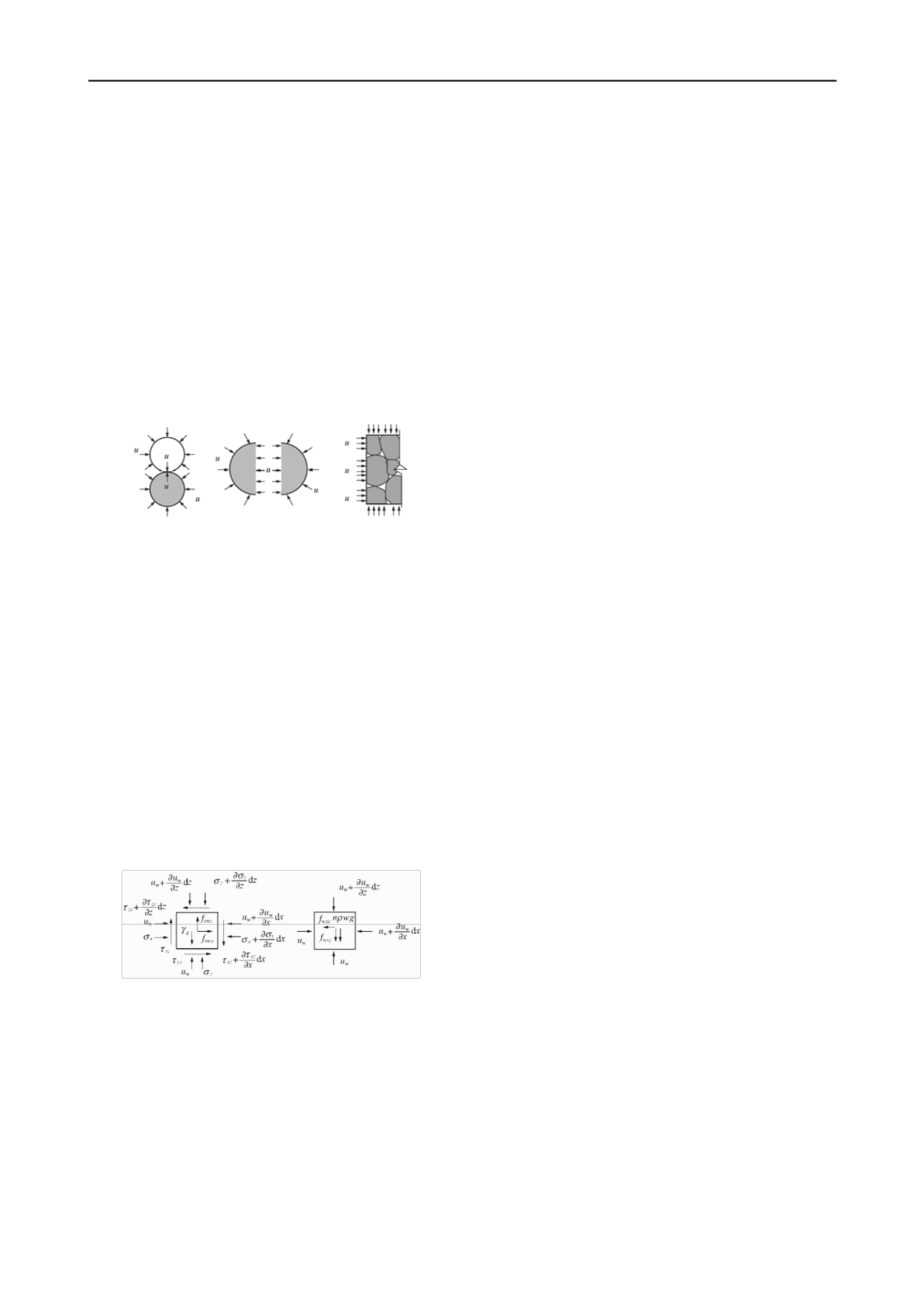
inter-phase acting force, as indicated in Figure 2.
