475
Technical Committee 102 /
Comité technique 102
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
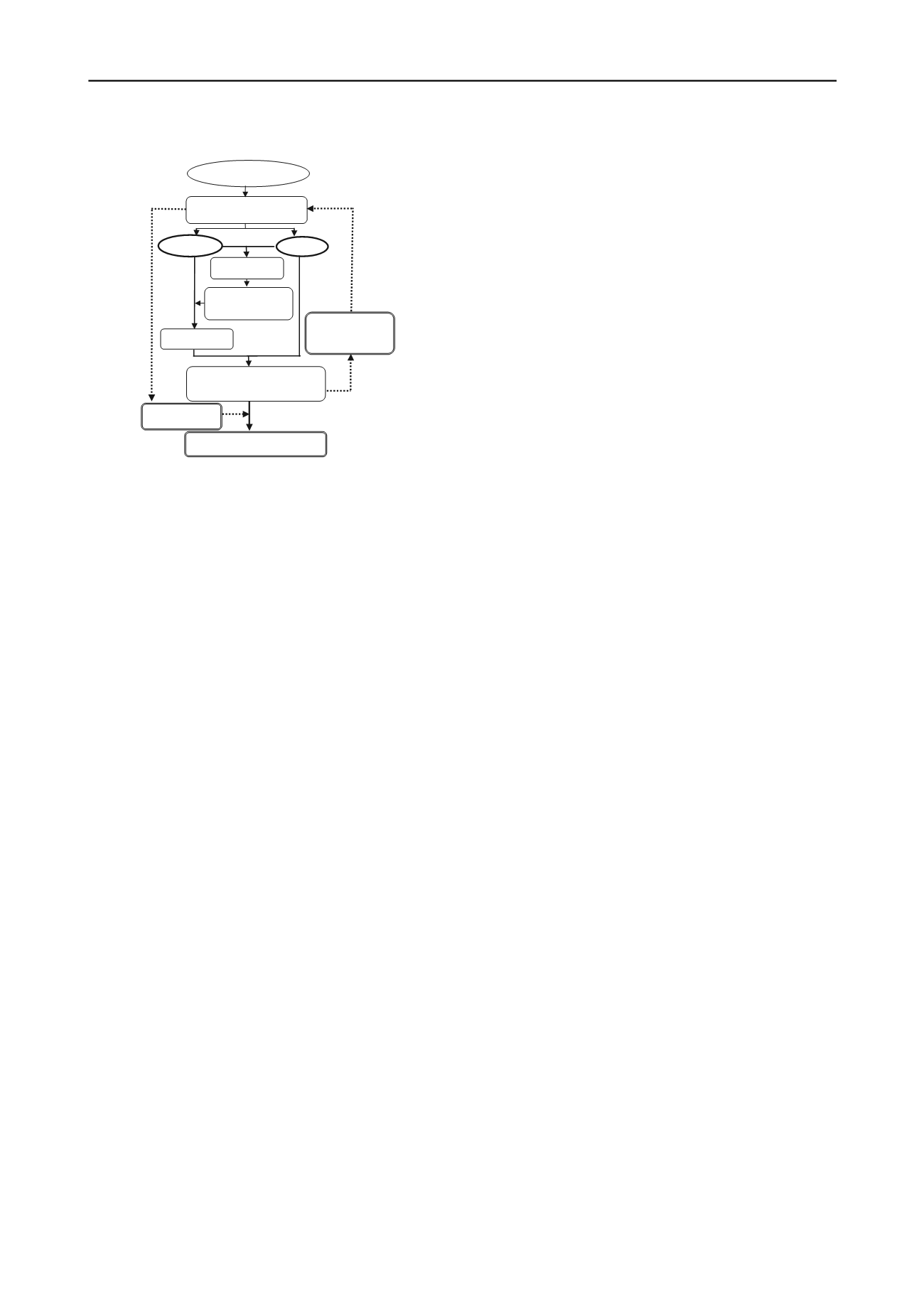
Design of foundation
Assessments based on
Geotechnical considerations
Investigation
design
Select of possible
models
Decision of sort and
number of field & lab.
tests
Modeling of ground
• Careful selection of soil parameters
• Determination of adequate model
Reconsideration of
safety factors et al.
Implementation of rational and
Economical design in total
Verification by
site investigations
• Full scale load tests
• Field observations
(
Collaboration
)
Implementation of
site investigation
(
Feedback
)
(
Reassessment
)
Figure 8. Collaboration of geotechnical investigations with design
(
Yasufuku et al
).
Amoroso’s et al.
paper presents a case history emphasizing
the use of the seismic dilatometer (SDMT) as a powerful site
investigation tool on the restoration design of an historical
building which was damaged by the 2009 L’Aquila earthquake.
The investigation of the foundation also included boreholes and
laboratory cyclic simple shear tests. The paper presented the
interpretation of SDMT for determination of soil profiling,
shear wave velocity, constrained modulus and horizontal stress
index, which when, combined with lab data, allowed a better
understanding of the building’s response during the earthquake.
