474
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
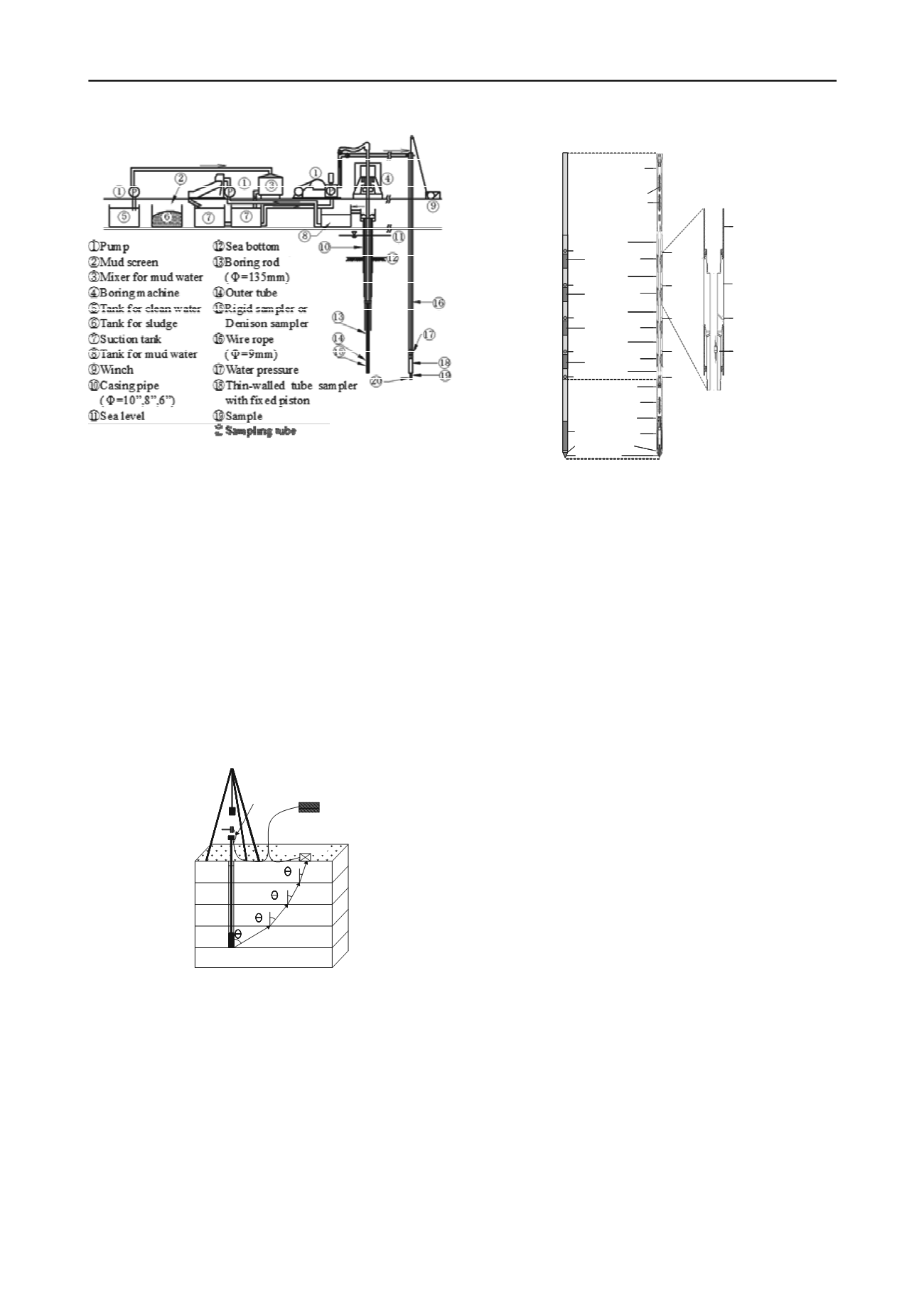
Figure 5. The
Koken wire line
sampling system
(Rito & Emura)
.
The paper from
Kayser et al
describes an approach to assess
soil scour potential through the use of the In-Situ Erosion
Evaluation Probe (ISEEP), which is advanced by water jetting.
Soil erosion parameters were assessed for silty sand in terms of
a critical stream power (critical shear stress and detachment rate
coefficient). Scour depths around a circular bridge pier were
also computed using ISEEP data, and compared with an
empirical approach available in literature.
