2479
Technical Committee 211 /
Comité technique 211
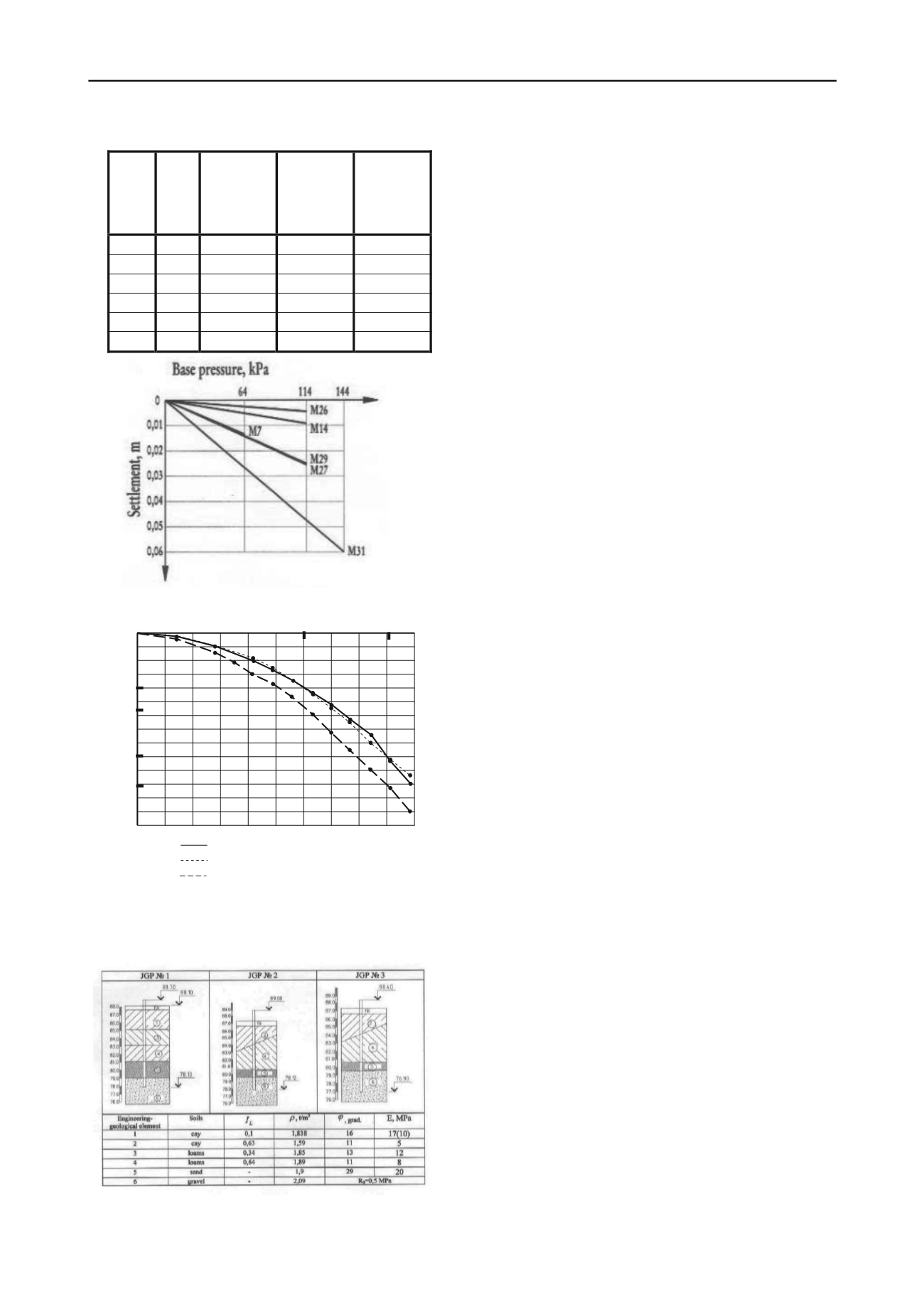
Table 2
Mark
number
(fig.1)
Foundat
ion type
Settlement
before
construction
restart, mm
Base pressure
before
construction
restart, kH/m
2
Coefficient
of subgrade
reaction,
kH/m
3
М7
post
13,5
64
4700
М14
strip
9,3
114
12200
М26
strip
5,4
114
20000
М27
strip
25,5
114
4400
М29
strip
25,0
114
4500
М31
post
60,0
144
2400
Fig.3. Diagrams of field investigations
a – base pressure-settlement of post- and strip foundations; b– load-
settlement of test piles
Table 3
425 mm diameter and 10…11 m length jet grouted piles were
deepened into gravel soil to the depth of 1 m and more. To
evaluate the pile design load, the pile vertical load test of trial
piles with the diameter 425 mm, 10,6 m length (pile No. 1),
10,88 m length (pile No. 2) and 11,5 length (pile No. 3) (table
3) have been carried out. The piling was realized with the unit
SBU 100 GA50.The engineering-geological characteristics of
soils are presented in table 3.
