1332
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
with sheetpile and supplementary reinforcement combined with
ground anchors provide FS = 1.3.
3.3.2 Secant pile walls
-0.50
-0.45
-0.40
-0.35
-0.30
-0.25
-0.20
-0.15
-0.10
-0.05
0.00
0
50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 550 600
Settlement (m)
Days
Another strengthening method is by installing secant pile walls
with diameter 0.8 m (see Table 2) to a depth of 25 m from the
surface of the existing road. The results of stability analysis
provides FS = 1.65. The improvement of vertical geometry was
also considered in this analysis. There are two raising level
modeled in the models which are raising 0.7m consisting of ±
0.25 m selected material, ± 0.15 m subbase foundation and ±
0.3 m concrete pavement; and raising 1.2m consisting of 1m
raising using lightweight material (see Table 5) and 0.2m
asphalt. The FS of the road which strengthened by secant pile
walls combined with raising 0.70 m and 1.20 m are 1.31 and
1.37, respectively.
Settlement at point A, raising 1.2m using selected material
Settlement at point B, raising 1.2m using selected material
Settlement at point C, raising 1.2m using selected material
Settlement at point A, raising 0.7 m using lightweight material
Settlement at point B, raising 0.7 m using lightweight material
Settlement at point C, raising 0.7 m using lightweight material
Table 5. Design parameter of raising material
Element
Type
E
(
kN/m
2
)
c’
(
kN/m
2
)
’ (deg)
n
Lightweight
Non-
porous 3.0x10
4
50
45
0.15
Settlement analysis were performed at some points over the
pavement surface for all raising cases, i.e. at road centerline, at
the middle and the edge of the road directions to Tanjung Priok,
respectively. The result of settlement analysis can be seen in
Table 6.
Table 6. Predicted settlement value at Sta. 3+750.
Settlement
Raising 0.7
m
Raising 1.2 m
Center line
1.24 m
0.79 m
Middle
1.29 m
0.67 m
Edge
1.30 m
0.51 m
3.4 Zone 4: STA 6+497 - STA 7+333
The condition of this zone is similiar to that of in Zone 2 where
is very vulnerable to both submerged from overflow of Japat
River and from the surrounding environment, so raising works
should be considered to be implemented. Analysis of proposed
design in this zone is based on the road cross-section at
approximately Sta. 7+000.
Design parameters such as the friction angle, modulus of
elasticity obtained by correlating the CPT #13 on shore and
CPT #37 off shore and evaluation of laboratory tests on
undisturbed soil samples in BH13 at Sta. 7+000.
Based on analysis result, the existing road remains relative
stable with FS = 1.95. Eventhough the road seems to be stable, a
potential problem in this zone is flood. There are two raising
level modeled in the models which are raising 0.7m consisting
of ± 0.5 m selected material, and ± 0.2 m concrete pavement;
and raising 1.2 m consisting of ± 1m selected material and 0.2m
asphalt.
The results of stability analysis shows that the road is
relatively stable at the time of the raising 0.7 m and 1.2 m, with
FS = 1.54 and FS = 1.37, respectively. If lightweight material is
used to replace selected material in both raising 0.7 m and 1.2
m, FS = 1.93 and FS = 1.56.
