1614
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
5 CONCLUSION
After preparation
After cyclic loading
No preferential orientations of particle
long axes and contact normals
contact plane
contact normal
long axis
contact plane
contact normal
long axis
Preferential orientations of particle long
axes and contact normals
After preparation
After cyclic loading
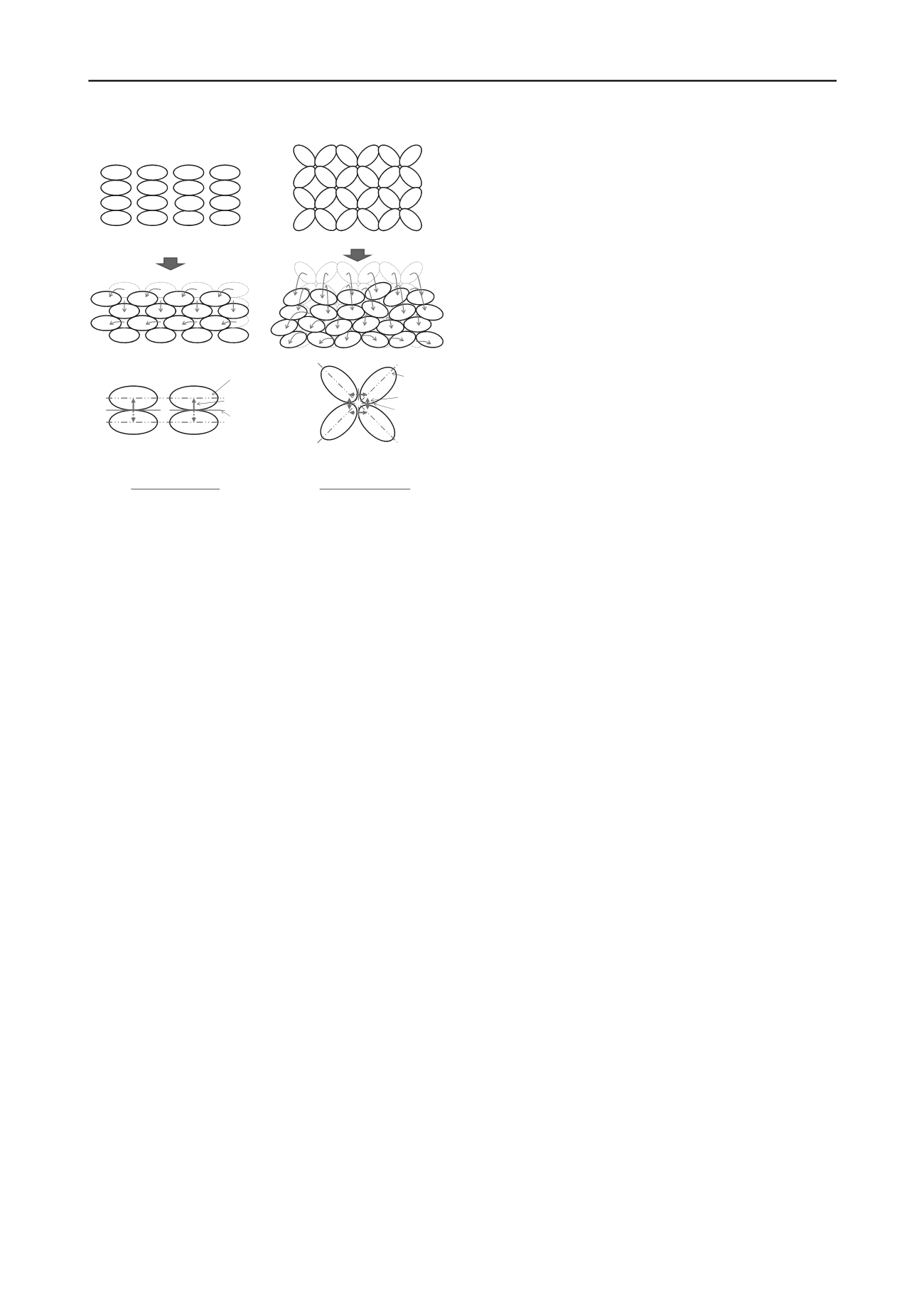
DD ASSEMBLY
MT ASSEMBLY
This experimental study offers crucial evidence on how initial
fabric affects the cyclic behavior of sand under distinctive initial
state and shear stress conditions. In the absence of initial static
shear (i.e. under symmetrical loading), loose sand always
exhibits a complete collapse behavior, featured by runaway
deformation by the triaxial specimens, irrespective of the fabric.
Dense sand, on the other hand, apart from performing the
classic cyclic mobility, it would undergo a phenomenon of
partial collapse if the fabric changes. In the laboratory, moist
tamped specimens are responsible for the former behavior while
the latter is featured by limited deformation by dry deposited
specimens. When an initial shear stress is present (i.e. under
unsymmetrical loading), the fabric effect is reversed. With a
change of initial fabric, loosely deposited specimens always
exhibit limited deformation whereas moist tamped ones
maintain the runaway failure. Dense sand is free from fabric
effect as it always behaves plastically under undrained cyclic
loading. The important practical implication is that apart from
accouting for the state and stress effect on design against cyclic
failure of soil, there is a need to incoporate a fabric parameter
into the design process.
