2610
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
better interface properties which is called sandwich technique
(sandwich technique), In fact, the basis of this method is to
provide a thin layer of sand with high strength on both sides of
Geotextile, in order to improve the shear strength and
deformation behavior of the reinforced clay soil
(Unikrishnan.N, Rajagopa.K and.Krishnaswamy,N.R. 2001).
1.1
Studies on clay reinforced
The Studies of Unikrishna et al. (2001) on the reinforced clay
with lens of sand (sandwich technique) did show that adding
sand improvesreinforced soil strength properties. Sand lens
thickness, humidity and type of geotextile was paid attention.
Abdi et al. (2009) during large-scale direct shear tests,
studied the resistance improvement due to providethe thin layers
of sand on either side of the geogrid (sandwich technique) in the
clay and reported the results of the study as follows.
- given the Figure (1) one can understand that providing a
thin layer of sand with high strength on both sides of
reinforceris very effective to improve plasticity and resistance
of clay soils.
- using the buried geogrid system in the sand of fine granular
soil (sandwich technique) increases the shear resistance
impressively. The buried geogrid system in the sand is more
effective on the internal friction of soil and less effective on the
coefficient of cohesion.
Figure 1. The relationship between shear stress - shear displacement
under confining stress 75 kPa with different thicknesses of sand layers.
(Abdi et al., 2009)
Abdi and Arjmand (2011) carried out various experiments on
the pullout testonreinforced clay with geogrid encapsulated with
thin layers of sand. The Samples have been prepared at the
optimum moisture content and maximum dry density weight
which have been obtainedfrom Standarddensity testing Proctor.
One-way geogridis used with a sand layer, 6, 10 and 14 mm in
thickness. Experimental results showed that the encapsulated
geogridin thin sandy layers increases reinforced clay pullout
resistance under the pullout conditions. The results showed that
the maximum resistance to pullout increased with confining
pressure and the optimal thickness of layer of sand is the same
