1333
Retrofit Technique for Asphalt Concrete Pavements after seismic damage
Technique de réhabilitation pour chaussée en béton d'asphalte après dommage sismique
Ohta H.
Chuo University Research and Development Initiative
Ishigaki T.
NIPPO Corporation Research Institute
Tatta N.
Maeda Kosen Co.Ltd.
ABSTRACT: Reducing the risk of earthquake-induced damage to road is needed to promote safety and disaster mitigation and
recovery. It is strongly needed for pavement performance to keep the emergency traffic remain in service despite severe earthquake.
This paper presents a retrofit technique of asphalt pavements using Confined-Reinforced Earth (CRE) consisting of 1) compacted soil,
2) geosynthetics and 3) post-tensioning anchors. Confining by the anchors is the application of both compressive and confining force
to the compacted soil layers, and gives a pre-tensile force to geosynthetics. The high flexural rigidity of CRE is for overcoming
weakness of base course or subgrade in tension and flex/bending. In this paper, 1) structure of the retrofit technique of asphalt
pavements using CRE, 2) construction method, 3) the results of full scale in-situ tests are presented.
RÉSUMÉ : La réduction du risque de dommage routier induit par un tremblement de terre est nécessaire pour la sécurité,
l'atténuation de l’effet de la catastrophe et la remise en service. La performance du pavement pour permettre le trafic d'urgence qui
doit rester en service est visée. L’article présente une technique de rehabilitation des chaussées d’asphalte à l’aide d’un sol renforcé
confiné (CRE) par 1) un sol compacté, 2) géosynthétiques, et 3) post-pension d’ancrages. Les ancrages en acier rigide sont placés
verticalement du haut vers la couche de base et verrouillé à la base des géosynthétiques. Le confinement des sols compactés s’effectue
par l'application des deux forces (de compression axiale et latérale) qui applique une pré-tension aux géosynthétiques. La grande
rigidité à la flexion de CRE contre balance la faiblesse de la couche de base ou de la couche de fondation en traction et flexion.
L’article présente 1) la structure de chaussées, 2) la méthode de construction, et 3) les résultats des essais « in situ » pleine échelle.
KEYWORDS: pavement, earthquake, seismic retrofit, confined-reinforced earth, geosynthetics.
1 INTRODUCTION.
Reducing the risk of earthquake-induced damage to road is
strongly recquired to promote safety, disaster mitigation and
recovery. Road pavements which are adjacent to highway
structures such as bridges and culvert boxes are often damaged
due to the differential settlement of highway embankments
around bridge abutments, edge of culvert boxes and wing walls
during and after severe earthquakes. Traffic is easily intercepted
by the earthquake damage to road pavements. In one of the
precept of the Great East Japan earthquake (2011), to keep the
emergency traffic remain in service after severe earthquake is
the most important subject especially for emergency activity.
This paper presents a newly developed seismic retrofit
technique of asphalt concrete pavements using Confined-
Reinforced Earth (CRE). CRE is composed by compacted soil,
geosynthetics and post-tensioning rigid anchors. Confining by
the anchors is the application of both compressive and confining
force to the compacted soil layers, and gives a pre-tensile force
to geosynthetics.
The basic idea of implementing pre-stresses in reinforced
earth was advanced technology even from a gloval perspective
as follows (Uchimura et al. 1996, 2003, 2005). The high rigidity
of CRE is apparently useful in preventing excessive differential
settlement of the road pavement despite severe earthquake.
In this paper, 1) structure of the seismic retrofit technique of
asphalt pavements using CRE, 2) construction method, 3)
application of actual highway embankment, 4) the results of full
scale in-situ tests are presented.
