1323
Technical Committee 202 /
Comité technique 202
3.3
California bearing ratio (CBR) Tests
The California Bearing Ratio (CBR) test is one of the most
widespread tests to determine strength and bearing capacity of
base, sub- base and subgrades for use in road, railway and
airfields pavements. To demonstrate the influence of lime-
microsilica additive on the bearing ratio of the silty soil, a series
of bearing ratio tests were carried out on stabilized and
unstabilized specimens. The tests were conducted according to
ASTM D 1883 – 99. The soil with different mixtures of lime
and microsilica were compacted in 6" modified proctor mold in
five layers by 56 blows in per layer at the soil optimum
moisture obtained from compaction tests. For curing the
samples, they were placed in constant moisture and temperature
for 28 days. To conduct the tests in soaked condition, they were
immersed in water for 96 hours under the 4.5 Kg (10 pound)
overload according to standard test method. The CBR tests were
carried out after 20 minutes to drain the samples. Meanwhile
swelling potential changes were measured during the soaking
time.
3.4
Wetting - drying tests
After performing the CBR tests, one mixture was chosen as a
desired sample from an economic and resistance viewpoint. To
evaluate the effect of wetting-drying cycles on strength of
selected sample, CBR tests were taken. The desired sample was
rebuilt three more times in the same previous condition on 6-
inch CBR molds. The samples were subjected to wetting-
drying cycles after 28-day curing time and required 96 hours for
soaking. The samples were placed in room to air-dry after
soaking for 24 hours. Then they were again submerged in water
for next 24 hours and thus to expose to one wetting-drying
cycle. This process was repeated 3 and 5 times for samples;
Then CBR tests were carried out on them.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1
Compaction tests
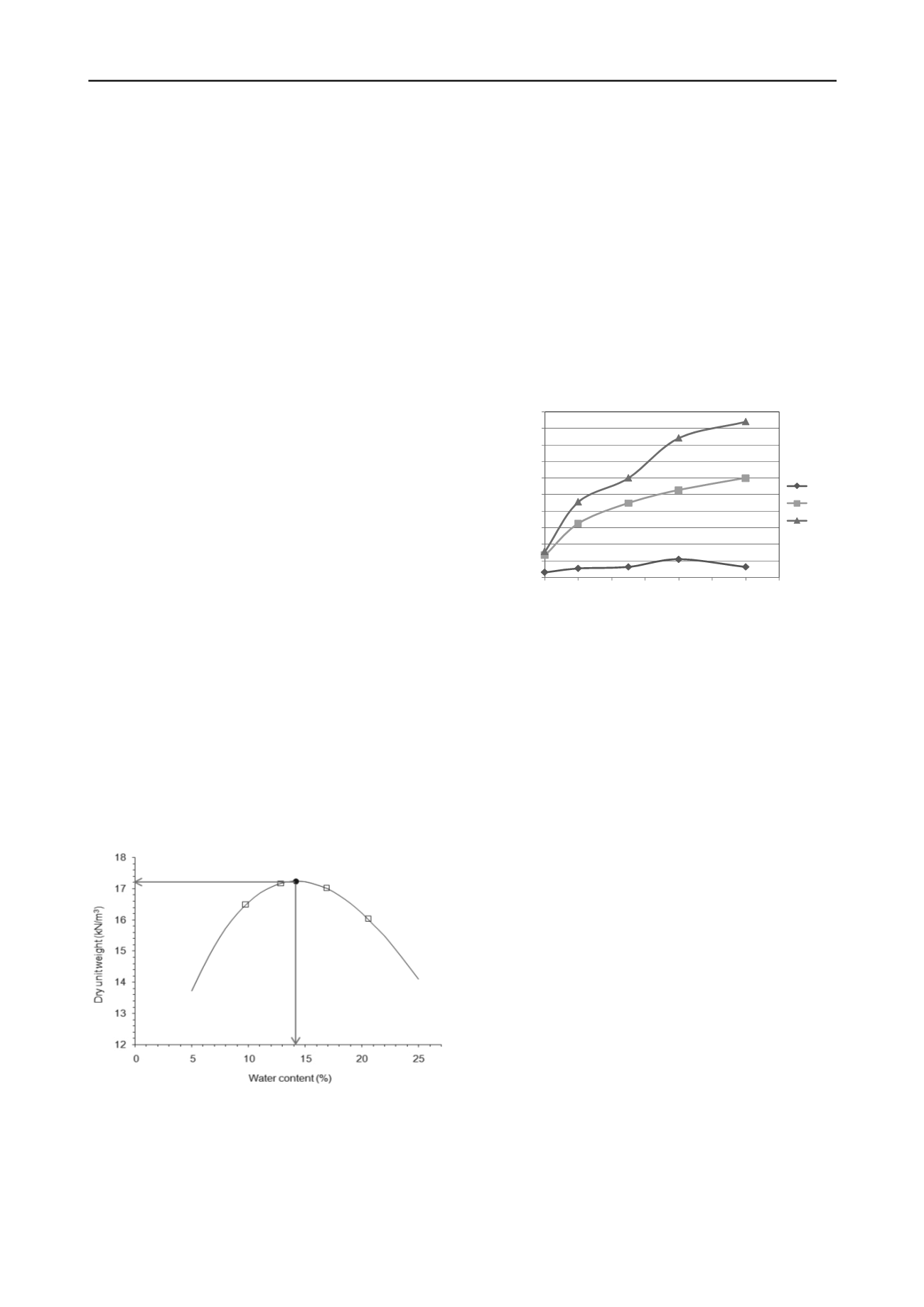
Compaction tests were carried out on the silty soil. The soil
optimum moisture and the soil maximum unit weight were
found to be 14.2% and 17.2 KN/m3 respectively. Compaction
tests results are drawn in Figure 2.
Figure 2. Compaction test curve
4.2
Effect of additives on the CBR
To compare the soil resistant with different amount of additive,
a series of samples were prepared in modified proctor mold.
The CBR tests were conducted in both stabilized and
unstabilized silty soils at the soil optimum moisture with
