1054
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
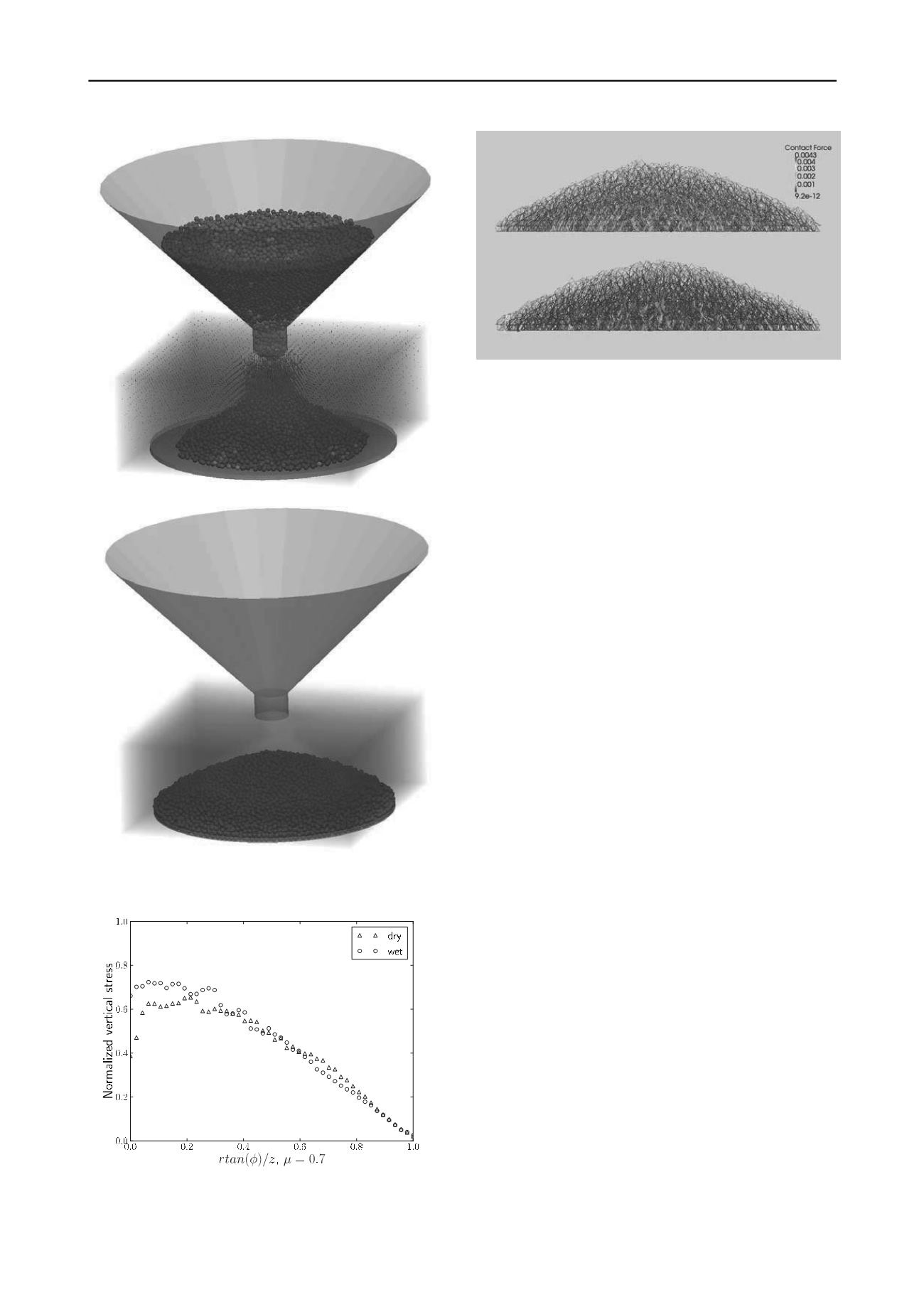
Figure 5. Normal contact force network in the sand pile formed in the
dry condition (top) and in water (bottom).
between the DEM and the CFD computations such interaction
forces as the drag force, the buoyancy force and the virtual mass
force. The coupled numerical tool has been benchmarked by
two classic soil mechanics problems and has been further
applied to the prediction of sandpiling in water. These examples
demonstrate that the proposed method is capable of capturing
the main feature of fluid-particle interaction from a microscopic
point of view. It is robust and efficient and has the potential to
be applied to a wider range of geomechanics problems where
fluid-particle interactions are important.
5 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The study was supported by Research Grants Council of Hong
Kong (through GRF
622910
).
6 REFERENCES
Anderson T.B. and Jackson R., 1967. Fluid mechanical description of
fluidized beds. Equations of motion.
Industrial & Engineering
Chemistry Fundamentals
6, 527-539.
Cundall P.A. and Strack O. 1979. A discrete numerical model for
granular assemblies.
Géotechnique
29, 47-65.
Di Felice R. 1994. The voidage function for fluid–particle interaction
systems.
Int. J. Multiph. Flow
20, 153-159.
Figure 3. Simulation of sandpiling through hopper flow into a water
tank. (a) During the hopper flow; (b) Final stable sand pile.
Shan T. and Zhao J.D. 2012. The role of water on the pressure dip in
sand piles.
The 23rd International Congress of Theoretical and
Applied Mechanics
(
ICTAM2012
). 19-24 August 2012, Beijing,
China.
Stokes G.G. 1844. On the theories of internal friction of fluids in motion
and of the equilibrium and motion of elastic solids.
Trans. Cambr.
Phil. Soc.
8(9), 287-319.
Terzaghi K. 1943.
Theoretical soil mechanics
. New York: Wiley.
Tsuji Y., Kawaguchi T. and Tanaka T. 1993. Discrete particle
simulation of two-dimensional fluidized bed.
Powder Technology
77, 79-87.
Zhao J.D. and Shan T. 2012a. Coupled CFD-DEM simulation of fluid-
particle interaction in geomechanics.
Powder Technology
, under
review.
Zhao J.D. and Shan T. 2012b. Numerical modelling of fluid-particle
interaction in granular media.
Theoretical and Applied Mechanics
Letters
. In press.
Zhao J.D. and Shan T. 2013. Discrete modeling of fluid-particle
interaction in soils. In Yang Q., Zhang J.M., Zheng H. & Yao Y.P.
(eds)
Constitutive Modeling of Geomaterials: Advances and New
Application, Proceedings of the Second International Symposium
on Constitutive Modeling of Geomaterials
(15-16 Oct 2012,
Beijing, China). Springer, pp. 297-301.
Figure 4. Profile of normalized vertical pressure at the base of sand piles
for both the dry and the wet cases.
Zhu H.P., Zhou Z.Y., Yang R.Y. and Yu A.B. 2007. Discrete particle
simulation of particulate systems: theoretical developments.
Chemical Engineering Science
62, 3378-3396.


