3004
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
0
1
10
100
0,1
1
10
100
PV*
SO
4
2-
(g/l)
K2SO4 H2SO4
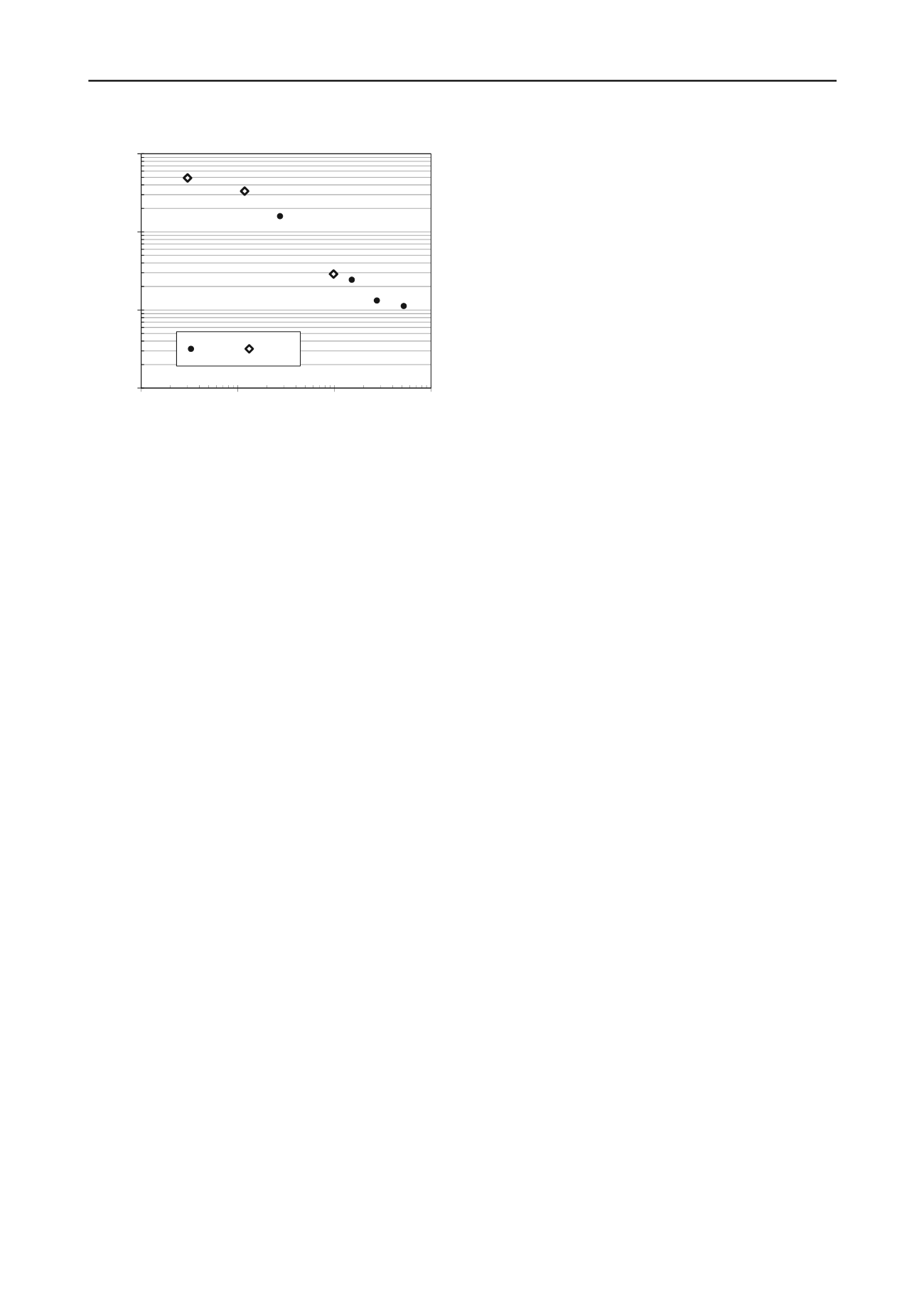
Figure 3. Critical number of pore volumes, PV*, as a function of the
SO
4
2-
concentration in sulphuric acid and potassium sulphate solutions.
4 CONCLUSIONS
On the basis of the available results it is possible to state that
aqueous solutions of H
2
SO
4
and K
2
SO
4
may adversely affect the
hydraulic performance of CB mixture depending on SO
4
2-
concentration and pH. At concentration of the order of g/l or
more, both solutions produce an initial decrease in the k value,
followed by an increase and finally an almost constant trend of
hydraulic conductivity with curing time. Swelling and a dense
net of fixtures were detected on the samples after permeation
mainly due to ettringite formation, both in samples permeated
with the acidic and saline solutions.
The number of pore volumes of flow at which the change in the
k trend occurs is greater the higher the SO
4
2-
concentration. The
PV at which this change of trend occurs (PV*) does not seem to
be affected by the pH when SO
4
2-
concentration exceeds 1 g/l.
A correlation between PV* and SO
4
2-
concentration was found
that can be useful from the practical point of view to estimate a
cut-off wall durability on the basis of the expected flow rate
through it. This criterion is on the safe side because it is based
on the PV related to the requirement of decreasing k with time:
a constant or increasing k with time does not necessarily imply
a bad performance, at least immediately. Moreover, the
chemical conditions adopted in the tests are not expected to
occur continuously in the field if a pumping system is provided
so that there is an advective flow of groundwater and not of
pollutant across the barrier.
5 REFERENCES
Bensted J. 1995. The standardisation of sulphate-resisting cements. Part
I + Part II. World Cement, Vol. 7 and 8.
Brianzoni V. 2012. Factors affecting the hydraulic performance of
plastic cut-off walls for confinement of polluted sites. Ph.D. Thesis,
Università Politecnica delle Marche (in Italian).
Fratalocchi E., Giorgini S. and Pasqualini E. 2010. Migration of
sulphate solutions through cement-bentonite diaphragms. Proc.VI Int.
Congress on Envir. Geotech., NewDelhi, India.
Fratalocchi E., Pasqualini E., Balboni P. and Mozzi R. 2005. Durability
assessment of the confinement cut-off wall for a phosphogypsum
landfill. Proc. 16
th
ICSMGE, Osaka, Japan.
Gollop R.S. and Taylor H.F.W. 1992 Microstructural and
microanalytical studies of sulphate attack. I. Ordinary Portland
cement paste. Cement & Concrete Research, 22 (6), 1027-1038.
Gollop R.S. and Taylor H.F.W. 1995. Microstructural and
microanalytical studies of sulphate attack. III. Sulphate-resisting
Portland cement: reactions with sodium and magnesium sulphate
solutions. Cement & Concrete Research, 25 (7), 1581-1590.
Jefferis S.A. 1992. Contaminant-grout interaction. Proceedings of the
Specialty Conference on Grouting, Soil Improvement and
Geosynthetics, New Orleans, 1393-1402.
Jefferis S.A. 2003. Long term performance of grouts and the effects of
grout by-products. Proc. 3
rd
International Conference on Grouting &
Ground Treatments, New Orleans, ASCE Geotechnical Special
Publication, No. 120.
Jefferis S.A. and Fernandez A. 2000. Spanish dyke failure leads to
developments in cut-off wall design. Proc. Int. Conference on
Geotechnical and Geological Engineering, Melbourne, Australia.
Manassero M., Fratalocchi E., Pasqualini E., Spanna C., Verga F. 1995.
Containment with Vertical Cutoff Walls, ASCE Geotechnical Special
Publication No. 46, 1142-1172.


