1326
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
dry unit weight. Following compaction, the cylindrical
specimens were subsequently removed from the split mold
sampler, placed, isotropically consolidated and sheared in the
cyclic triaxial apparatus.
2.1
Testing Apparatus
The one-way compressive cyclic triaxial device supplied by
M/s. Geotechnical Instruments International Limited, Germany,
was used in this research. The apparatus is computer controlled
and has a provision for testing cylindrical soil specimens under
both drained and un-drained conditions, with programmed
deviatoric loading sequences and data acquisition rates at eight
readings per applied loading or stress cycles. The system
consists of a pneumatic stress-controlled actuator which is
capable of generating reasonable representation of multiple
cycles of compressive axial deviatoric stresses at multiple
applied loading frequencies between 0.1
Hz
and 10
Hz
(cycles
per second), with three types of built-in semi-sine, triangular,
and square waveforms defined by means of external input. The
vertical cyclic compressive deviatoric stresses could be applied
to the specimen via the top specimen cap connected to the
vertically movable frictionless shaft or loading piston going
through the plexi-glass triaxial pressure cell. The loading ram or
piston is directly connected to the actuator for application of
one-way cyclic compressive loading. A load transducer with a
capacity of 5 kN located below the bottom end platen, inside the
plexi-glass triaxial pressure cell was used to monitor and
measure the applied deviatoric stresses during testing. It is a
constant confining pressure triaxial set-up applying the
confining pressure with the use of pressurized air, which
remains the same during consolidation and shearing. A sensitive
Linear Variable Displacement Transducer (LVDT) of capacity
50 mm (resolution 0.01 mm) located outside of the triaxial
pressure cell was used to monitor and measure the low-
amplitude axial/vertical deformations of the specimen with high
accuracy during testing. The applied initial effective confining
pressure, back pressure, one-way compressive cyclic
deviatoric/axial load, development of axial deformations etc.
could be monitored using a built-in data acquisition system and
recorded in a notepad file during testing with a computer
connected to the device. The apparatus is supported by software
which enables the user to perform stress-controlled testing only.
A plexi-glass triaxial tank with full of de-aired water at the
bottom of the one-way cyclic triaxial test set-up was used to fill
the triaxial pressure cell when necessary and has the provision
of draining the water from the triaxial pressure cell by
gravitation after each testing
2.2
Testing Procedure
It was clear from the literature that, compositional and
environmental factors primarily influence the permanent
deformation characteristics of subgrade soil under one-way
induced traffic loading. In the field, presence of moisture plays
a vital role in either a road or railway pavement system and is
one of the most important environmental considerations for
strength and deformation behavior of material under cyclic
loading. The moisture content may vary during the life time of
the structure from the construction moisture content to full
saturation with the ingress of moisture with seasonal changes or
capillary action. Hence specimens were reconstituted to
different moisture contents giving different initial degree of
saturation. Three compaction moisture contents and dry density
conditions were selected for the study.
