2500
Proceedings of the 18
th
International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris 2013
0
100
200
300
400
500
Time (days)
0
1
2
3
4
5
Embankment Height (m)
0
100
200
300
400
500
Time (days)
1.6
1.2
0.8
0.4
Settlement (m)
Field
Prediction
0
100
200
300
400
500
Time (days)
0
20
40
60
80
Excess pore pressure (kPa)
Field
Prediction
(a)
(b)
(c)
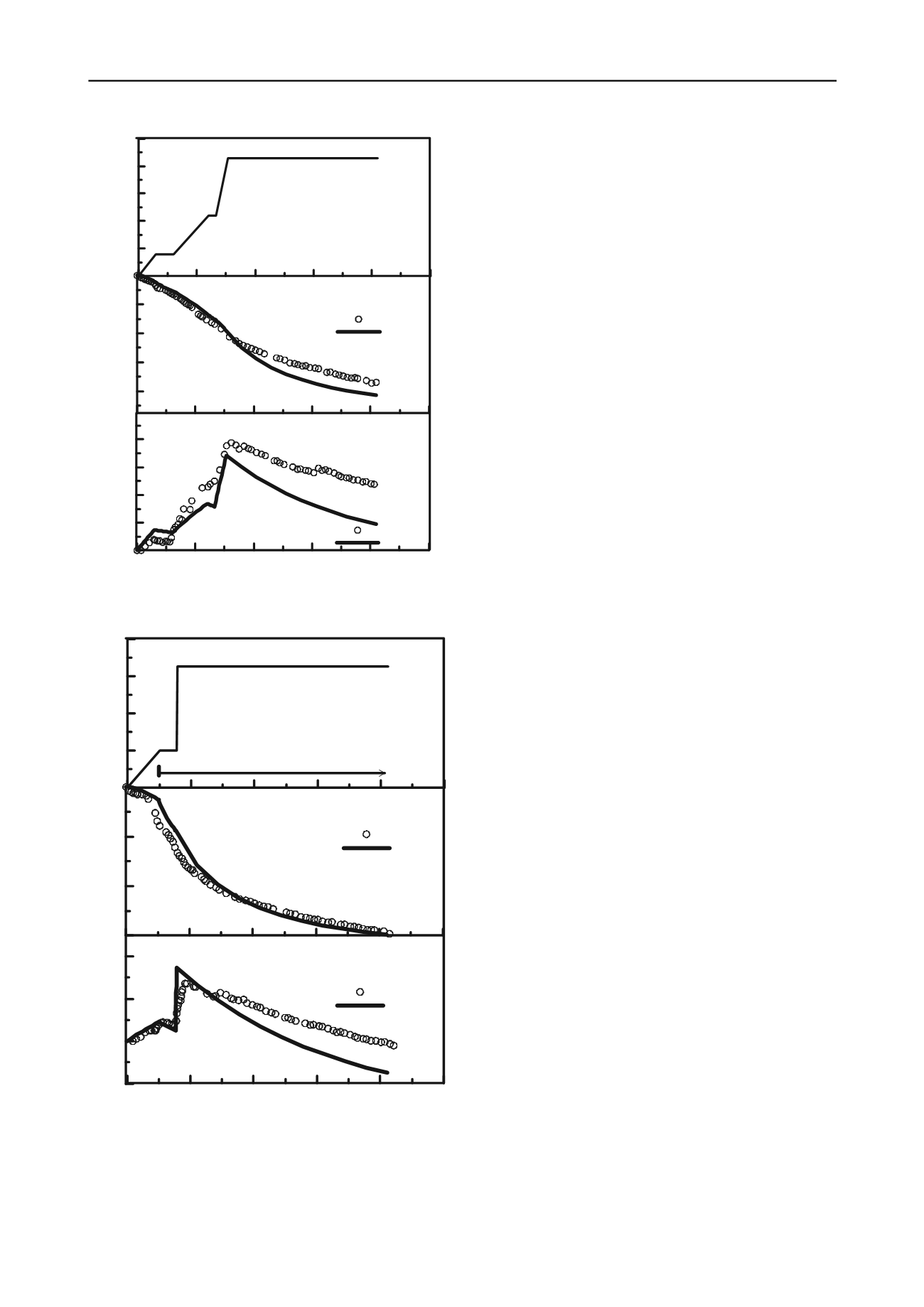
figure 5. Wd1 area: (a) stages of loading, (b) surface settlements at the
embankment centreline and (c) excess pore pressures at 9.2m deep
0
100
200
300
400
500
Time (days)
0
1
2
3
4
Embankment Height (m)
0
100
200
300
400
500
Time (days)
1.2
0.8
0.4
Settlement (m)
Field
Prediction
0
100
200
300
400
500
Time (days)
-40
0
40
80
Excess pore pressure (kPa)
Field
Prediction
(a)
(b)
(c)
Vacuum application of 70 kPa
figure 6. Vc1 area: (a) stages of loading, (b) surface settlements at the
embankment centreline and (c) excess pore pressures at 14.1m deep
(indraratna et al. 2011)
5 conclUsions
a system of vertical drains with vacuum preloading is an
effective method for speeding up soil consolidation. the
analysed and discussed. the dredged materials from the seabed
were placed in the reclaimed area. a total of 8 areas were
selected to examine the performance of vacuum consolidation,
and the vertical drain spacing varied from 1-1.3m for 3 different
drain types. the vacuum application induces an inward lateral
movement, whereas the conventional surcharge fill creates
outward movement. When the vacuum pressure combined with
surcharge fill is employed, the overall lateral movement is
decreased due to the isotropic consolidation induced by vacuum
pressure. from a stability point of view, vacuum pressure
reduces the ratio of lateral displacement to surcharge fill height
at any given time.