Pile vertical load tests have been carried out according to
standard method. The limit resistances while testing reached
980 kH. Figure 3 presents diagrams of pile tests.
Considering different structural concepts of the foundations and
the building, analysis have been carried out according to these
features and four types of the foundations strengthening have
been suggested (see figures 1 and 4).
I. Strengthening of
post foundations
of a building in axes 15’ –
1. Practically all extra load is taken into account to be
transferred to jet grouted piles, i.e. the load is not transferred to
post foundation, as the construction of the reinforced concrete
raft strengthening is not absolutely stiff.
That’s why only insignificant part of the extra load is
transferred to the foundation base, so the foundation in
combination with the strengthening construction and piles
behaves as combined piled foundation.
II. Strengthening of
strip foundations without piles
by means of
geometrical dimensions increase with use of technology
“HILTI”.
III. Strengthening of
pile group foundations
with increased
loads was carried out by means of jet grouted piling around the
raft and including them into pile group behavior through the
reinforced concrete slab fixed with the column and the raft (with
the anchors HILTI). With such method of strengthening jet
grouted piles start to work in a pile group together with the
driven piles.
0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 Р,kН
0,001
0,003
0,004
0,005
0,006
0,007
0,008
0,009
0,010
0,011
S,m
0,012
0,013
S=f(P)
(test Nо.1)
(test Nо.3)
(test Nо.2)
N
1
N
2
S
1
(3,2)
S
1
(1)
S
2
(3,2)
S
2
(1)
0,002
IV. Strengthening of
foundations
without piles
in axes 1 – 29
was carried out by means of insignificant part of load transfer to
the foundation. Jet grouted piling use is based on insufficient
reinforcing with in situ reinforced concrete strip under the
columns, the load of which is more than twice increased
compared to design one. Such strengthening construction
partially loads the existing foundation including it into work.
The jet grouted piles together with the foundation accept the
ultimate design load. Pile strengthening is carried out along the
whole length of the strips, as otherwise the different stiffness of
the strip base will lead to its deterioration.
Irrespective of strengthening type, the main design requirement
is continuation of foundations loading only after completion of
all works on strengthening considering the terms of strength
increase of in-situ concrete of structures.
4 THE MAIN DESIGN PRINCIPLES
Analysis of foundation strengthening has been carried out
considering the deformability of the foundation base and jet
grouted piles. Due to special features of constructions of the
foundations under strengthening and different extent of works
completion on above foundations structures construction, the
following design assumptions were taken.
While the building
post foundations
strengthening in axes
1’…15’, analyses of loads transferred to the foundation after its
strengthening were carried out i.e. when construction restarting
considering the loads after the building starting (fig.5). Analysis
of the column joint and strengthening construction was done for
the total design load. Deformability indices of the foundation
base and jet grouted piles quantitatively evaluated with the
coefficients of subgrade reaction of the foundation base under
strengthening and pile stiffness respectively, were determined