Fig. 2 Equilibrium analysis for solid and pore water phase
In Figure 2, n is the porosity of the soil,
the pore water
pressure,
w
u
, , ,
x z xz zx
sw ws
sw
,
,
positive stress and shearing stress
respectively,
ws
,
x
x
z
z
f
f
f
f
the acting force and reacting
force of the soil skeleton and pore water in the direction of x
axis and z axis with same vale and opposite direction.
In the balance condition, the force acting on the skeleton and
the pore water control its own state respectively. Therefore, the
soil skeleton stress is also the effective stress to control the
deformation and strength of the skeleton (or the soil body),
which is the measurement of all external forces acting on the
skeleton, exceeding the pore fluid pressure.
According to the internal force analysis figure, the equation
of equilibrium of the soil skeleton and that of the pore water
under the static balance state can by obtained respectively.
Soil skeleton:
,
w,
sw s
(1 )
0
ij j
i
i
i
n u f
X
(1)
Pore water:
w,
sw w
0
i
i
i
nu f
X
(2)
Where,
is the soil skeleton stress,
,
,
ij
0
y
,
, ,
i j x y z
s
s
x
X X
s
d
z
X
,
,
w
w
0
x
y
X X
w
w
z
X n
.
To add formula (1) to (2), then obtain the equation of
equilibrium after cancelling the terms of inter-phase acting
force:
,
w,
sw
0
ij j
i
i
u X
(3)
where,
sw
s
w sw
sw
sw sat
,
0,
i
i
i
x
y
z
X X X X X
X r
.
Taking the soil skeleton and pore water as a whole system
for the balance analysis, the differential equation of equilibrium
of total soil stress in the static condition can be obtained:
t ,
sw
0
ij j
i
X
(4)
To compare formula (3) and (4), then
t ,
,
w
ij j
ij j
ij
u
(5)
where,
is the total stress and
is Kronecker symbol.
t
ij
ij
This is the saturated soil skeleton stress equation, consistent
with the traditional effective stress equation, where the soil
skeleton stress is the generally accepted soil effective stress.
The soil skeleton stress equation indicates the relationship
between the total stress and the skeleton stress and pore water
pressure, of which the physical property is the interaction of
forces between the soil skeleton and pore water. From the
deduction of the equation of equilibrium, it’s unnecessary to use
the effective stress equation in the balance analysis with the soil
skeleton and pore water as the free body separately. In other
words, it’s required to introduce the soil skeleton stress equation
to get the effective stress to control the soil skeleton
deformation and strength in the force analysis on the whole
structure of the soil skeleton and pore water to obtain the
differential equation of equilibrium. Besides, it's noticeable that
the equation (5) is applicable for saturated soil or porous
materials with communicating pores filled with water, whatever
the contacting property of grains is.
4 DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION OF EQUILIBRIUM AND
SOIL SKELETON STRESS EQUATION OF
UNSATURATED SOIL
The soil skeleton stress is still defined to be the internal force
resulting from the external forces excluding the pore fluid
pressure acting on the soil skeleton of a unit area for the
unsaturated soil. Selecting free bodies for balance analysis
requires meeting the following two conditions: � the water and
air in the communicating pores is immiscible;
the interacting
force of the pore water and pore air is ignored. For simple and
easy understanding, it may be supposed that the pore air
pressure acts on the whole surface of the soil skeleton, just as on
the saturated soil. The pressure difference (matrix suction) of
pore water and pore air acts on the surface of the occupied by
the pore water, as indicated in Figure 3(a).
Figure 3(b,c) indicates the force condition of the free body of
unsaturated soil infinitesimal element and soil skeleton in the
direction of x axis. For the homogeneous soil, the area ratios
occupied by the pore water and pore air on the unit area are
and
respectively,
and
is the corresponding
porosity of the phase of the pore water and that of the pore air.
/
w
n n
/
a
n n
w
n
a
n