the unit cell th
performance of 2 treatment schemes at the port of Brisbane was
eory considering time-dependent surcharge
6 acKnoWledGements
ort of the port of Brisbane
7 references
drain wells on the consolidation of
chu
Gen
indraratna, B., an
ind
ind
ric
sha
Yan
load and vacuum application was employed to predict the
settlement and associated excess pore pressure, which provided
a good agreement with the field measurements. after 1 year, the
degree of consolidation in the vacuum areas was much higher
than the non-vacuum areas for the same total stress.
Writers acknowledge the supp
corporation, coffey Geotechnics and austress menard. the
research funding from the australia research council is
acknowledged. the assistance of prof. a.s. Balasubramaniam
of Griffith University, daniel Berthier of austress menard, prof
harry poulos, cynthia de Bok, tine Birkemose and chamari
Bamunawita of coffey Geotechnics is appreciated. most of the
contents reported in this paper are also described in greater
detail in a number of and asce Journal of Geotechnical and
Geoenvironmental engineering.
Barron, r. a. 1948. the influence of
fine-grained soils. diss., providence, U s eng. office.
chai, J.c., carter, J.p., and hayashi, s. 2005. Ground deformation
induced by vacuum consolidation
. Journal of Geotechnical and
Geoenvironmental Engineering
, 131(12):1552-1561.
, J. Yan, s.W., and Yang, h. 2000. soil improvement by the
vacuum preloading method for an oil storage station.
Geotechnique
,
50(6): 625-632.
g, X. Y., indraratna, B. and rujikiatkamjorn, c. (2012). analytical
solutions for a single vertical drain with vacuum and time-
dependent surcharge preloading in membrane and membraneless
systems.
International Journal of Geomechanics
, asce, 12(1), 27-
42.
d redana, i. W. 1998. laboratory determination of
smear zone due to vertical drain installation.
J. Geotech. Eng.,
asce, 125(1): 96-99.
raratna, B., sathananthan, i., rujikiatkamjorn c. and
Balasubramaniam, a. s. 2005. analytical and numerical modelling
of soft soil stabilized by pVd incorporating vacuum preloading.
International Journal of Geomechanics
, 5(2). 114-124.
raratna, B., rujikiatkamjorn, c., ameratunga, J., and Boyle, p. 2011
performance and prediction of Vacuum combined surcharge
consolidation at port of Brisbane.
J. of Geotechnical &
Geoenvironmental Engineering
, asce, 137 (11), 1009-1018.
hart, f.e. 1957. a review of the theories for sand drains.
Journal of
the Soil Mechanics and Foundations Division
, asce, 83(3): 1-38.
rujikiatkamjorn, c., indraratna, B. and chu, J. 2008. 2d and 3d
numerical modeling of combined surcharge and vacuum preloading
with vertical drains
. International Journal of Geomechanics
, 8(2):
144-156.
ng, J.Q., tang, m., and miao, Z. 1998. Vacuum preloading
consolidation of reclaimed land: a case study.
Canadian
Geotechnical Journal
, 35: 740-749.
, s.W. and chu, J. 2003. soil improvement for a road using a
vacuum preloading method.
Ground Improvement
, 7(4): 165-172.