different amount of lime and microsilica. The CBR value of the
unstabilized soil was 4.8%. The effect of various amount of
additive on CBR values of samples are shown in Figure 3.
From Figure 3, it can be observed that in low amount of lime
(1 percent of dry soil) increase in microsilica amount up to 8%
causes increase in CBR values and then decrease but for 3% and
5% lime increase in microsilica amount causes increase in CBR
values. The maximum CBR value of the samples was occurred
in 5% lime and 12% microsilica. CBR value in this composition
was increased from 4.8% for unstablized soil to 470.8% for the
stabilized soil. So it is seen that up to 466% increase in CBR
value of stabilized soil in compare of unstabilized silty soil.
In addition, it is observed that the dry unit weights were
increased by adding the lime-microsilica additive to samples
and samples moistures were decreased by adding the lime-
microsilica additive to them in overall.
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
500
0
2
4
6
8
10 12 14
1% Lime
3% Lime
5% Lime
Microsilica Content (%)
CBR (%)
Figure 3. The effect of various amount of lime- microsilica additive on
CBR values of stabilized soil
4.3
Effect of additives on samples swelling
The samples swelling were measured during the 96-hour of
CBR samples soaking. There were seen swelling potential rate
were decreased reverse of strength. Unstabilized soil swelling
was 0.55mm and stabilized swelling samples were decreased up
to 0 mm.
4.4
Effect of wetting - drying cycles on samples CBR values
The sample stabilized with 3% lime and 2% microsilica was
chosen as the most desirable sample in terms of economy and
resistance and alternate wetting-drying cycles were conducted
on it. The result of wetting-drying cycles on CBR values of the
sample are given in Figure 4. It is observed that the CBR value
was increased after first wetting- drying cycle. Thereafter the
sample CBR starts to decrease gradually. The reason for
increasing CBR at first is assessed by decreasing in permeation
due to lime- silica fume stabilizer that 96 hours submerging was
not enough for required moisture for the reaction between lime,
silica fume and soil that noticed in introduction section. It is
noteable that the CBR rate after fifth cycle is still more than
initial CBR rate. Therefore wetting- drying cycle not only had
no negative effect on specimen strengths but also help to gain
the soil strength stabilized with lime- silica fume additive.