The applied level of confining pressure and deviatoric
stresses also affect the deformation characteristics of the
material under traffic loading. Hence, tests were conducted
under a range of initial effective confining pressure (
3
c
) of 15,
25, and 35 kPa, which is the range of stresses for embankment
of small height. All the remolded specimens were isotropically
consolidated under an initial effective confining pressure.
Following, samples were sheared cyclically under undrained
condition. Tests were performed with different deviatoric stress
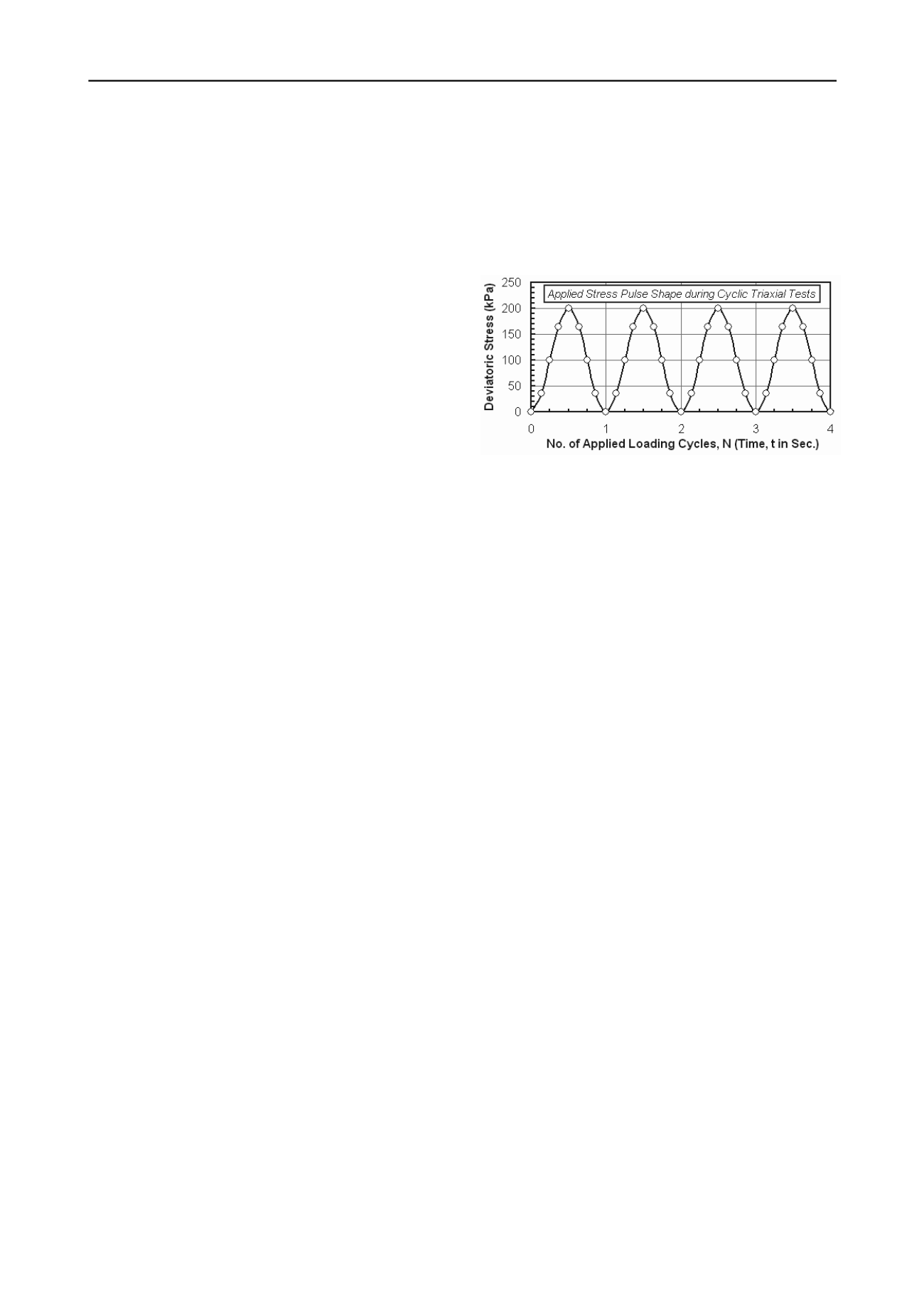
levels. Fig. 1 shows the typical sinusoidal semi-sine wave cyclic
load applied during the cyclic triaxial compression tests, with
corresponding response recorded using data acquisition system
during testing.
Figure 1. Typical sinusoidal semi-sine wave cyclic load form applied on
the specimen and the response received using data acquisition system
during the one-way cyclic triaxial compression tests
Each test was of constant-amplitude, consisted of cycling the
stress pulse at only one level of cyclic deviatoric stress varying
between zero and a preset value at a frequency of 1
Hz
. During
the tests, only a deviatoric stress (σ
d
) is applied cyclically while
the confining pressure (
3
c
) remains constant. Tests were
conducted on unsaturated or partially saturated specimens, i.e.
the degree of saturation (
S
r
) employed during reconstitution of
the sample was maintained same during the testing, without a
back pressure saturation. Few samples were reconstituted at
relative compaction dry unit weight equal to 95% giving degree
of saturation of 52.70% and the samples were partially saturated
by applying back pressure to obtain degree of saturation ranging
between 65 and 95% before shearing, to study the effect of
degree of saturation (post compaction) on the deformation
response of the material. Since during the application of cyclic
shear stress, the samples were not fully saturated, pore water
pressure was not measured during shearing. During the test, the
software presents the results in the form of a table in a note pad
file. The raw data was then transferred to an excel sheet and
plots of the desired quantities were obtained for the study.
The performance of road and railway pavements resting on
compacted material primarily depends upon the stiffness or
load-deformation characteristics of the material. Hence, in the
present study, during each one-way cyclic triaxial test, the total
and permanent deformations of the specimens were monitored
and recorded to calculate the plastic or permanent (
p
) and
resilient axial strains (
a
). The accumulation of permanent axial
strain with load cycles is presented in this paper. As the
development of permanent deformation in the specimen under
repeated loading is a gradual process during which each load
cycle contributes a small increment to the accumulation of
strain, all the tests were conducted up to the development of
sufficient permanent strain in each of the specimens tested.
During the test, as the stiffness of the material gradually
increases, causing a reduction in the development of permanent
deformation under subsequent repetitive loading, tests were
stopped after 10,000 applied load cycles.
3 TEST RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Permanent axial strain mainly depends on the intensity of
applied cyclic axial deviatoric stress and number of loading
cycles and generally used to study the deformation
characteristics of the compacted material. In this study, the
effects of various factors such as applied cyclic deviatoric