2 STRUCTURE
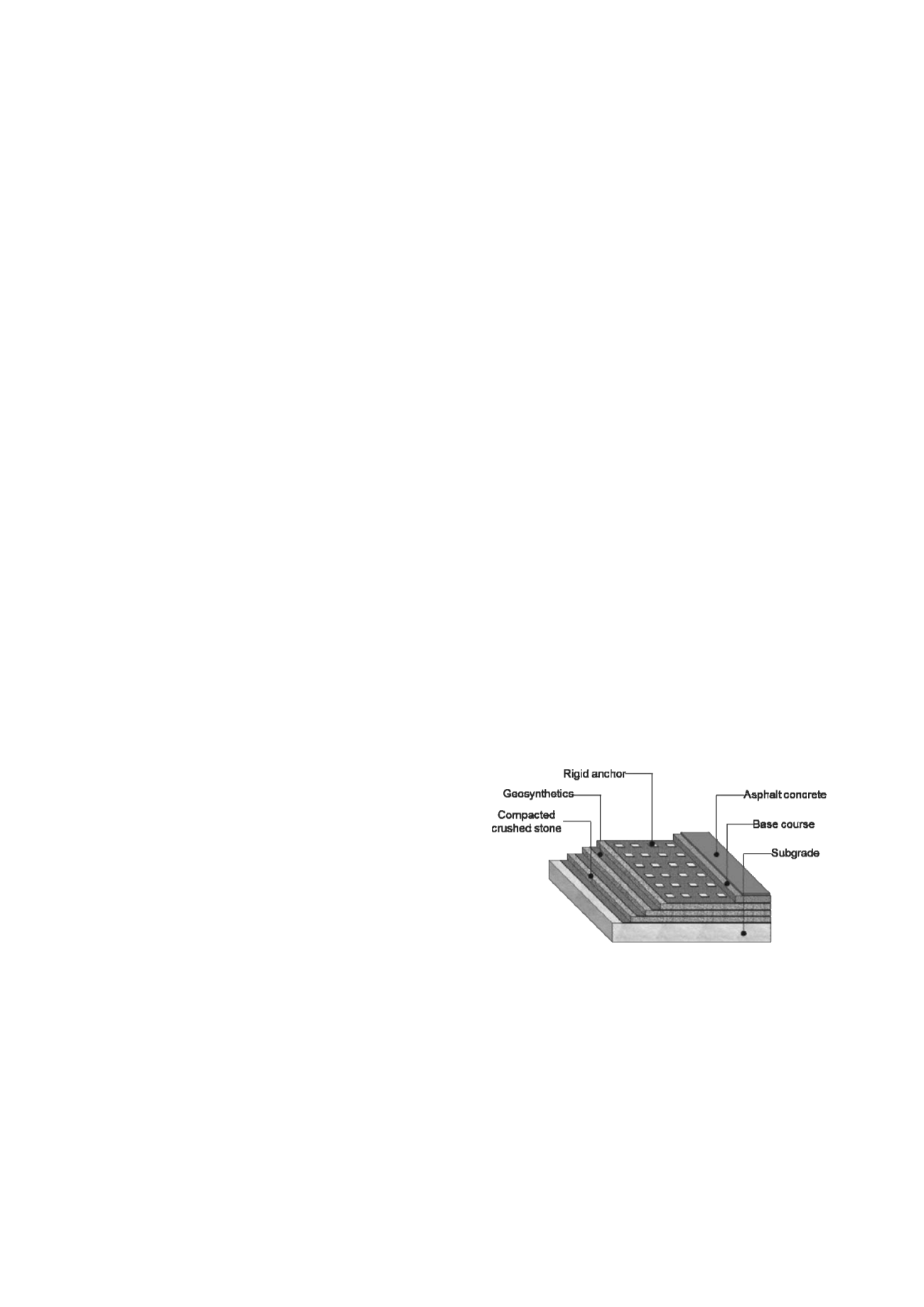
Figure 1 shows the structure of CRE applied to road subgrade of
asphalt concrete pavement. CRE is a composite structure
consisting of compacted crushed stone, geosynthetics and post-
tensioning anchors. The high flexural rigidity of CRE is for
overcoming weakness of base course or subgrade intension and
bending.
Figure 1. Structure of Confined-Reinforced Earth applied to asphalt
concrete pavement.
Compacted soil is a key material for use in CRE. Selection
of soil material is very important to keep the reinforced
performance of CRE. Crushed stone for mechanical
stabilization is the best material due to the high compression
and shear strength. High degree of compaction is also effective
to the reinforced effect of CRE. The crusshed stone layers are
sandwitched by four layers of geogrid and confined by
confining rigid steel anchors.
Photograph 1 (1) shows geosyntheyics used in this method.
The geosynthetics for use in CRE has high tensile strength of
200kN/m with low strain of 4.5%. The width of a sheet of
geosynthetics is maintain as same as road lane width.