Giacheti et al
briefly describes a test which associates the
up-hole technique to the SPT, the “seismic SPT” (Figure 6).
This hybrid test allows the determination of the maximum shear
modulus (G
0
) together with the N value in a unique test. The
paper also presents and discusses cross-hole, down-hole, SCPT
and SPT test data for a Brazilian tropical sandy soil to
emphasize the advantage of using the interrelationship between
the small strain stiffness (Go) and the ultimate strength (N
value) to identify and characterize different soil behaviors.
Case with
geophones
H1
H2
H3
Hi
DAQ
System
Manual SPT Equipment
Trigger &
Anvil
L1
L2
L3
Li
1
2
3
i
Figure 6. S-SPT test and a seismic refracted path (
Giacheti et al
).
Frost & Martinez
enhances the well-established cone
penetration test with an extra multi-sleeve penetration
attachment (Figure 7). The new CPT probe incorporates a series
of friction sleeves with varying surface textures and a torsional
load sensing capabilities along with a series of pore pressure
sensors, in addition to the standard smooth friction sleeve and
pore pressure sensor located behind the tip. They advocate that
the multiple measurements made with this device allow it to
provide a new insight into the characterization of soil types,
besides of establishing relations between stratigraphic variations
and in-situ shear strength with the texture height of the sleeves.
The authors really consider that the multi-sleeve technology
CPT offers significant benefits over other devices to measure
the mechanical response of soils.
f
s
f
a1
u
2
f
a2
f
a3
f
a4
Attachment
Digital
Housing
Digital Housing
u
a1
u
a0
u
a4
u
a3
u
a2
q
c
Friction Sleeve
Pore Pressure
Tip Load
Dual Axis
Inclinometer
Digital
Board
Attachment
Digital
Boards
Friction
Sleeve
Friction
Sleeve
Friction
Sleeve
Friction
Sleeve
Mandrel
Mandrel
Mandrel
Mandrel
Mandrel
Piezo
Sensor
Piezo
Sensor
Piezo
Sensor
Piezo
Sensor
Piezo
Sensor
Attachment
Sleeve
Mandrel
Replaceable
Attachment
Friction
Sleeve
Attachment
Individual
Load Cell
Attachment
Individual
Piezo Sensor
(0.67)
(0.81)
(0.88)
(1.07)
(1.14)
(1.33)
(1.40)
(1.59)
(1.66)
Figure 7. The multi-piezo-sleeve friction penetrometer along with a
standard CPT probe (
Frost & Martinez)
.
Monet
presents a new in-situ testing device called the
“Geomechameter”, i.e. an evolution of the pressuremeter. This
new device uses the forces generated by water flow around the
probe. The hydraulic flow allows the control of the level of
vertical stress at the test depth. The influence of this stress is
hence taken into account in the test interpretation. The new
probe can also evaluate the soil permeability and sensibility to
erosion. It was validated by direct comparison with mechanical
properties from triaxial tests and permeability values from
Lefranc type injection tests.
4. GEOTECHNICAL ANALYSIS AND BEHAVIOR
Fourteen papers in this Conference Session were grouped in the
topic of geotechnical analysis and behavior; four of them dealt
with design improvement and the other ten addressed field
conditions and/or site performance.
4.1. Design improvement
The paper from
Yasufuku et al.
emphasizes the importance of
integrating the geotechnical investigations with pile foundation
design. Figure 8 shows the policy and concept of geotechnical
investigation & design for the studied case, i.e. the construction
of the connecting bridge for New-Kitakyushu airport. A rational
method for evaluating the pile bearing capacity was presented
which reflected the soil characteristic values and the geological
environmental history. They concluded that field and laboratory
investigations with a reasonable geotechnical consideration
sharply decreased the total cost of the bridge in the studied case.
The paper from
Cao et al.
studied the performance of a deep
excavation in downtown Toronto. They presented field
measurements of soldier pile walls installed into clayey soils
and shaly rock. The authors assessed the method of deducing
wall bending moments from inclinometer measurements, among
other aspects. The paper provides recommendations for such
walls when designed in similar geotechnical conditions.
The paper from
Hokmabadi et al.
studies the seismic
response of superstructures on soft soils. Shaking table tests and
three dimensional numerical simulations using FLAC3D were
carried out to investigate the influence of the soil-pile-structure
interaction on the seismic response of a 15-storey moment
resisting building, supported by end-bearing pile foundations.
The authors observed a good agreement between the numerical
predictions and the experimental data confirming the reliability
of the numerical approach.