for all normal stresses.
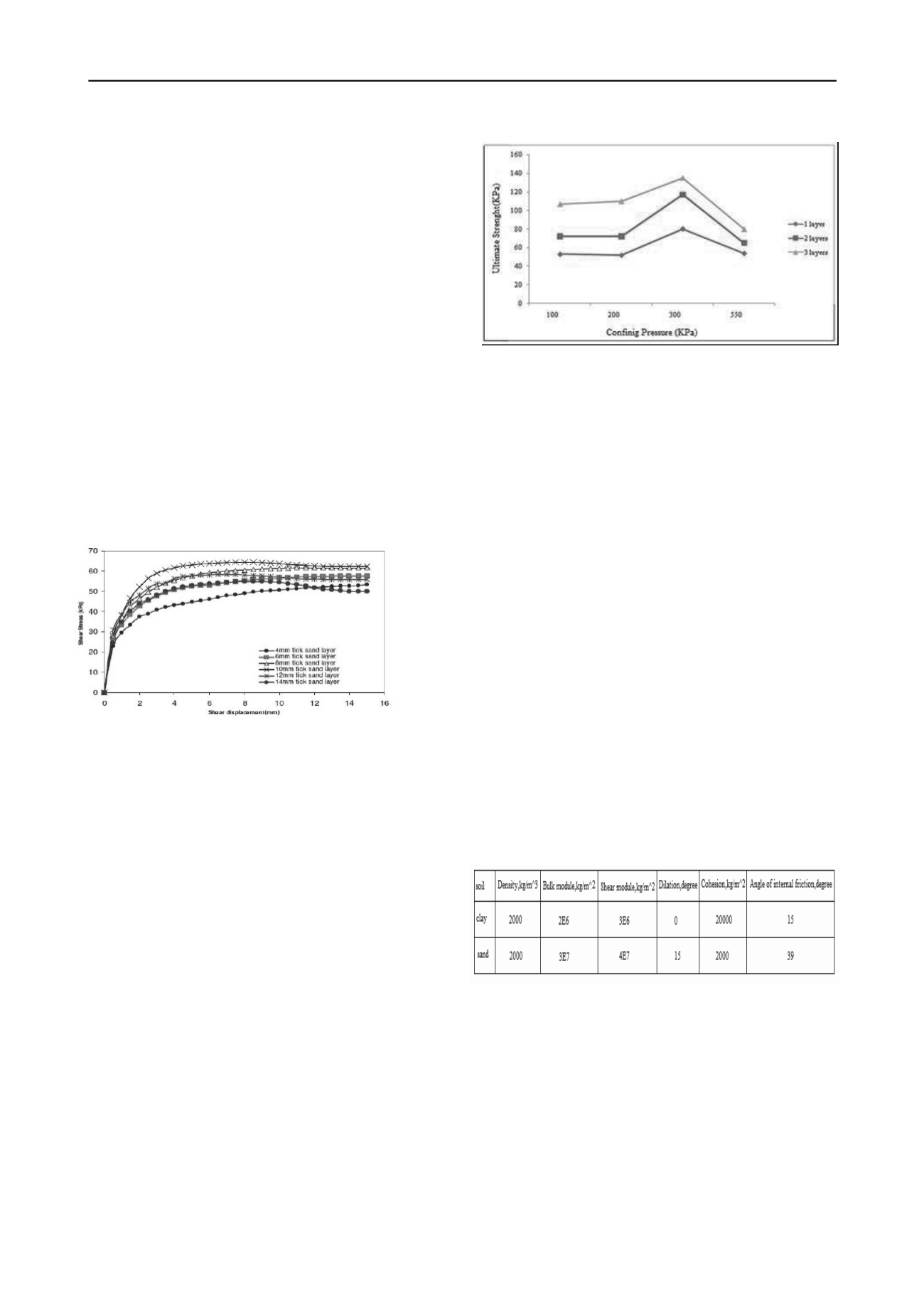
Studies of Tabarsa and Radmehr (2011) on the reinforced
clay with lens of sand (sandwich technique) yielded the
following results.According to this research the increasing
reinforcement layers caused to increase ultimate strenght . Also
improved the recovery of samples increasing confining stress
from 100 to 550 kPa and to confining stress300 kPathe
improvement trend increases and then decreases. (Figure 2)
Figure 2. Effect of confining pressure on the reinforced sample, with
geotextile and sand in 4 mm thick.(Tabarsa and Radmehr 2011)
Given the abovementioned forms it can be perceived that
sample plasticity diminishes increasing the thickness of the
layer of sand. Also, recovery percentage of resistance has
increased slightly increasing the thickness of the sand in low
confining stresses.And in highconfining stresses (550 kPa) the
high resistance percentage has increased significantly and
therefore it can be stated that the high confining stresses impact
on the sand performance in the composite system desired result
is achieved Because of the angle of high internal friction of the
sand. The Results and research, suggest few studies on the
subject of numerical simulation techniques for soil slopes
stability analysis which the research has been done in this
direction.
2 MODELING AND NUMERICAL ANALYSIS
FLAC software is based on the finite differential method. Finite
differential methodis used in various engineering issues.Its
application in the soil and rock mechanics is common because
one can model the big displacements and stresses of soil and
rock masses.in the research FLAC 2D software has been used.
3 CHARACTERISTICS OF THE STUDIED MATERIALS
In this study, to analysis the slope stability, the behavioral
models Mohr - Coulomb is used. Also nonwoven geotextile
have been used for modeling the slopes.
Table 1. details the parameters considered in this study
4 GEOMETRIC PROPERTIES OF SLOPES
In the analysis, four types of slope with different heights of 6, 9,
12 and 15 m with the same slope of 56 degrees have been
considered. The method of geotextiles arrangement is shown in
Figure 3 in the sandwich technique for the slope 12 meters.