4.2. Field condition and/or site performance
Haza-Rozier et al.
study the behavior of a soil foundation
improved by rigid columns to support wind turbines. This
foundation was fixed on a rigid slab, lying on a granular layer,
improved by 84 rigid columns. The authors monitored the
structure behavior during excavation, machine construction, and
over a period of time for the working service of the wind
turbine. They observed that the working platform induced an
important confinement of the columns’ heads with subsequent
small levels of displacement.
Svinkin’s
paper discusses the controversial and
contradictory evaluations of ground vibrations from pile driving
theories. He pointed out that pile driving is a powerful and
wide-spread source of construction vibrations which may
detrimentally affect adjacent or remote structures. The paper
thus presented several issues in the assessment of ground
vibrations generated by pile driving.
The paper from
Matešić et al.
presents a case history with
the use of hydro test results for designing steel tanks on
improved ground with 660 stone columns. The authors
described the conducted hydro tests as part of a technical
monitoring assessment from all elements of the tank structure.
The paper presents and discusses all experimental data and
states that they could be wisely used to improve the tank design.
Jeon and Mimura
present elasto-viscoplastic FEM analyses
to assess the long-term deformation of a reclaimed island over a
Pleistocene foundation from the adjacent construction of an
offshore (twin) airport. It is a numerical modeling paper where
simulation was compared to instrumentation results. The
authors introduced the concept of “mass permeability” to model
the excess pore water pressure dissipation and concluded that it
functioned well to assess the long-term deformation of the
foundation, including the interactive construction behavior.
Chou´s et al.
paper discusses survey results of damaged
areas after a flood disaster caused by the 2009 Morakot
Typhoon in Taiwan. A comprehensive site survey was
conducted after the flood disaster and ten failure mechanisms
were identified depending on the different geological
environments. The paper presented the site survey observations,
analyzed the causes and mechanisms of failures, and drafted
strategies and suggestions for the restoration projects.
The paper from
Lin et al.
uses a multi-scale sediment
monitoring device to assess the remediation effectiveness on a
watershed reservoir after sedimentation processes were
originated by the same typhoon cited on
Chou et al
. It is stated
that it caused unprecedented landslide and sediment-related
disasters in mountain areas of the Tsengwen reservoir
watershed, drastically reducing its storage capacity. Hence, the
paper describes the method and how to systematically study and
analyze soil erosion and landslide areas with the aid of sediment
accumulation trapping dams and aforementioned device.
Al-Saudi et al.
is another paper that deals with a non-text
book type geomaterial: gypseous soils, another “problematic”
soil given its intrinsic characteristics. According to the authors,
it covers about 20 to 30 % of total Iraq area. An important
characteristic of this soil is the collapsibility, a sudden and large
volumetric strain when exposed to water. Proposals for soil
treatment are presented, focusing on the control of settlement by
reducing or even preventing humidity changes within the soil
foundation.
Shulyatiev´s et al.
paper presents a case study related to the
construction of the Okhta-center high-rise tower in St.
Petersburg. Static load tests on real scale barrette pile types
were carried out to adjust the design soil parameters. The paper
also presents a comparison between the derived bearing
capacity values and those from Russian and foreign building
codes. The authors concluded that pile tests are an effective way
to calibrate design parameters for usage in real case designs.
The paper from
Chen et al.
presents a generalized
(dimensional analysis type) solution to be used into
underground geological-mechanical interaction excavation
problems. The model groups the geological characteristics into
three categories: brittle (rock-like), ductile (soil-like), and
brittle-ductile (gravel-like), with respect to thrust and force
cuttings. Two case histories are presented to validate the
approach to assess the efficiency of a tunnel cutting machine.
Bellato´s et al.
paper presents a case study to discuss the
quality control of Cutter Soil Mixing (CSM), i.e., a relatively
new deep mixing method suitable for various types of ground
improvement. The materials and the testing program were
described in the paper. The obtained results under an innovative
experimental apparatus underline the influence of the physical,
and chemical, characteristics of the natural soil on the strength
gain of the stabilized materials.
5. SOIL AND ROCK PROPERTIES
In this Conference Session, fifteen papers were selected to be
part of this main topic where seven of them presented new
theoretical advances as a major subtopic and eight dealt with the
evaluation of geotechnical parameters.
5.1. New theoretical advances
The paper from
Baud et al.
discusses stress-strain hyperbolic
curves obtained with a self-boring Ménard PMT test. The
authors determined E-moduli values by assimilating the
pressure-volume plot of a Ménard PMT to a 2
nd
degree
hyperbolic arc. The self-boring Ménard PMT tests were carried
out using a self-bored steel slotted tube implemented either by
the STAF
®
technique, or by the ROTOSTAF
®
method. The
authors derived the hyperbolic best fit of the plotted readings to
obtain an original equation of the radial borehole expansion, ε =
f(G
0
, p
o
, p
LM
, P
L
). After that, they derived the tangent modulus
G
t
for each reading and the corresponding G
t
/G
0
ratio as a


