1198
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
using the dynamic state moisture distribution model is shown in
Fig. 10.
5.2
Assumption of unsaturated hydraulic conductivity
5 MOISTURE DISTRIBUTION IN RESPONSE TO
HYDRAULIC PROPERTIES
5.1
Moisture characteristic curve
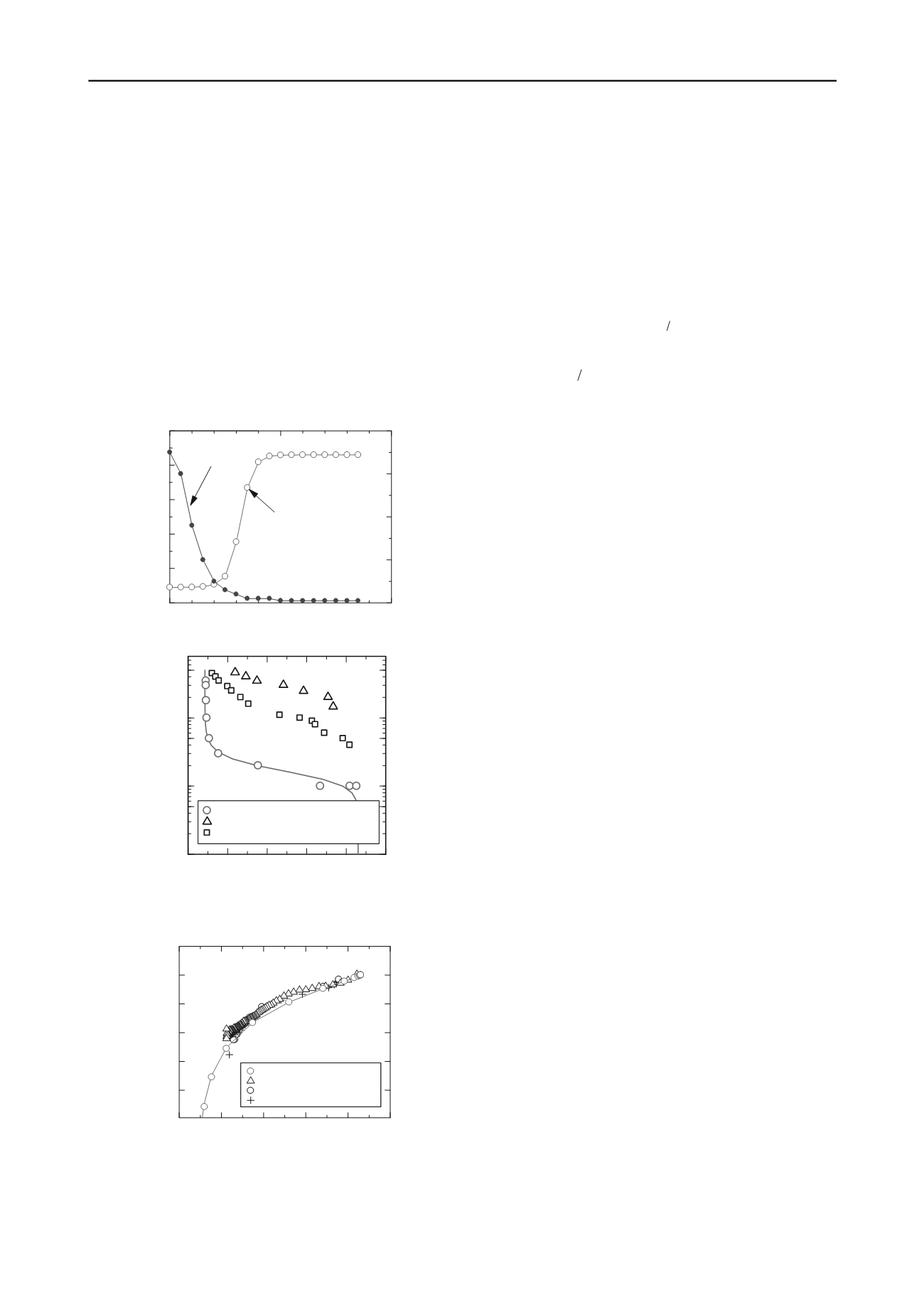
Fig. 11 shows the relationship between the water volume
presumed from the pressure head and moisture distribution
model for a depth of 50 mm, which is installing the tensiometer.