(sandwich technique), In fact, the basis of this method is to
provide a thin layer of sand with high strength on both sides of
Geotextile, in order to improve the shear strength and
deformation behavior of the rei forced clay soil
(Unikrishnan.N, Rajagopa.K and.Krishnaswamy,N.R. 2001).
1.1
Studies on clay reinforced
The Studies of Unikrishna et al. (2001) on the reinforced clay
with lens of sand (sandwich technique) did show that adding
sand improvesreinforced soil strength properties. Sand lens
thickness, humidity and type of geotextile was paid attention.
Abdi et al. (2009) during large-scale direct shear tests,
studied the resistance improvement due to providethe thin layers
of sand on either side of the geogrid (sandwich technique) in the
clay and reported the results of the study as follows.
- given the Figure (1) one can understand that providing a
thin layer of sa d with high strength on both sides of
re nforceris very effective to improve plasticity and resistance
of clay soils.
- using the buried geogrid syst m in the s nd of fin gra ular
soil (sandwich technique) increase the shear r sistance
impr ssiv ly. The buried geogrid system in the sand is mo e
e fective on t internal friction of soil and less ffectiv on
oefficient of cohesion.
Figure 1. The relationship between shear stress - shear displacement
under confining stress 75 kPa with different thicknesses of sand layers.
(Abdi et al., 2009)
Abdi and Arjmand (2011) carried out various experiments on
the pullout testonreinforced clay with geogrid encapsulated with
thin layers of sand. The Samples have been prepared at the
optimum moisture content and maximum dry density weight
which have been obtainedfrom Standarddensity testing Proctor.
One-way g ogridis used with a sand layer, 6, 10 and 14 mm in
thickness. Experimental results showed that the encapsulated
geogridin thin sandy layers increases reinforced clay pullout
resistance under the pullout conditions. The results showed that
the maximum resistance to pullout increased with confining
pr ss re and the optimal thi kness of laye of sand is th same
for al no mal stresses.
St dies f Tabarsa and Ra mehr (2011) on the reinforced
clay with lens of san (sandwich technique) yielded he
follo ing results.According to this research the increasing
re nforcement layers caused to increase ultimate stre ght . Also
improved t e recovery of sampl s increasing confining stress
from 100 to 550 kPa and to confining stre s300 kPathe
improvement trend increases and then de reas s. (Figure 2)
Figure 2. Effect of confining pressure on the reinforced sample, with
geotextile and sand in 4 mm thick.(Tabarsa and Radmehr 2011)
Given the abovementioned forms it can be perceived that
sample plasticity diminishes increasing the thickness of the
layer of sand. Also, recovery percentage of resistance has
increased slightly increasing the thickness of the sand in low
confining stresses.And in highconfining stresses (550 kPa) the
high resistance percentage has increased significantly and
therefore it can be stated that the hig confining stress s impact
on he sand performance in the composite system desired result
is achieved Because of the angle of high internal friction of the
sand. The Results and research, suggest few studi s on t e
ubject of numerical s mulat on techniqu s for soil slopes
stability analysis which the research has been done in t i
direction.
2 MODELING AND NUMERICAL ANALYSIS
FLAC software is based on the finite differential method. Finite
differential methodis used in various engineering issues.Its
application in the soil and rock mechanics is common because
one can model the big displacements and stresses of soil and
rock masses.in the research FLAC 2D software has been used.
3 CHARACTERISTICS OF THE STUDIED MATERIALS
In this study, to analysis the slope stability, the behavioral
models Mohr - Coulomb is used. Also nonwoven geotextile
have been used for modeling the slopes.
Table 1. details the parameters considered in this study
4 GEOMETRIC PROPERTIES OF SLOPES
In the analysis, four types of slope with different heights of 6, 9,
12 and 15 m with the same slope of 56 degrees have been
considered. The method of geotextiles arrangement is shown in
Figure 3 in the sandwich technique for the slope 12 meters.
better int rface prop rties which is called sandwich tec n que
(sandwich t chnique), In fact, the basis of t is method is to
provide a thin layer of sand with hig strength on both sides of
Geotextile, in order to improve the she r strength and
deformation behavior of the reinforced clay soil
(Unikrishnan.N, Rajagopa.K an .Krishnaswamy,N.R. 2001).