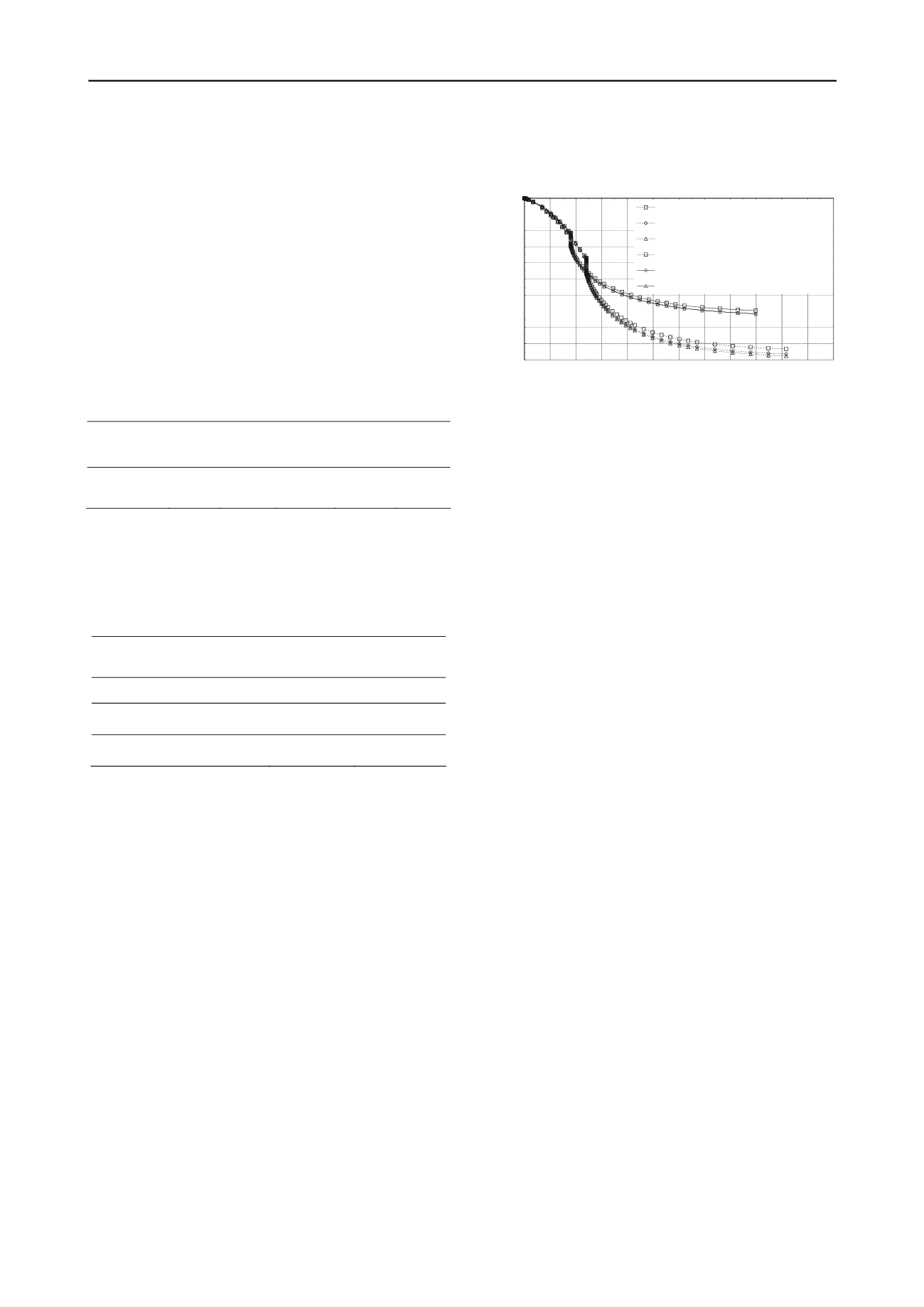
The results of settlement analysis show that the predicted
settlement of point A at the center line of the road after raising
0.7 m and 1.2 m using selected material are 0.35 m and 0.47 m
within 449 days and 508 days, respectively. If lightweight
material is used in raising, the predicted settlement will be
0.27 m and 0.31 m within 420 days and 452 days, respectively
(see Fig. 4).
Figure 4. Time – settlement curve of raising using selected material and
lightweight material at point A, B and C at Sta. 7+000
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the observations of field conditions, soil test results,
evaluation of the existing condition of the road, and analysis
result, performance of road embankments over North Jakarta-
soft soil can be summarized as follows :
1. To fulfil stability and settlement analysis, the road at Zone
1, and 3 should be strengthened by secant pile walls
combined with raising 0.7 m and in some places raising 1.2
m should be implemented. If this strengthening method is
applied at Zone 1 and Zone 3, FS is 1.67 and 1.31-1.37,
respectively.
2. To fulfil stability and settlement analysis, the road at Zone 2
should be strengthened by concrete sheet piles and ground
anchor. If this strengthening method is applied, FS is 1.55.
3. Although the results of the analysis of the stability of the
existing road at Zone 4 shows that the road is still in a stable
condition, a potential problem in this zone is flood.
Therefore, raising 0.7 m and in some places raising 1.2 m
should be implemented. If this strengthening method is
applied, FS is 1.31-1.37.
5 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors very gratefully acknowledge to Mr. Bambang
Hartadi, Chief of Sub Directorate of Freeways and Urban Road,
for giving all data used in this paper.
6 REFERENCES
Rahadian H., Hendarto and Prasetya B. 2011. The failure of a road
embankment over north java soils.
Geotechnical Engineering for
Disaster Mitigation and Rehabilitation, Semarang.
Institute of Road Engineering, Ministry of Public Works. 2011. Laporan
evaluasi teknik Jalan RE. Martadinata
, Jakarta.