Figure 6. Schematic illustration of DD assembly and MT assembly
before and after cyclic loading.
6 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
4.2
Observation 1: Occurrence of Limited Deformation
Shearing leads to fabric reconstruction which keeps increasing
the degree of anisotropy (Oda 1972b) as a result of particle
rearrangement. Assuming the ultimate anisotropy at failure of a
granular structure is fixed, the change of anisotropy in the MT
assembly is considered more significant than the DD one. It is
because the change in MT is from “isotropic” to “anisotropic”
but DD is from “anisotropic” to “more anisotropic”. Therefore,
the particle rearrangement involved in the process of changing
anisotropy is higher in the former. Correspondingly, more
substantial PWP build-up is resulted leading to complete
collapse of the structure. As shown in Figure 6, the DD
assembly apparently undergoes a lesser degree of collapse.
Macroscopically, it is reflected by an axial deformation in a
sudden but controlled manner. Right after the initial collapse,
particles repack and the stable configuration is reconstructed. It
thus leads to its subsequent post-collapse dilative stabilization.
The work was supported by the Research Grants Council of
Hong Kong (No. 719105) and by the University of Hong Kong
through the Seed Funding for Basic Research scheme (No.
10208227). This support is gratefully acknowledged.
7 REFERENCES
Casagrande, A. 1975. Liquefaction and cyclic deformation of sands, a
critical review.
Proc., 5th Pan-American Conf. on Soil Mech. and
Found. Engrg
., Buenos Aires, 5, 79-133.
Miura, S. and Toki, S. 1984. Anisotropy in mechanical properties and
its simulation of sands sampled from natural deposits.
Soils Found
.
24(3), 69-84.
Mulilis, J.P., Seed, H.B., Chan, C.K., Mitchell, J.K. and Arulanandan,
K. 1977. Effects of sample preparation on sand liquefaction.
Journal of Geotech. Engrg. Div
.,
ASCE
103 (GT2), 91-108.
Oda, M. 1972a. Initial fabrics and their relations to mechnical properties
of granular material.
Soils Found
. 12 (1), 17-35.
Oda, M. 1972b. The mechanism of fabric changes during compressional
deformation of sand.
Soils Found
. 12 (2), 1-18.
4.3
Observation 2: Distinctive Behavior under Differential
Initial State & Stress Conditions
The presence of preferential contact normal orientation gives
rise to the higher compressibility nature of DD specimen
especially when the major principal stress
1
is perpendicular to
the contact normal (Yamashita & Toki 1993, Oda et al. 2001).
Therefore, DD behavior is particularly contractive when
subjected to cyclic loading with stress reversal. It explains why
DD specimen exhibits collapse behavior even at a denser state
(D
rc
= 50%). But when initial shear presents such that the cyclic
loading becomes non-symmetrical, DD behavior becomes less
contractive due to the rotation of
1
away from its preferential
particle orientation. It is evidenced by the occurrence of plastic
strain accumulation in both DD and MT specimens (D
rc
= 35%)
at higher
level. On the other hand, D
rc
= 20% results in a
highly contractive state so both exhibit collapse behavior. Under
non-symmetrical loading condition, the occurrence of limited
deformation has been discussed above.
Oda, M., Kawamoto, K., Suzuki, K., Fujimori, H., and Sato, M. 2001.
Microstructural interpretation on reliquefaction of saturated
granular soils under cyclic loading.
Journal of Geotech. and Geoen.
Engrg
.,
ASCE
127 (5), 416-423.
Vaid, Y.P., Stedman, J.D. and Sivathayalan, S. 2001. Confining stress
and static shear effects in cyclic liquefaction.
Canadian Geotech.
Journal
38 (3), 580-591.
Yamashita, S., and Toki, S. 1993. Effects of fabric anisotropy of sand
on cyclic undrained triaxial and torsional strengths.
Soils Found
. 33
(3), 92-104.
Yang, J. and Sze, H.Y. 2011a. Cyclic behaviour and resistance of
saturated sand under non-symmetrical loading conditions.
Géotechnique
61 (1), 59-73.
Yang, J. and Sze, H.Y. 2011b Cyclic strength of sand under sustained
shear stress.
Journal of Geotech. and Geoen. Engrg
.,
ASCE
137
(12), 1275-1285.
Yang, Z.X., Li, X.S., and Yang, J. 2008. Quantifying and modelling
fabric anisotropy of granular soils.
Géotechnique
58 (4), 237-248.
4.4
Observation 3: Higher PWP Accumulation Rate
Due to the higher contractiveness of DD specimen, the higher
pace of PWP build-up as well as higher deformation rate
become understandable. It hence results in higher cyclic failure
potential usually observed with DD-induced fabric.