1.1
Studies on clay reinforced
The Studies of Unikrishna et al. (2001) on the reinforced clay
wit len of sand (sandwich techniqu ) did how th t addi g
sand improvesreinforced soil strength prop rties. Sand lens
thicknes , humidity and type f geotextil was paid a te io .
Abdi et al. (2009) during large-scale rec shear tests,
studi d the r sistanc improvemen due to providethe thin layers
of sand on ither side of the geogrid (sa wich technique) in the
clay a d reported the results of t e study as follows.
- given the Figur (1) one can understand that providing a
thin layer of sand with high strength on both sides of
reinforcer s very effectiv to improve plasticity and resistance
of clay soils.
- using th buried geogri system in th sand of fine granular
soil (sandwich technique) increases the shear res stance
impressively. The buried geogrid system in the sand is more
effective on the internal friction of soil and less effective on the
coefficient of cohesion.
Figure 1. The relationship betwe n shear stres - shear displacement
und r confining str ss 75 kPa with different thicknesses of sand layers.
(Abdi et al., 2009)
Abdi and Arjmand (2011) c rried out various ex erim nts on
the ullo t test nreinforced clay with geogrid encapsulated ith
thin layers of sand. The Samples have b prepared at the
optimum moisture content a d maximum dry density weight
which hav b en obtainedfrom Standardd nsity t sting Proctor.
One-way geogr dis used with a sand layer, 6, 10 an 14 mm in
thickness. Experimental results showed that the ncapsulated
geogridin thin sandy l yers increases reinforc clay pullout
resistance under the pullout conditions. The result showed th t
the m ximu resistance to pullout increased with confining
pressure and the optimal thickness of layer of sand is th same
for all normal stre ses.
Studies of Tabarsa and Radmehr (2011) on the reinfo ced
clay with lens of sand (sandwi h techn que) yi lded the
following results.According to this research the increasing
reinf rcement layers caused to increase ult mate str nght . Also
improved the recovery of samples increasing confining stress
from 100 to 550 kPa and to confining stress300 kPathe
improvement trend increases and then decreases. (Figure 2)
Figure 2. Eff ct of confining pressure on the reinforced s mple, with
geotextile and sand in 4 m thick.(Tabarsa and Radm hr 2011)
Given the abovementioned forms it can be perce ved that
sample plasticity diminishes increasing the thickness of the
layer of sand. Also, recovery percentage of resistance has
increased lightly increasin the thick ess of the sand i low
confining stresses.And in highconfining stresses (550 kPa) the
high resi tance percentag has increased significantly and
therefore it can be stat d that the high confini g stresses impact
on the sand performance in the compo ite system desired result
is achi ved Because of the ang e of high i ternal friction of the
sand. The Result and research, uggest few studies on the
subject f numerical simulation techniques for soil slopes
stability analysis which the research has been done in this
direction.
2 MODELING AND NUMERICAL ANALYSIS
FLAC sof ware is ba ed on the finite differential method. Finite
differ ntial
ethodis used in various engineering issues.Its
appli ation in the soil and rock mechanics is common because
one can model the big displacements and stresses of soil and
rock masses.in the research FLAC 2D software has been used.
3 CHARACTERISTICS OF THE STUDIED MATERIALS
In this study, to analysis the slope stability, the behavioral
models Mohr - Coulomb is used. Also nonwoven geotextile
have en used for modeling the slopes.
Table 1. details the parameters considered in this study
4 GEOMETRIC PROPERTIES OF SLOPES
In the analysis, four types of slope wi h differe t heights of 6, 9,
12 and 15 m with the sam slope of 56 degr es have been
considered. The method of geotextiles arrangement is shown in
Figure 3 in the sandwich technique for the slope 12 meters.