Moreover, what showed the relation of the moisture
characteristic from these is shown in Fig. 11. The moisture
characteristic curve obtained in the laboratory experiments for
reference is also shown in Fig. 12. Compared to the laboratory
experiments, the absolute value of the pressure head was low. In
order to carry out load of the water pressure of 100 mm to a
permeation surface with the start of test, the air below a
The parameters of the van Genuchten model can be estimated
by our moisture characteristic curve of Fig. 12. The unsaturated
hydraulic conductivity obtained using the Mualem model and
the estimated parameters is shown in Fig. 13. The result of the
proposed method was in agreement with other laboratory
experimental results. By using the van Genuchten and Mualem
models, since parameter n of the moisture characteristic curve is
used, as shown in an Eq.7, it is considered that the slope of the
moisture characteristic curve was evaluated correctly.
n n
nn
e
e
sat
unsat
S
S k
k
/11 )1 (
5.0
11
(7)
where,
r
s
s
e
S
,
k
unsat
is the hydraulic conductivity of
unsaturated soil,
k
sat
is the hydraulic conductivity of saturated
soil, and
n
is the parameter of the Genuchten and Mualem
model.
0
100
200
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0
10
20
30
40
Volumetric water content,
θ
Pressure head |h
p
|,
(cm)
Volmetric water content
(Estimated)
Pressure head
(Observed )
Elapsed time, t (sec)
6 CONCLUSIONS
The experimental results of the permeation tests and dynamic
state soil moisture distribution model, the following conclusions
could be drawn:
1) When there is no volume change, not only the wetting front
but the depth of the saturation front is proportional to the
square root of time.
2) The measurement values obtained for the amount of
infiltration by permeation and the pore pressure of one point,
can be used to calculate the parameters of a dynamic state
moisture distribution model.
Figure 11. Presumed data from experimental results.
3) Hydraulic properties of the unsaturated foundation could be
evaluated using the observed value of the presumed moisture
distribution and pore pressure.
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5
10
-1
10
0
10
1
Estimated value(Invasion process)
Pressure method(Invasion process)
Pressure method(Drying process)
Pressure head |h
p
|, (cm)
Volumetric water content,
θ
4) The pressure head of the moisture characteristic curve was
affected by gap air and shifted to positive pressure; this needs
to be improved in the future.
7 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to acknowledge Ikuya Sasa, who
conducted the experiments presented in this paper. This work
was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 22360189.
8 REFERENCES
Yong, R.N. and Warkentin, B. P. 1975. Soil Properties and behavior,
155-163, Elevier Scientific Publishing Co.
Figure 12. Data inferred from experimental results.
Sugii, T. 2005.Modeling of soil moisture profile during infiltration into
vadose zone, Proceedings of 16th International Conference on Soil
Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, pp.2449-2452.
0
0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5
10
-8
10
-7
10
-6
10
-5
10
-4
10
-3
Estimated value
AMP method (Sugii(2000))
Pressure method
Instanteneous profile method
Volumatric water content,
θ
Hydraulic conductivity, k
w
(m/s)
Sugii,T., Yamada,K. and Uemura,M. 2000. Measuring hydraulic
properties of unsaturated soils with unsteady method, Proc. Of the
2nd Asian Conference on Unsaturated Soils, 439-444.
Richards, S. and Weeks, L. 1953. Capillary conductivity values from
moisture yield and tension measurements on soil columns, Soil Sci.
Am. Proc., 17, pp.206-209.
Watson, K. K. 1966 . An instantaneous profile method for determining
the hydraulic conductivity unsaturated porous materials, Water
Resour. Res., Vol.2, pp.709-715.
van Genuchten, M.Th. 1980 A closed-form Equation for Predicting the
Hydraulic Conductivity of Unsaturated Soils. Soil Sci Am. J.44
pp.892-893
.
Figure 13. Presumed hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soil.
permeation surface is confined. Therefore, it is considered that
the pore air pressure became higher than the atmospheric
pressure.
Finally, it is measured lower than actual pore water
pressure.


